A series of improvements to LinkedIn’s search system for posts will allow it to deliver faster and more relevant results within a simplified user interface.
LinkedIn details the journey of developing new system architecture while explaining the complexity of its old system.
Search results for posts were previously served by two indexes – one for posts in LinkedIn’s main feed and one for articles.
The complex nature made it difficult to build upon, so LinkedIn decided to decouple the two indexes. LinkedIn reveals the entire process in excruciating detail in a new blog post.
Here it is summed up in a diagram:
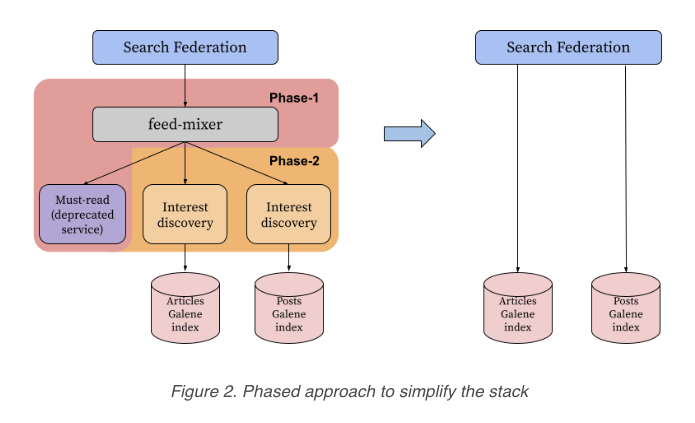 Image credit: Screenshot from engineering.linkedin.com/blog/2022/improving-post-search-at-linkedin, August 2022.
Image credit: Screenshot from engineering.linkedin.com/blog/2022/improving-post-search-at-linkedin, August 2022.
Much of the information LinkedIn shared is geared toward software engineers. In this post, I’ll skip over the technical details and explain what the changes mean for regular users on LinkedIn.
LinkedIn Post Search Delivers Faster, More Relevant Results
To make search results more relevant, LinkedIn set out to create a system that considers the following aspects:
- Relevance of the post to a query
- Quality of the post
- Personalization
- User intent
- Engagement
- Freshness/recency
LinkedIn says its new system must also deliver results from diverse sources.
LinkedIn is leveraging several machine learning techniques to satisfy searcher expectations to meet these goals for relevance and diversity.
Further, LinkedIn crowdsourced human ratings for search results and leveraged the data to ensure its new system meets a certain threshold for quality.
LinkedIn notes that the crowdsourced human annotation data also provides valuable training data to improve the ranking of results.
New System Vs. Old System
LinkedIn’s new system, powered by machine learning, improves on the old system in the following ways:
- Relevance: It enables personalization by leveraging deeper and real-time signals for members’ intent, interests, and affinities.
- Diversity: It increases the discovery of potentially viral content for trending queries and reduces duplication of similar content.
- Ranking: It utilizes post-related metadata from the index to improve the ranking of posts when blended with other types of results.
- Navigation: It has a new user interface that allows people to search for posts from a specific author, posts that match quoted queries, recently viewed posts, and more,
Data Shows New System Is Better
LinkedIn says search results delivered by its new system have increased user satisfaction, reflected by a 20% increase in positive feedback.
Results that are highly relevant to a user’s query, which LinkedIn identifies as “pertinent results,” have led to an aggregate click-through rate improvement of over 10%.
Greater diversity of posts from within the searcher’s social network, their geographic location, and their preferred language has led to a 20% increase in messaging within the searcher’s network.
The time it takes to deliver search results has been reduced by ~62ms for Android, ~34ms for iOS, and ~30ms for web browsers.
Future Improvements
LinkedIn shares how it will continue to improve search results for posts. Future updates will involve:
- Implementing natural language processing to understand the semantic meaning of queries.
- Surfacing fresher results for queries on trending topics, reducing the feedback loop from hours to minutes.
- Expanding document understanding capabilities to include handling multimedia content such as images, short-form videos, and audio.
See LinkedIn’s full blog post for all the technical details behind these changes.
Source: LinkedIn
Featured Image: /Shutterstock
