Many businesses create global websites hoping to replicate the success from online business in their home country in other countries.
Some companies see the return on investment put into creating multiple websites, and some companies struggle to grow their business in foreign countries.
Creating effective global websites requires attention to several essential factors to ensure they resonate with local audiences.
In this article, we learn from successful global businesses such as IKEA, McDonald’s and KFC and apply that to global website best practices.
Language And Cultural Product Adaptation
It is essential to understand and implement locally unique customer interests and preferences. In many cases, global websites are created by translating/localizing the main site multiple times.
IKEA
IKEA is known for its giant warehouse-style buildings. In the U.S. and most countries, people drive to IKEA prepared to purchase large items that can only be transported by car.
In Japan, while most people own a car, they don’t drive on a daily basis. Having cavernous warehouse stores was limiting their business potential in Japan.
In order to increase business in Japan, IKEA pivoted to tap into people shopping on foot in the bigger cities. It opened a much smaller footprint in the middle of Harajuku in 2020.
In the city center shop, people can purchase 1,000 items, which they can easily carry out, as well as place orders for larger items through a kiosk for delivery.
Based on this initial test, it also opened additional shops in the high-traffic areas of Shibuya and Shinjuku. These shops not only increased the sale of items in the stores but also enabled easy access to an additional 9,400 items available online.
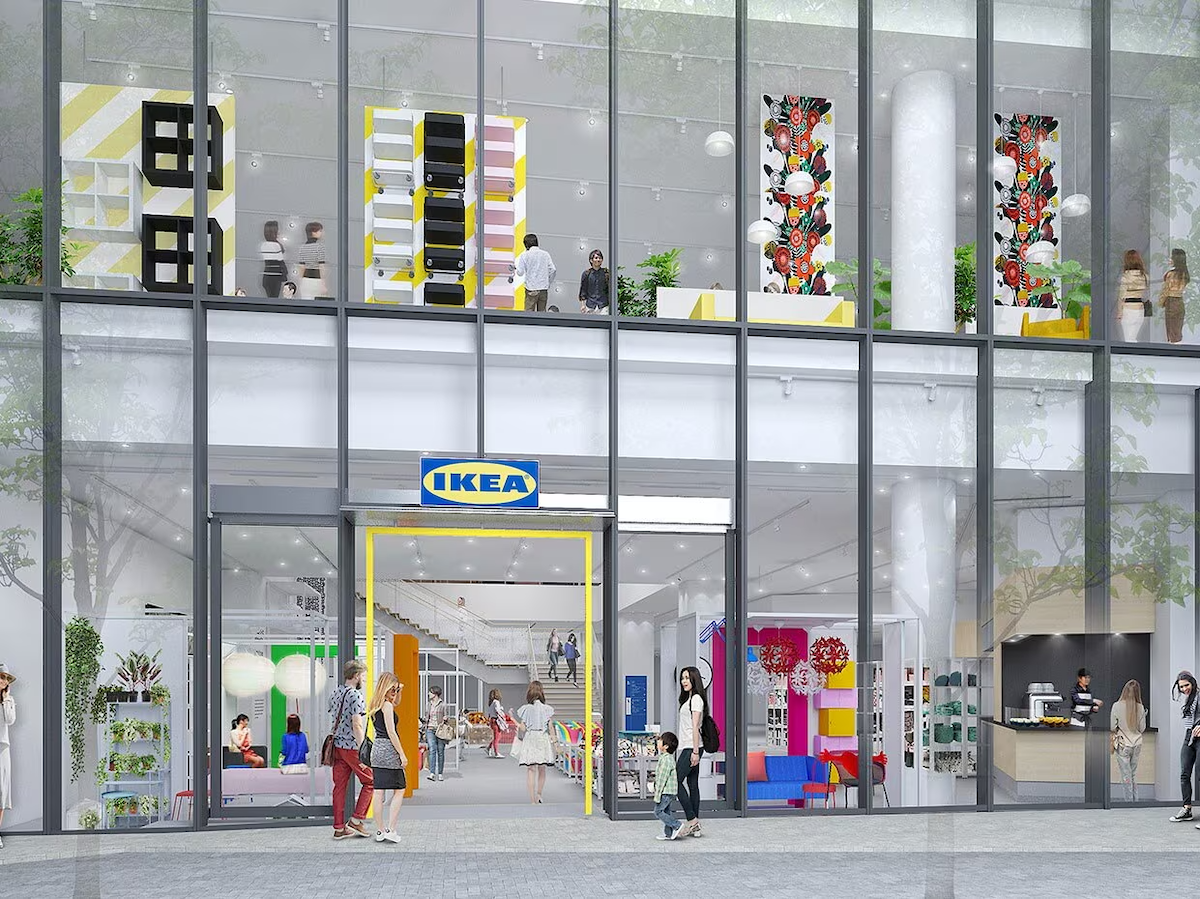 Image from IKEA Japan, November 2024
Image from IKEA Japan, November 2024While this is a physical store example, the idea of understanding the customers’ needs and putting it into practice can be applied equally to their online business as well.
Because IKEA has tailored many of its products specifically for the Japanese market, where home sizes are generally smaller, space-saving is a priority.
On its Japanese website, it emphasizes compact, multifunctional furniture that fits Japanese urban apartments, with suggestions for optimizing smaller living spaces.
McDonald’s And KFC
Similarly, both McDonald’s and KFC’s websites are localized by pushing locally popular items in each country, as shown below.
By creating special menu items that cater to local Japanese culinary preferences, McDonald’s conveys a sense of cultural sensitivity, making the brand feel more “local” rather than foreign.
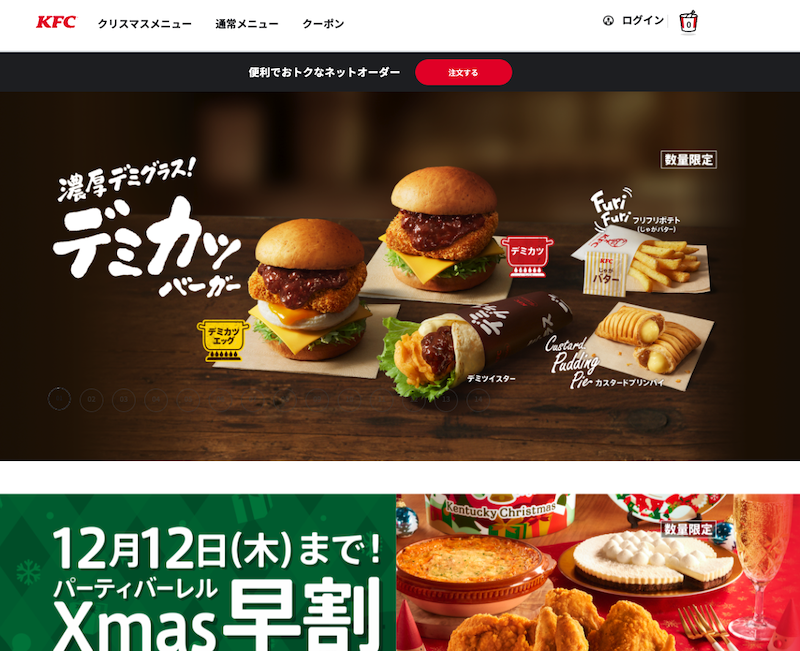 Screenshot from KFC Japan website, November 2024
Screenshot from KFC Japan website, November 2024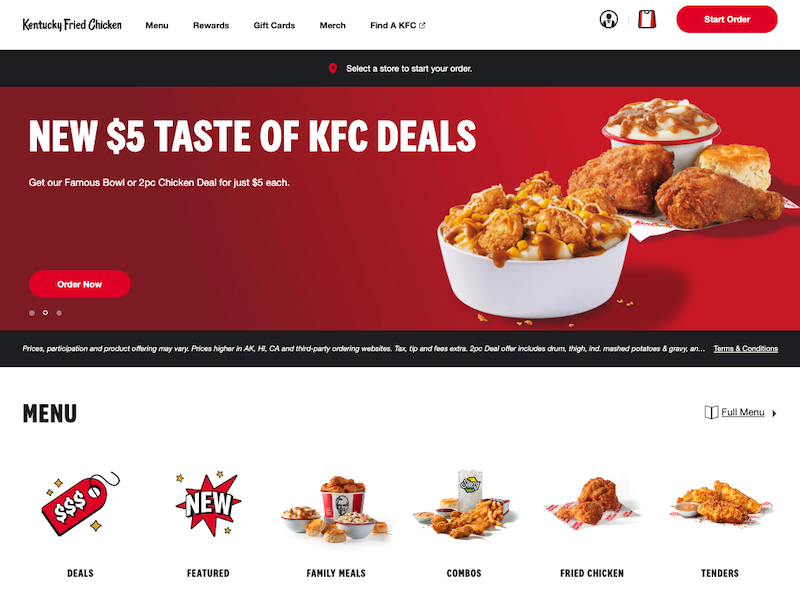 Screenshot from KFC USA website, November 2024
Screenshot from KFC USA website, November 2024During the holiday season, the KFC Japan website prominently displays its Christmas offerings, featuring family meal packages and seasonal items.
The site encourages early reservations, as these special holiday meals are extremely popular.
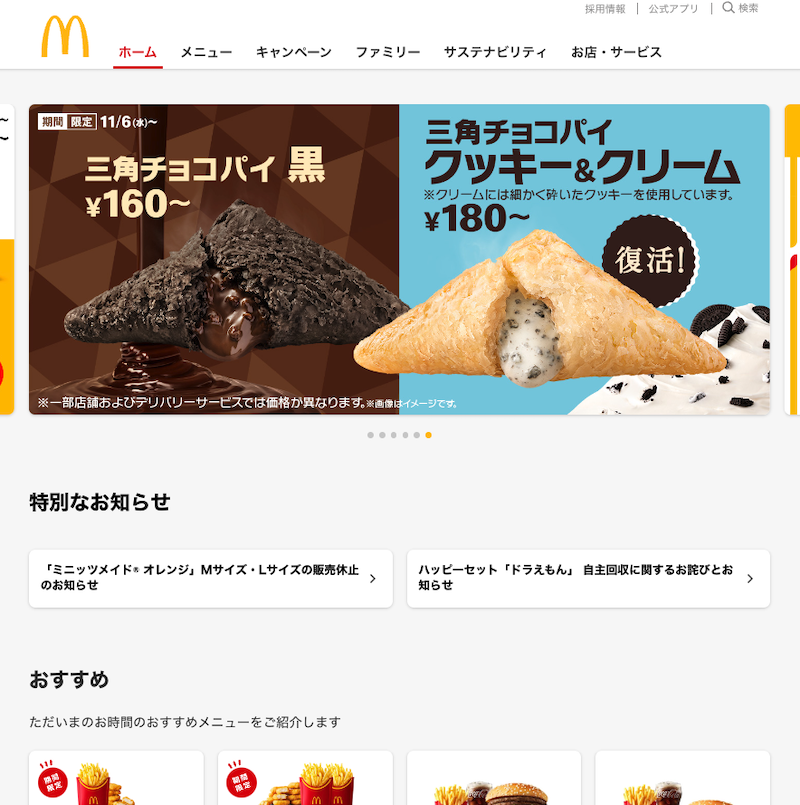 Screenshot from McDonald’s Japan website, November 2024
Screenshot from McDonald’s Japan website, November 2024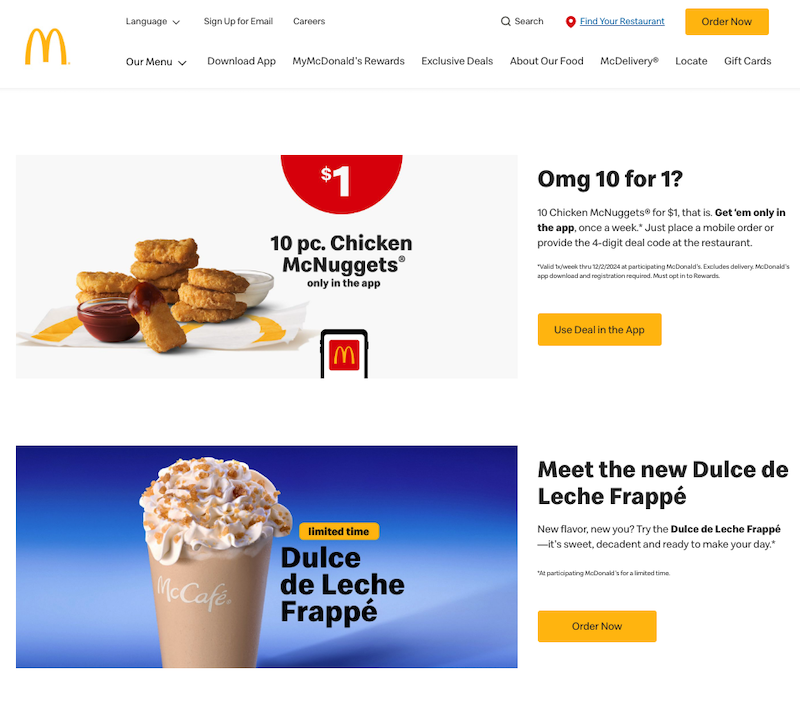 Screenshot from McDonald’s USA website, November 2024
Screenshot from McDonald’s USA website, November 2024By understanding the local audience, you will know which products to promote and when to promote them on the site.
By promoting special web offers around local holidays and cultural events, such as Christmas in Japan or Ramadan in the Middle East, KFC and McDonald’s position themselves as a brand that celebrates local traditions. These market-specific adjustments will generate greater conversions/sales.
In many markets like Japan and India, locals tend to use mobile devices to access content.
Ensuring your website and apps are mobile-friendly with a user-friendly experience, including fast load times, simplified interfaces, and intuitive navigation that appeal to a preference for efficiency and speed.
This makes it easy for users to quickly locate nearby stores, order online, and access promotions.
Best Practices For Adapting Your Website To Global Audiences
Translate All Content
Website translation and localization projects require significant resources and budget. It is understandable that some websites are not 100% localized.
I used to sympathize with those sites, especially the ones owned by small businesses. However, with the AI advancements in localization, there is no excuse. You should translate the entire site, including user-generated content.
More than just translation, the type and depth of content reflect an understanding of local shopping preferences.
In Japan, customers highly value detailed product descriptions and customer reviews, which must be in Japanese.
This level of localized and market-specific detail aligns with the Japanese tendency to do extensive research before making a purchase.
Optimize The Website With Localized Colors, Images, And Videos
From language and product selection to seasonal promotions, adapting your site’s content to reflect local tastes and practices helps establish a sense of authenticity and resonance with users.
All too often, local markets only have the text translated, leaving the website design and media content the same across the sites.
Needless to say, the site feels much more relatable when they see images and videos that they feel familiar with. To the audience in some countries, the color scheme could unfavorably change the site’s impression.
IKEA Japan localizes the site using faces that look like those in the local market.
 Screenshot from IKEA Japan website, November 2024
Screenshot from IKEA Japan website, November 2024With free and inexpensive AI image design tools, the cost is no longer an excuse not to optimize the images.
You can also run the website through Google’s Vision API to review your images and assist in localizing alternate image text. More importantly, you can use the safe search function to flag sensitive content, as well as any colors or situational elements that might become a problem in the market.
Make It Easier For Users To Convert
It goes without saying that you need to build trust by ensuring secure transactions, reliable delivery, and buyer protections on par with local ecommerce sites.
You must integrate with local payment platforms and methods to enable your brand to become a part of the local digital landscape, making it easier for users to interact and transact.
Ensure all forms – especially those involved in engagement or conversion flow (registration, contact, order, etc.) – are adapted to the local market.
As these are your most important pages, you want to ensure that you remove any ambiguity and friction as they move through the conversion process.
Regardless of how people land on the website, organic, ads, or direct traffic – if the forms are not well-tuned for the local audience – they may abandon the form and will not convert for you, even when they want your services or products.
For example, if you take orders from foreign countries but the form is formatted for the U.S. (or wherever your HQ is), requiring information or a format not recognized by the local market, customers may be unable to complete the form.
Make your forms and checkout pages flexible enough to accept different digits and styles for phone numbers, postal codes, and addresses; ensure you don’t require a U.S. state name.
Typically, Japanese addresses are quite lengthy, combining both numbers and characters. If your form has a maximum character limit that is too short for the market, they may not be able to complete it.
If you have a multinational website, display a specific target country name at the top of the “country” selection of the form.
In addition to form localization, there are other critical website functions that should be considered.
For example, a variety of login methods and payment options are used worldwide.
In the U.S., in addition to email/ID login, many websites offer social media logins, such as LinkedIn and Facebook, as well as Google and Microsoft logins.
While it works fine in many countries, in some countries, such as China, your standard options may not be as popular or even available.
Conclusion: Building A Cohesive Global Presence
Creating a successful multinational website is a strategic investment that requires careful planning and continuous adaptation.
By focusing first and foremost on the local users’ experience, including localization and local adaptations coupled with geo-targeting, SEO, technical infrastructure, compliance, and analytics, executives can develop a website that aligns with local expectations while reinforcing a consistent brand identity.
As your global website evolves, keep listening to your audience and monitoring performance to better understand consumer behavior and adapt to the unique demands of each market to maintain a competitive edge.
The digital landscape constantly changes, and proactive adjustments will keep your brand competitive in the diverse global market.
More resources:
Featured Image: LookerStudio/Shutterstock
