Whether you run an ecommerce or brick-and-mortar retail business, chances are you’ve heard a thing or two about Google Shopping.
But what is Google Shopping, exactly? Is it worth using? And, if so, how should you use it?
This post will cover all the fundamentals of Google Shopping and explain everything you’ll need to get up and running on the world’s most popular retail search engine.
So let’s kick off with some basics.
What Is Google Shopping?
Google Shopping is a comparison shopping engine provided by Google that allows consumers to research, compare, and purchase products from a broad range of online vendors.
Products listed on Google Shopping often appear as ads within regular Google Search results, usually inside a carousel at the top of the results page.
Users can also access the platform by heading directly to the Google Shopping website or by selecting the Shopping tab in Google Search.
Google Shopping organizes millions of products and reviews into an easily searchable and visual format, making it easier for consumers to find the right product at the best price. Shoppers can also use the platform’s many filters to refine further their product searches, including by price range, location, or brand.
Moreover, product listings that include the Google Cart icon can be bought directly through the platform (so that shoppers don’t need to visit third-party stores) and come with a Google-backed guarantee for additional peace of mind.
How Does Google Shopping Work?
Merchants must submit a file known as a product feed to Google to have their products featured on Google Shopping.
The product feed contains all the relevant data from the merchant’s inventory, including product titles, descriptions, images, and prices.
Google’s algorithm processes this data to surface the merchant’s products whenever users search for related product queries.
When users click on one of these product listings, they’re taken to the merchant’s website to complete the purchase (provided the item can’t be bought directly through Google Shopping).
Until April 2020, merchants had no option but to pay for product listings in Google Shopping.
Since then, however, Google has introduced free product listings within the Google Shopping tab and Google Search.
Google Shopping Ads
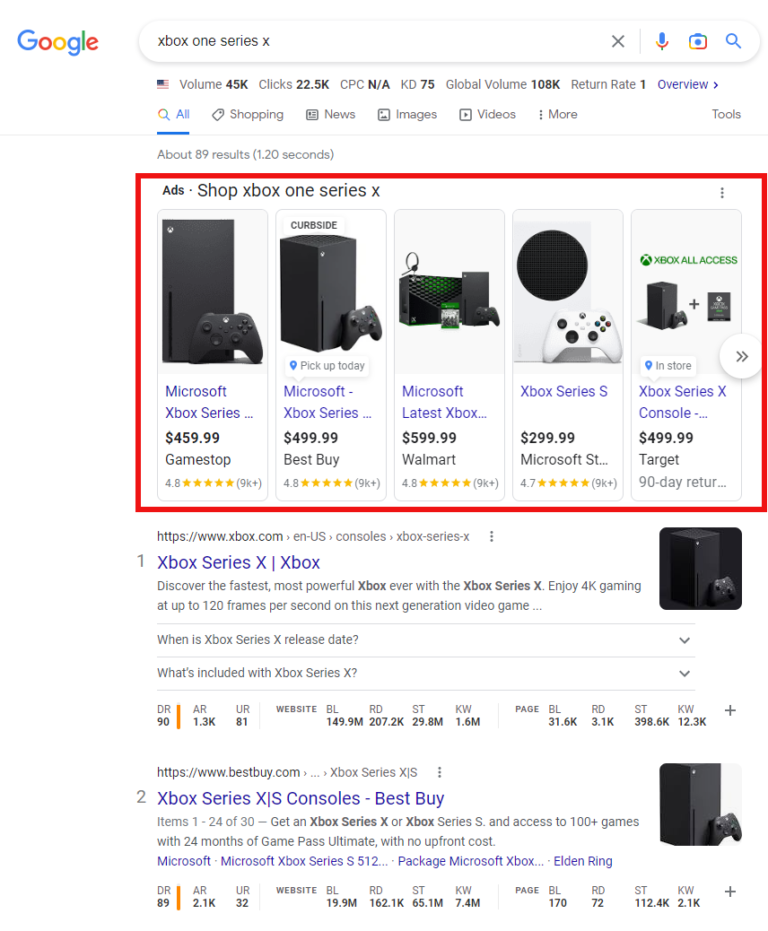 Screenshot from search for [xbox one series x], Google, October 2022
Screenshot from search for [xbox one series x], Google, October 2022You can pay for more prominent product listings by creating Shopping ad campaigns in Google Ads.
As with other ad formats, the placement of your Shopping ads is determined in an ad auction, and you get charged on a cost-per-click (CPC) basis.
Unlike traditional text ads, Google Shopping ads are visual, showing an image of the product and information like title, price, and shop name.
They can appear within the Shopping tab, Google Search, Google Images, and on Google Search Partner websites.
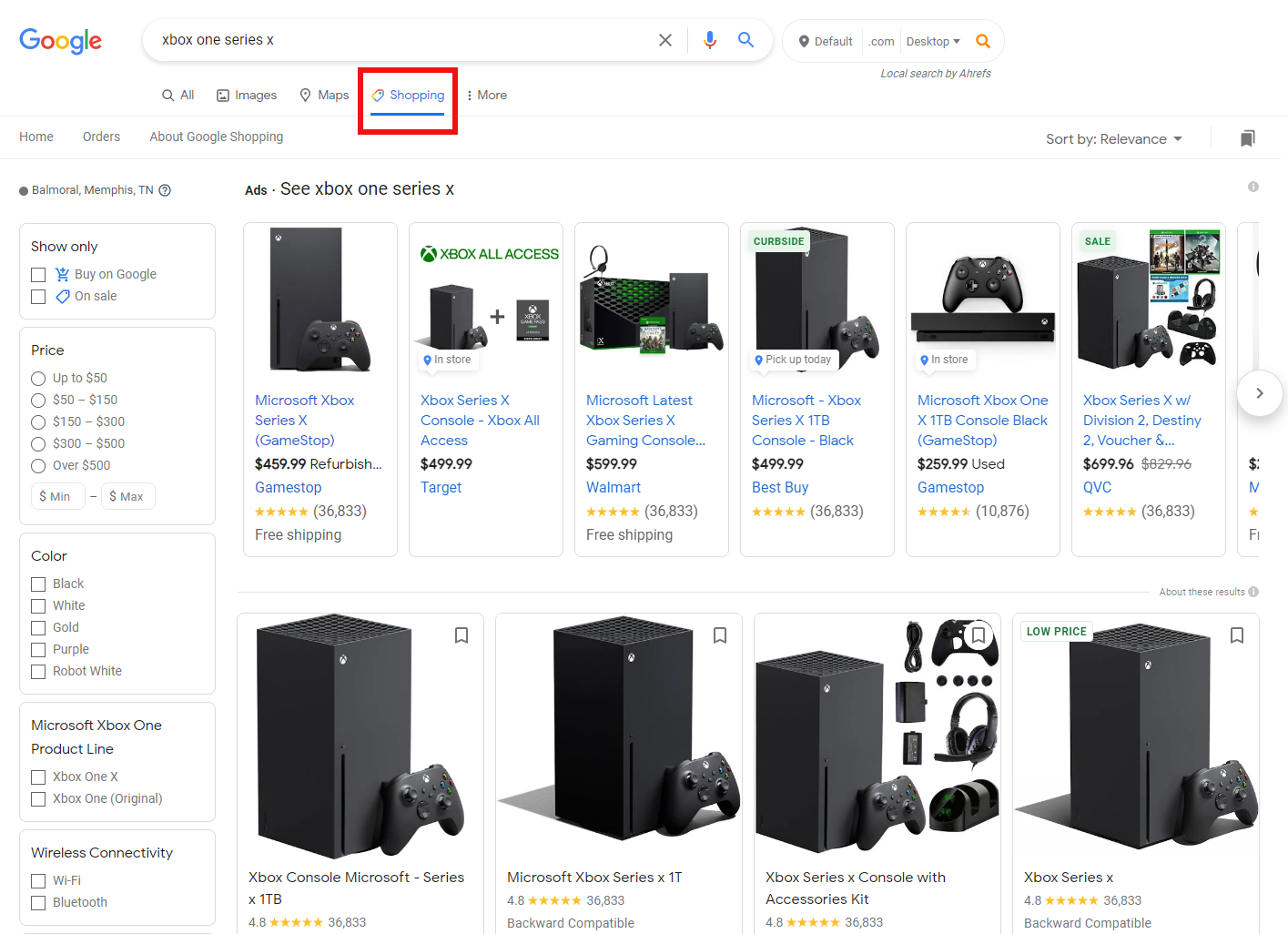
Google Shopping Free Listings
You can now list your products on Google Shopping for free, just as you can list your website on the Google Search index without needing to pay.
Of course, free listings don’t enjoy the prominence of sponsored listings, but they do appear across the Google ecosystem, including on the Shopping tab, Google Search, Google Images, and YouTube.
Here’s an example of free listings appearing on Google Search within a product knowledge panel:
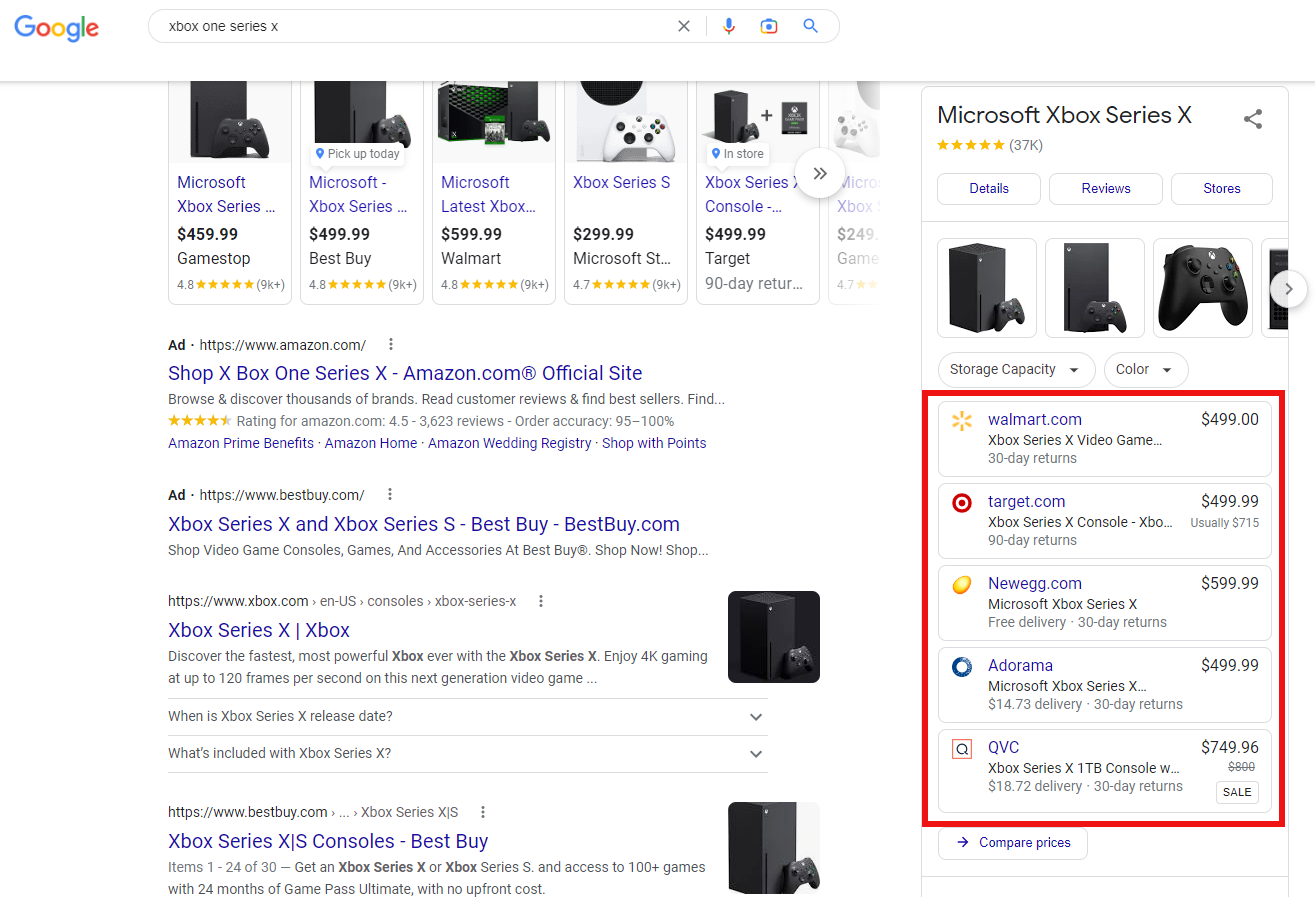 Screenshot from search for [xbox one series x], Google, October 2022
Screenshot from search for [xbox one series x], Google, October 2022Should I Be Listed On Google Shopping?
In short, yes!
Here are some of the major ways Google Shopping can benefit your ecommerce or retail business:
Greater Product Visibility
Powered by the world’s most popular search engine, listing your products on Google Shopping can significantly boost your customer reach.
Moreover, using the service allows your brand to appear several times within a single Google Search results page, thereby multiplying your exposure to potential customers.
For example, if you combine free and paid Google Shopping listings with traditional Search ads — and your website ranks organically for the query in question — Google could display all four in the search results simultaneously.
Exposure To Users With High Purchase Intent
Naturally, users that head directly to the Google Shopping platform generally do so intending to buy something. So it’s a no-brainer to try to get your products listed for free on one of the world’s most popular storefronts.
Moreover, free and paid Google Shopping listings only appear in Google Search if they are deemed to be a relevant match for the user’s search intent.
Visual Appeal
Shopping ads are more eye-catching than their text-only counterparts.
Whenever users search for a specific product or conduct some research to find out what colors, styles, and sizes are available, they are more likely to find results that feature actual product images useful.
This, in turn, can translate into more clicks and higher conversion rates.
How To Add Products To Google Shopping
Now that you’re up to speed on the basics of Google Shopping and how it can help your business grow, let’s look at what you need to do to get set up on the platform.
1. Create A Google Merchant Center Account
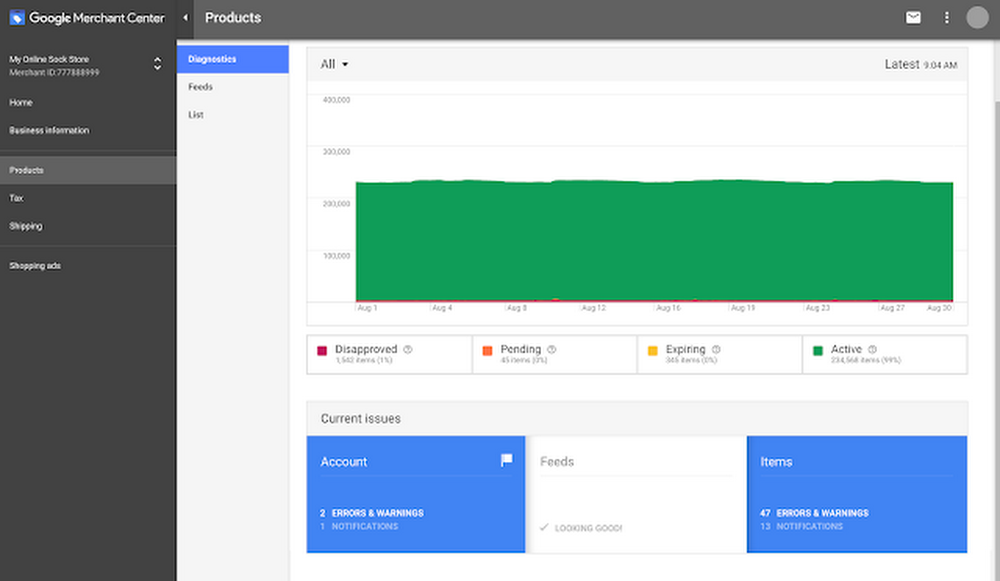 Screenshot from Google Ads & Commerce Blog, October 2022
Screenshot from Google Ads & Commerce Blog, October 2022The first step towards listing your products on Google Shopping is to set up a Google Merchant Center account.
This will serve as a central hub where you can manage how your product catalog appears throughout Google.
The setup process is pretty self-explanatory.
You’ll be asked to provide some basic business information, choose how you want your customers to check out (e.g., on your website or through Google), and be instructed to verify your website.
You’ll also be given the option to opt-in for free product listings!
2. Create High-Quality Product Images
We’ve already seen how product images play a central role in Shopping ads, which is why you need to ensure all your product images are of high quality.
This means each image should present the product clearly and accurately using a clean background.
So be sure to avoid any image overlays, image borders, or multicolored backgrounds. You should also stick to one product per image unless the product is part of a bundle.
3. Upload Your Product Feed
The next step is to submit your product feed. As we mentioned earlier, the product feed is a file that lists all the products you want to promote through Google Shopping.
You can format the product feed in a spreadsheet, giving each product its own row and specifying the product attributes in different columns.
You can find a template data feed within Google Merchant Center.
Here are some of the attributes that Google will need to generate both paid and free product listings:
- Identification: Such as a stock keeping unit (SKU) to uniquely identify the product.
- Title: An accurate, top-level description of the product.
- Description: A more detailed description of the product.
- Availability: Specifying whether the product is currently available.
- Price: Detailing how much the product costs.
- Link: Specifying the URL of the product landing page.
- Image link: A URL to the product’s main image.
Once you’ve completed your product feed, upload the file to Google Merchant Center.
After submitting your product feed to Google Merchant Center, each product will be assigned a product status: Active, Pending, Disapproved, or Expiring.
You can find instructions on how to check your product statuses, as well as a detailed breakdown of each status and what it means, here.
For more guidance on creating and uploading your product feed, check out this video from Google:
Note: Each file is limited to a maximum of 100,000 items by default. (Although you can modify this by sending a request.)
4. Link Your Google Merchant Center And Google Ads Accounts
To promote your products through Google Shopping ads, you’ll need to set up an Ads account (if you haven’t already) and connect it to Google Merchant Center.
Click the Account linking option within the Google Merchant Center settings menu to link both accounts.
Then, click Link account beneath the Google Ads section.
5. Set Up Your Google Shopping Campaign
Once both accounts are linked, you’ll need to create a Google Shopping campaign.
You can set this up in either Google Merchant Center or Google Ads. Here’s the process for the latter:
- Select Campaigns, then New Campaign.
- Choose your campaign objective and select Shopping under Campaign type.
- Specify your campaign settings, such as campaign name, locations, bidding strategy, daily budget, and campaign schedule
- Choose which type of ad group you want to build for your campaign (a Product Shopping ad group is best for Google Shopping newcomers)
- Name your ad group, specify your maximum CPC bid (or cost-per-engagement bid if you choose a Showcase Shopping ad group), and save!
Final Thoughts
Google Shopping provides consumers with a simple yet powerful way to discover the products they want at the best price, all in one place.
Not only does the platform save shoppers from the hassle of visiting different online stores one by one just to find the right deal, but it also empowers them to make better-informed buying decisions by neatly collating various product data and customer reviews.
For ecommerce and retail businesses, Google Shopping offers the potential to reach a huge audience of highly-motivated customers.
Moreover, Google’s recent decision to open up the platform to all merchants, free of charge, has created an unprecedented opportunity for businesses like yours to acquire new customers at minimal expense.
With that said, it’s time for you to seize this opportunity and start making the most of Google Shopping within your own business, whether you start with free listings, Shopping ads, or both.
Happy selling!
More resources:
