With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the ability to order online has become an essential feature for every webpage and business listing.
Pre-pandemic, the primary goal of local search engine optimization (SEO) was to drive visibility and foot traffic to a location.
Now businesses are focused on providing a seamless omnichannel experience to allow the customer to order online, whether it is directly within the listing or on an individual location page.
This also allows customers to choose how they want to receive their product with delivery or pickup options that best fit their needs.
With this shift, the strategy on how to maximize a brand’s online ordering experience has changed.
In this post, we will share our local SEO guide for ecommerce and online ordering to promote more conversions.
Maximizing Retail Listings For Online Ordering
When looking online for something to buy, customers will likely interact with a business listing as the first touchpoint.
Having the listing setup to direct customers to order online or visit your website is essential.
The ordering link should take the customer straight into the order flow so they can begin their purchase.
There should be as little friction as possible to allow them to start and place their order.
Lead your customer to a menu page, a breakdown of the main categories, or a simplified search function.
Within the listing, you can also share what options for receiving the order are available, such as in-store pick-up, curbside pickup, same-day delivery, or standard delivery.
These are known as attributes, and every applicable retail attribute should be selected for each of your listings to present as much information to a searcher as possible.
New Google attributes are updated and added on a consistent basis, so ensure you’re monitoring what is available and applicable to your brand regularly.
Local Inventory Ads For Retailers
To reduce as much friction as possible and increase rank for specific products, retailers should consider having Local Inventory Ads.
With these types of ads set up for a brand’s locations, customers are able to see specific products available at that location.
It also allows for the listing to rank for specific products a customer may search for on Google and shows what is currently available at the location if they are interested in picking their order up.
This creates a simplified omnichannel experience for the customer while encouraging quicker conversions.
Here you can see an example of Local Inventory Ads within a Google Business Profiles listing.
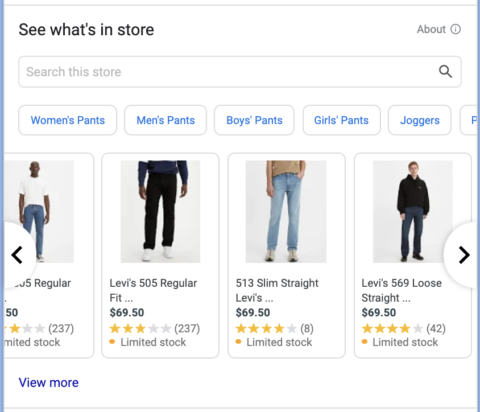 Image from Google Business Profile, February 2022
Image from Google Business Profile, February 2022The above listing displays products that are in stock at the locations and what is relevant to the customer’s search behavior.
When a customer clicks on one of the product ads they will be directed to Google’s hosted storefront for that retailer.
Google provides the necessary requirements to set up a local product feed to be able to take advantage of this feature within your listing.
Google provides metrics to allow brands to measure the performance of these digital ads.
The basic implementation onboarding details what is needed to get this set up for a retailer.
This is currently only available for brick and mortar locations in Australia, Austria, Brazil, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Sweden, Switzerland, the UK, and the US.
If you’ve implemented the basic setup for your local inventory product feed then there are several optimization features.
These enhancements include a merchant-hosted local storefront, display to order, and pickup today features.
To get started you may contact your Google representative of the local inventory ads support team.
Online Ordering For Restaurants
Locations that have their primary category set as a restaurant have the ability to display online ordering directly on their listing.
This function can be managed directly within a restaurant location’s Google Business Profile by navigating to the Food Ordering option on the left panel.
To turn it on you would go to set up your ‘Order online’ button.
By updating that functionality your listing will then show an option to order pickup or delivery, which will direct the customer to https://food.google.com/ for that individual location.
The below image shows what this would look like in practice.
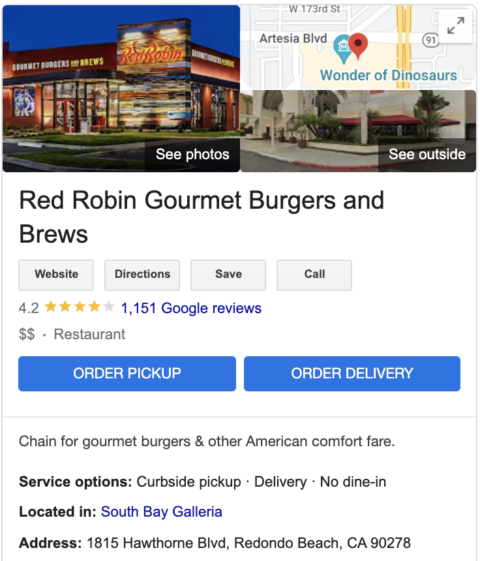 Image from Google Business Profile, February 2022
Image from Google Business Profile, February 2022A user will then be shown the different options available to order from the restaurant.
The customer can choose to order directly from the restaurant or can choose a third-party such as UberEats, DoorDash, Grubhub, Seamless, or any partners that location works with.
For locations that are integrated, customers will be able to order directly within Google.
It will display the menu items available at that location with the specific pricing.
It will also allow them to make any available modifications for their order.
When the order is ready to be completed, the customer will be able to checkout directly within Google.
This convenience allows for the customer to stay on Google and use any saved credit card info they already have with Google.
This creates a seamless and simplified ordering process where check-out can happen in a matter of seconds.
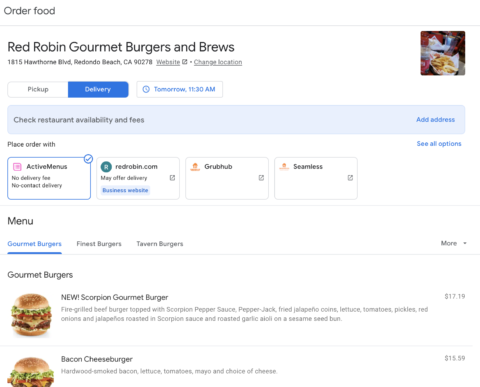 Image from Google Business Profile, February 2022
Image from Google Business Profile, February 2022Setting Up Orders With Google For Restaurants
If a restaurant wants to have the ability to allow customers to Order with Google directly, there are a few steps they need to follow.
Restaurants can visit Order with Google’s help page to see if they qualify for the service.
First, a restaurant must work with an approved third-party order provider like Olo.
This is required since these third-party order platforms have integrations with Google.
Next, brands will need to fill out an interest form with Google to begin the process.
Developers can review the documentation to make sure they are able to meet the necessary launch requirements.
There is also a launch readiness checklist that Google provides once you have been approved.
Maximizing Location Pages For Online Ordering
Location pages should also be optimized for online ordering just like a location’s listing.
There should be clear calls to action (CTAs) on the page to let the customer know they can start an order.
It should highlight what options are available for the customer to receive their products for pickup, curbside, or delivery.
The page should clearly lay out any key information about pickup or delivery procedures.
A good example is Target, which clearly describes all their options and then pushes customers directly into the order flow with a clear CTA.
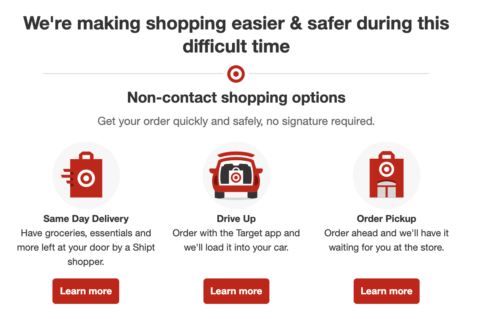 Image from Target, February 2022
Image from Target, February 2022Conclusion
Online ordering has become an essential part of a business’s strategy.
No matter your industry, making sure your listings and pages are optimized to create a seamless omnichannel experience will help your brand drive more sales.
It also improves your user’s experience, encouraging customer loyalty and positive sentiment.
More resources:
Featured Image: elenabsl/Shutterstock