This post was sponsored by DinoRANK. The opinions expressed in this article are the sponsor’s own.
Google is a great source of qualified and recurring traffic for your business – that’s a fact.
Many people say that the key to SEO success is to establish yourself as an authoritative source for all the keywords in your industry, even niche keywords.
Unfortunately, your competition is doing the same thing. In some cases, you may even be competing with yourself.
Everyone is creating the same content to rank high on Google. So, you need to set yourself apart.
Your competition may be using the same niche keywords as you, but are they optimizing their domain’s SEO by cleaning up cannibalized content and keyword cannibalization?
They may not be; so, this is a great way to propel your website to the top of Google.
What Is Keyword Cannibalization In SEO?
As you may know, sometimes two or more URLs on the same domain may rank for the same keyword or group of keywords.
When this happens, Google does not know which piece of content to show on search engine results pages (SERPs).
When these URLs compete for the same search terms, it is called SEO cannibalization.
How Cleaning Up Cannibalization Can Instantly Boost Your Rankings
When you and your competition are ranking for the same keywords, yet your position on SERPs is lower, you may have a cannibalization issue.
If your content is cannibalizing itself, you not only have to fight your competitors for a top position – you also have to fight your own pages.
There’s enough competition out there without having it at home, right?
Cannibalization is a detrimental factor when URLs compete with each other. They can even harm your domain authority if there are too many of them, especially if you haven’t told Google that there is a clear difference between two similar pieces of content.
As you can see, cannibalizations have a negative influence on your domain’s SEO.
To solve the cannibalization problem, we must first know how to find them.
How To Find Cannibalization On Your Website
There are different ways to find cannibalization on your domain:
- The Manual Way
- The Easy Way
How To Find Cannibalized Keywords By Hand
There are two ways to locate content and keyword cannibalization without using a tool:
- Use a rank tracker or Google Search Console to see which positions your pages are ranking in the search results, as well as the keywords they are ranking for; then, find matching URLs for the same keywords.
- Review your site’s content manually to see if there are several pages that address the same topic or include the same keywords. Then, go to Google and search for that keyword you suspect you are cannibalizing and check if you really do it or not; this can also help you prevent it from happening.
How To Locate Keyword Cannibalization With A Single Click
Using DinoRANK, you can simply click one button and instantly see all your cannibalized content.
All you’ll need to do is create a project in the tool, and sync it with your Google Analytics and Google Search Console account. DinoRANK does the rest.
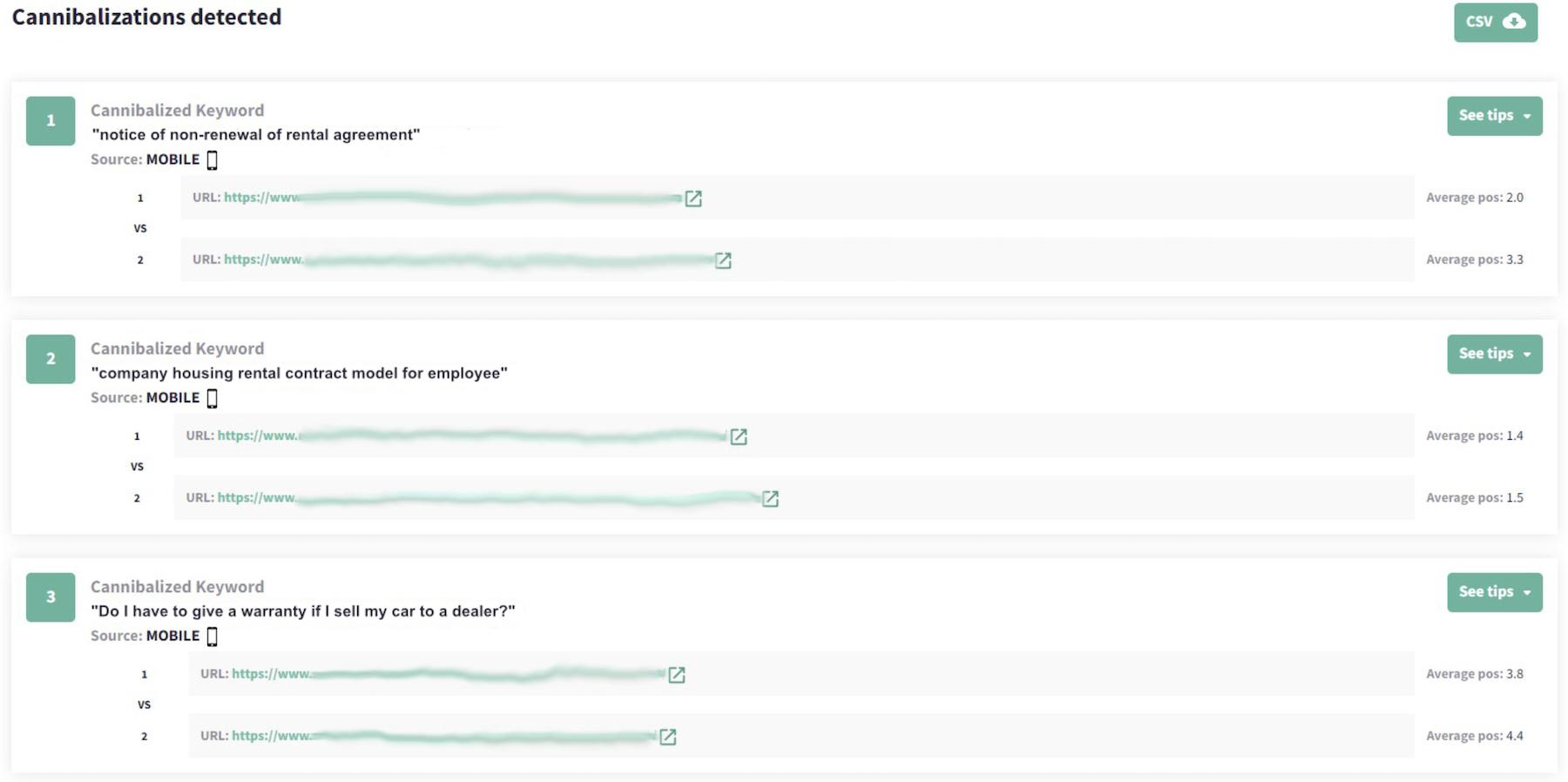 Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023
Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023See what content is cannibalized on your website now →
Now, once you have located all the cannibalizations that affect your website, what decision should you make?
What Is The Best Way To Fix Cannibalization?
Once you have found the cannibalizations on your website, you can take these steps to solve the problem:
- Join or merge two URLs into one.
- Make a 301 redirect.
- Make a shift in focus to one of the two contents and de-optimize or optimize for the word that it cannibalizes.
- Place a canonical tag in one of the two URLs.
- Remove one of the two contents if you consider it thin content or duplicate content.
How Do I Pick The Best Method?
What analysis should you do when facing cannibalization to perform the most optimal action?
Let’s say that you have 2 URLs of the same domain that are positioned for the same keyword; 1 URL is in position 5, and the other URL is in position 7 on the SERPs.
In this case, you should:
- Check the content of both pages to see if they are addressing the same topic or include the same keywords. If so, they are probably competing with each other and causing cannibalization.
- Review the page authority of each page, as measured by the number of inbound links, quality of links, site structure, etc. The page with higher authority will likely perform better in search results.
- Check the traffic received by each page to see which one is receiving more visits, and analyze which URL is responding better to the search intention of that or those keywords.
- Check the conversion rates of each page to see which is generating more sales or conversion actions.
Once the analysis is done, you will have enough elements to recognize what action you should take in each cannibalization.
Still not sure?
Don’t worry. DinoRANK will show you recommendations on how to proceed, depending on the case.
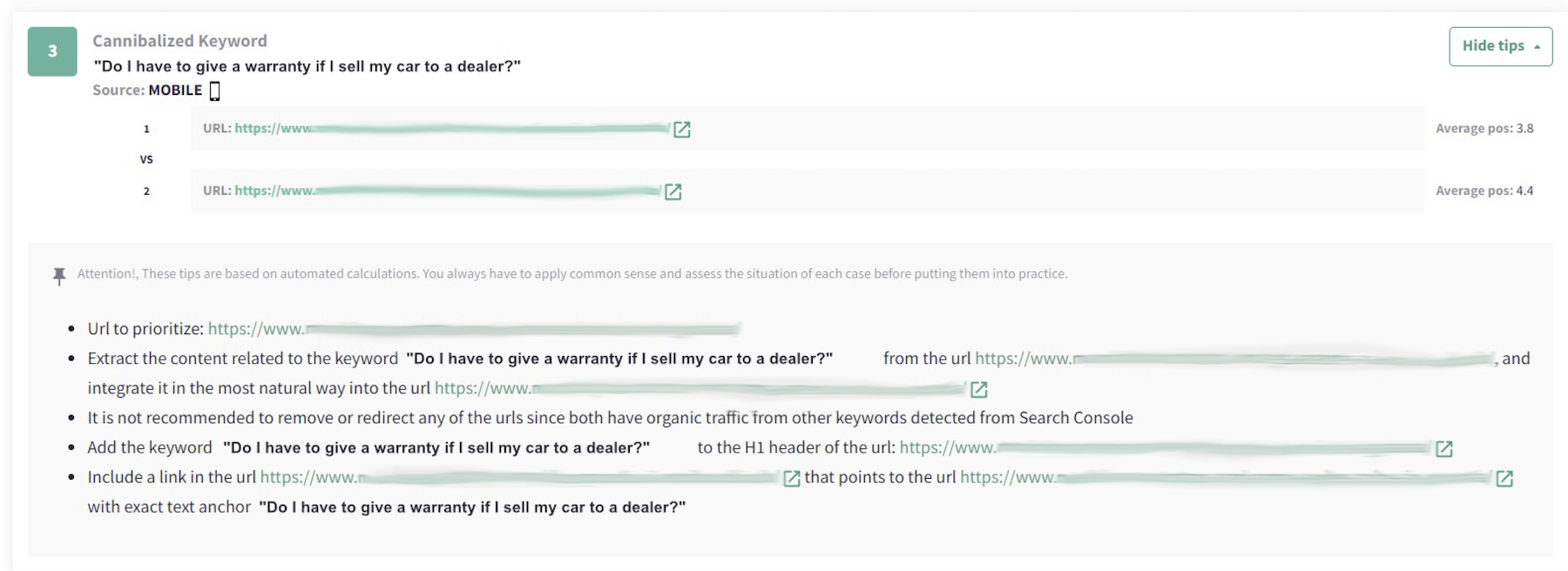 Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023
Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023Usually, content is consolidated into one of the two cannibalized URLs (the one with higher authority or higher traffic), and the discarded URL should become a 301 redirect.
The impact of this repair is usually positive in a very high number of cases.
Although if both contents fulfill their function (for example, one URL belongs to the product card and the other to a blog post), a better option would be to optimize or de-optimize the content as appropriate or choose to implement a canonical tag to one of the URLs to indicate to search engines which is the main page.
In any case, it is important to continuously monitor the performance of the pages and make adjustments if necessary to avoid cannibalization in the future; with DinoRANK you will have this under control.
How To Optimize Or De-Optimize Content That Is Cannibalizing
Search engines use algorithms to determine the relevance of a web page for a given search query, and one of the ways they do this is by identifying the keywords that appear most frequently on a page, relative to the keywords that appear on other similar pages.
Before optimizing or de-optimizing one of the two contents, it’s important to know all the keywords for each URL being cannibalized.
Then, you’ll need to analyze their semantic content with TF*IDF analysis.
So, analyzing a URL whose content you want to optimize/promote for a specific keyword with TF*IDF will allow you to understand which keywords are relevant to that content.
-
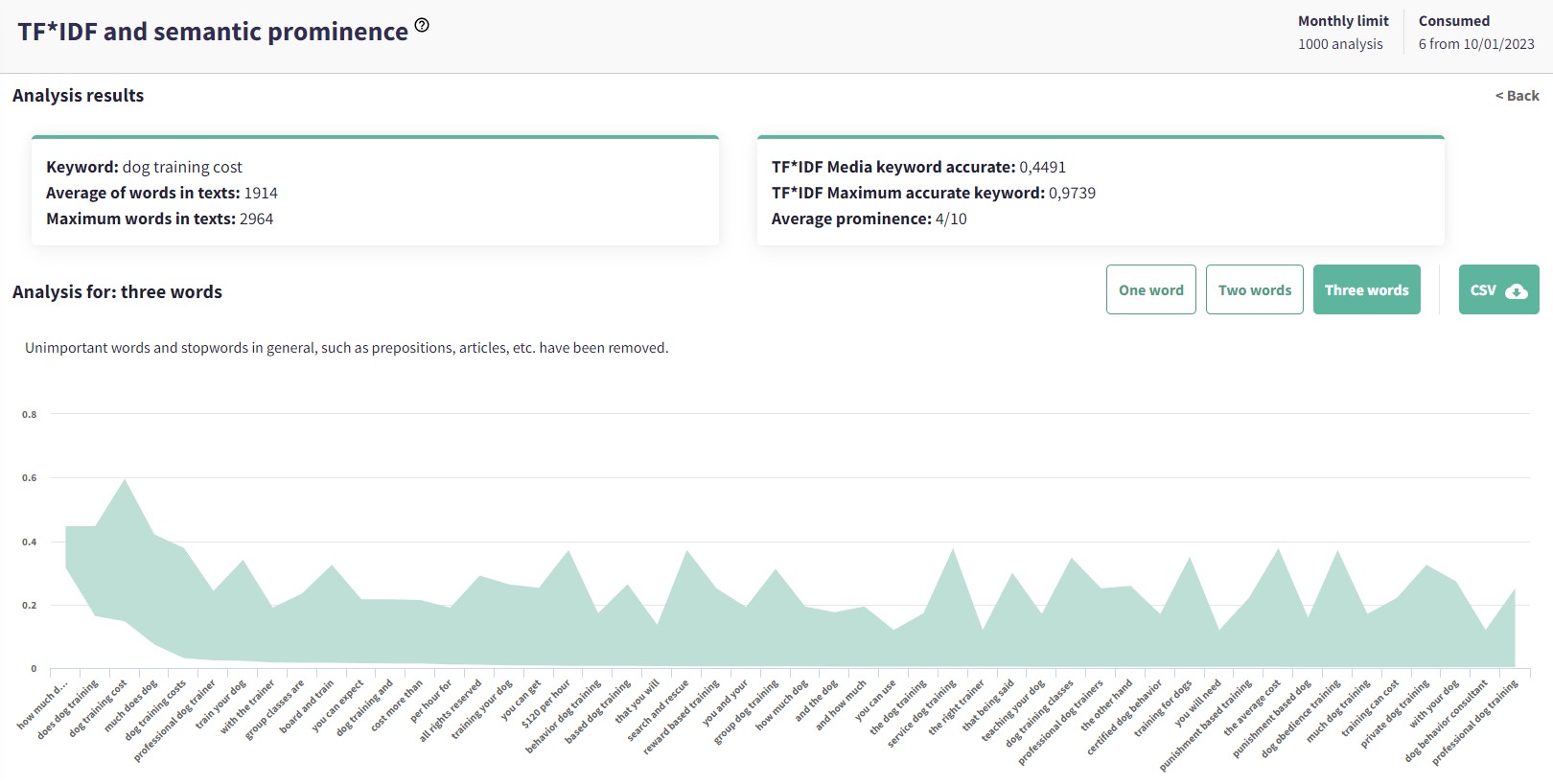 Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023
Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023
Expanding and semantically optimizing content that is already ranking highly, whether it is cannibalizing or not, is one of the best ways to gain more relevance for those terms that only received impressions or a few clicks. This is because you are now providing a greater semantic richness to that content.
With DinoRANK, you can use TF*IDF analysis on already published URLs to see how to optimize them.
You can also use this feature when you want to create new content based on a keyword or a group of keywords you want to rank for.
-
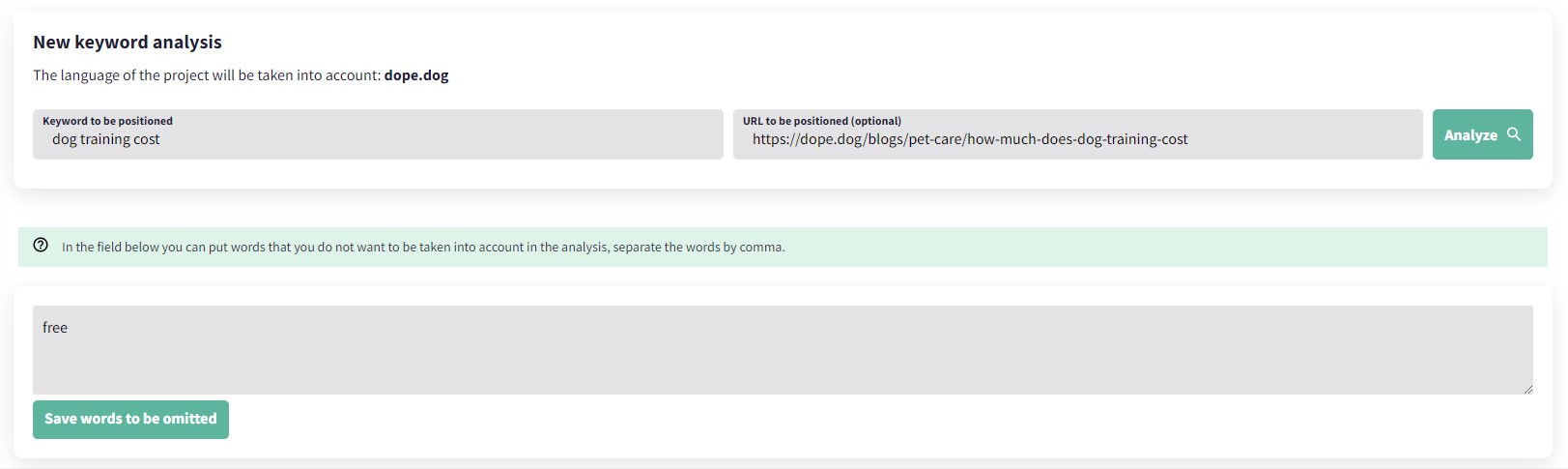 Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023
Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023
DinoRANK arranges the information visually, separating the graph into three filter layers: one keyword, two keywords, and three keywords.
-
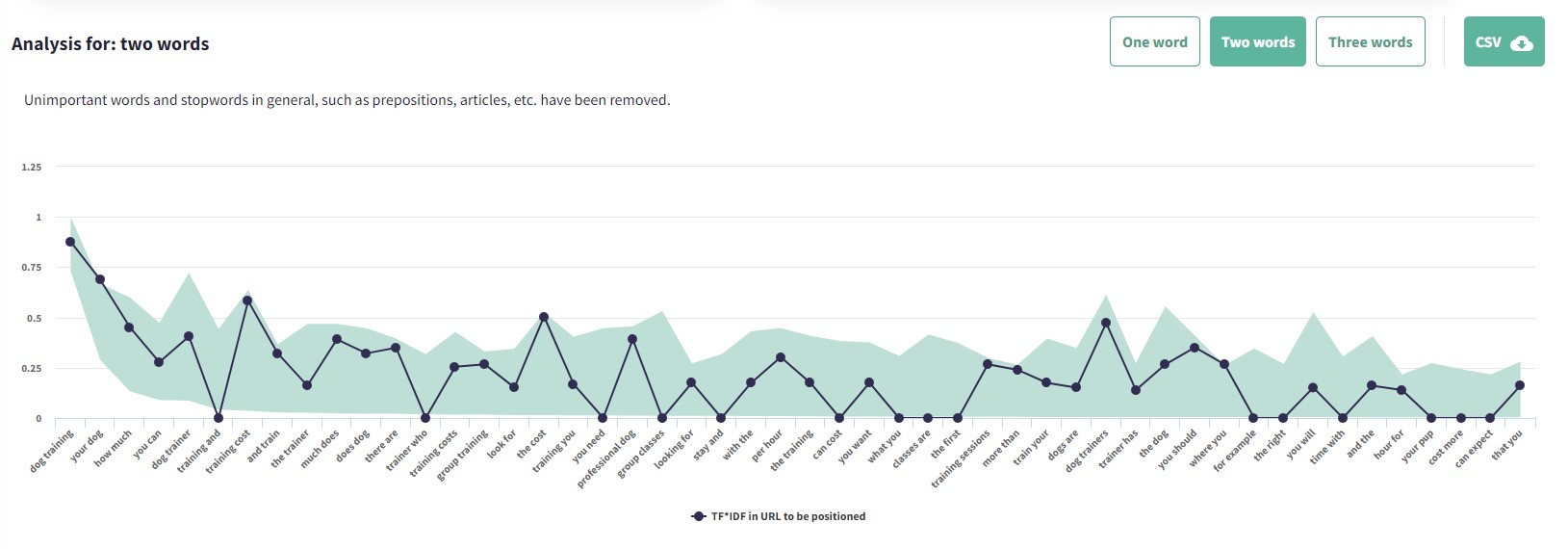 Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023
Screenshot from DinoRANK.com, January 2023
In addition to the recommendations, you will also be able to quickly see the header structure used by your most direct competitors in Google’s Top 10.
In a very short time, you’ll discover opportunities and content ideas with an optimal heading structure, including the related semantic keywords needed to rank.
If, in addition, this semantic content extension is complemented by some internal links to that optimized URL, and you do it with anchor text of the primary keyword or exact semantic keywords, you will strengthen the authority and the typicality of that URL you want to promote.
With internal links, you derive a greater semantic context and strengthen the authority of that page already optimized, thanks to the semantic prominence analysis TF*IDF.
If you want to use these features to work the SEO of your projects in a simple but effective way, you can try DinoRANK.
All the SEO your website needs can be found in DinoRANK.
