Keyword relevance is a key part of Google Search, including both organic and paid search results. It helps make sure that the results Google shows are directly related to what people are searching for and match their needs.
Google determines relevance in search results by understanding the intent behind user queries, considering exact and related keyword matches, and analyzing user engagement with pages. It also takes into account factors like internal links, localization, personalization, and whether the content is up-to-date.
Think of relevance as the bedrock of your content. First and foremost, your content needs to align with the meaning of the query and the reason why someone could be searching for it. You can also use SEO techniques to improve the relevance of your content and get more traffic.
Keyword relevance is more than just matching words. Google uses at least these seven different factors to decide not just if any given page is relevant, but how relevant it is. Make sure your content checks all the right boxes.
- The intent behind the query. Google aims to understand what users want when they search. If your content is about the topic but not in a way that would fulfill the needs of the user, it’s simply less relevant to the user (source)
- Exact keyword matches. Content containing the same words as the search query is considered relevant. However, Google doesn’t rely solely on exact matches (source).
- Other relevant keywords and content. Beyond exact matches, Google looks for related words and media such as videos or pictures. If a page covers a topic comprehensively, it’s likely to include relevant terms (source).
- Searchers’ behavioral data. If users engage with a page they found in the SERPs, it indicates relevance (source).
- Links. External and internal links help Google understand the page’s context. Google also examines the page’s anchor text and the surrounding text (source).
- Localization and personalization. Search results can vary based on the user’s location, search history, and preferences. This personalization helps in delivering more relevant results (source).
- Freshness. Regularly updated content is more likely to be relevant, especially for topics that evolve over time. Google may prioritize newer content for certain queries (source).
That said, relevance is not the only principle or system that Google uses for ranking. In the video below, Paul Haahr, Distinguished Engineer at Google, explains two types of signals: those that take into account the user’s query and those that score the page itself, regardless of the query.
Relevance, in my opinion, would be in the query-dependent category.
Google uses the idea of keyword relevance in ranking local results and choosing winners of Google Search Ads. If you ever step into the territory of search engine marketing, it’s good to know the difference.
- Local relevance refers to how well a local business profile matches what someone is searching for (source). This can include name of the business, business category and attributes. When people look for products or services in their vicinity, Google takes this into account and weights against other factors (prominence and distance).
- Ad relevance is how well the content of the ad and the landing page fit the intent behind the query (source). Google claims that you get a higher position for your ad than someone who’s willing to pay more for their ads, just because you’ve hit a higher ad relevance.
First, make sure you have a good target keyword that’s worth the time and effort put into search engine optimization. You can check that with our guide to keyword research.
Google tends to favor what it already ranks highly, which is why the top 10 search results often look very similar. To ensure your content is keyword-relevant, it’s often more effective to align with existing successful content rather than trying something entirely new and hoping that Google will recognize your effort.
And this is also my advice to you. Make your content relevant before you make it unique. Don’t skip any of these seven steps.
1. Make sure you’re aligning with search intent
Search intent is what the searcher expects to see in the SERPs when they type in a search query. It could be a list of the best products, a video, a Wikipedia-like page, or a simple, direct answer that doesn’t require clicking on anything.
Nobody types in queries like “give me the best places to buy the doona liki trike but if there’s something important I should know before buying, lmk”. They will just type “doona liki” because they’re used to writing simple queries and expecting Google to figure them out. Google expects content creators (you) to make that content so they can index it, rank it, and show it to their users.
The most reliable way to align with search intent is to look at what’s already ranking and identify the 3Cs of search intent:
- Content type. Typically one of the following: blog post, video, product page, category page, landing page.
- Content format. This applies mostly to informational content. For example, a how-to guide will be a different content format than a listicle or product review.
- Content angle. The specific focus or unique selling point that makes top-ranking posts and pages stand out.
For example, all the the posts below are blog posts in the listicle format. Some angles you can spot here are “that actually matter”, “important”, “key”.
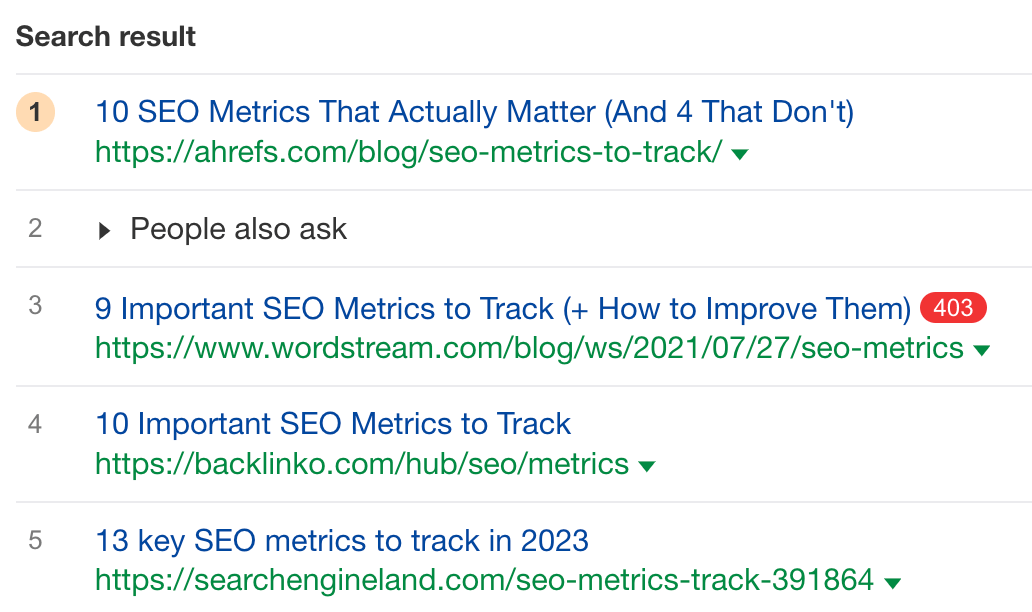
Another great way to examine search intent is to check the amount of traffic generated by each type of page. To make this fast and easy, use Ahrefs’ Identify intents feature.
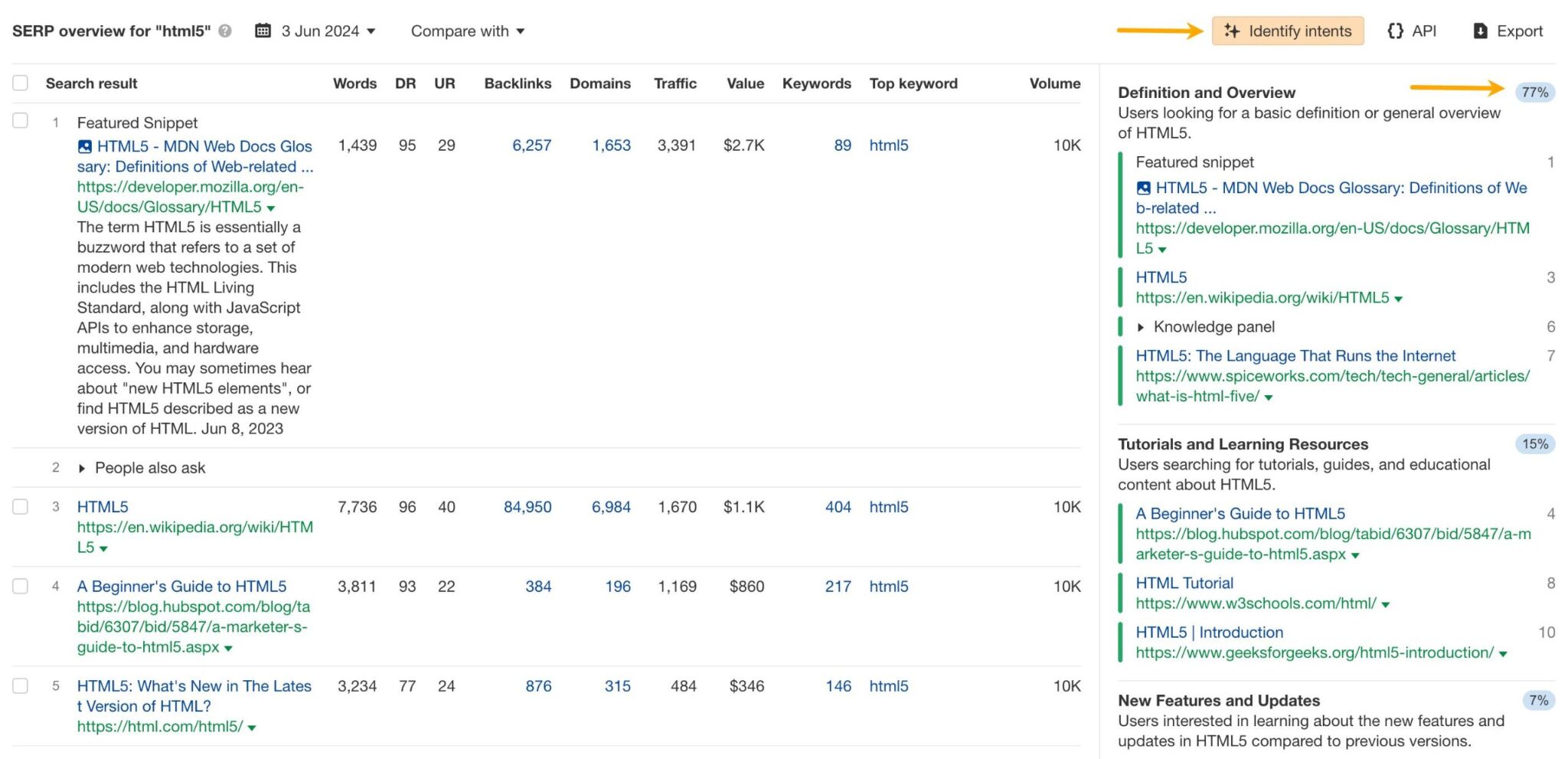

If you’re curious to learn more about search intent, head on to our guide.
2. Include your target keyword in relevant places
On any page, there are a few places that Google likes to look for signals of relevance.
- Page title.
- URL.
- Main header (H1).
- Subheaders (some of your H2s, H3s, etc.).
- Intro paragraph.
Here’s an example with highlighted page elements:
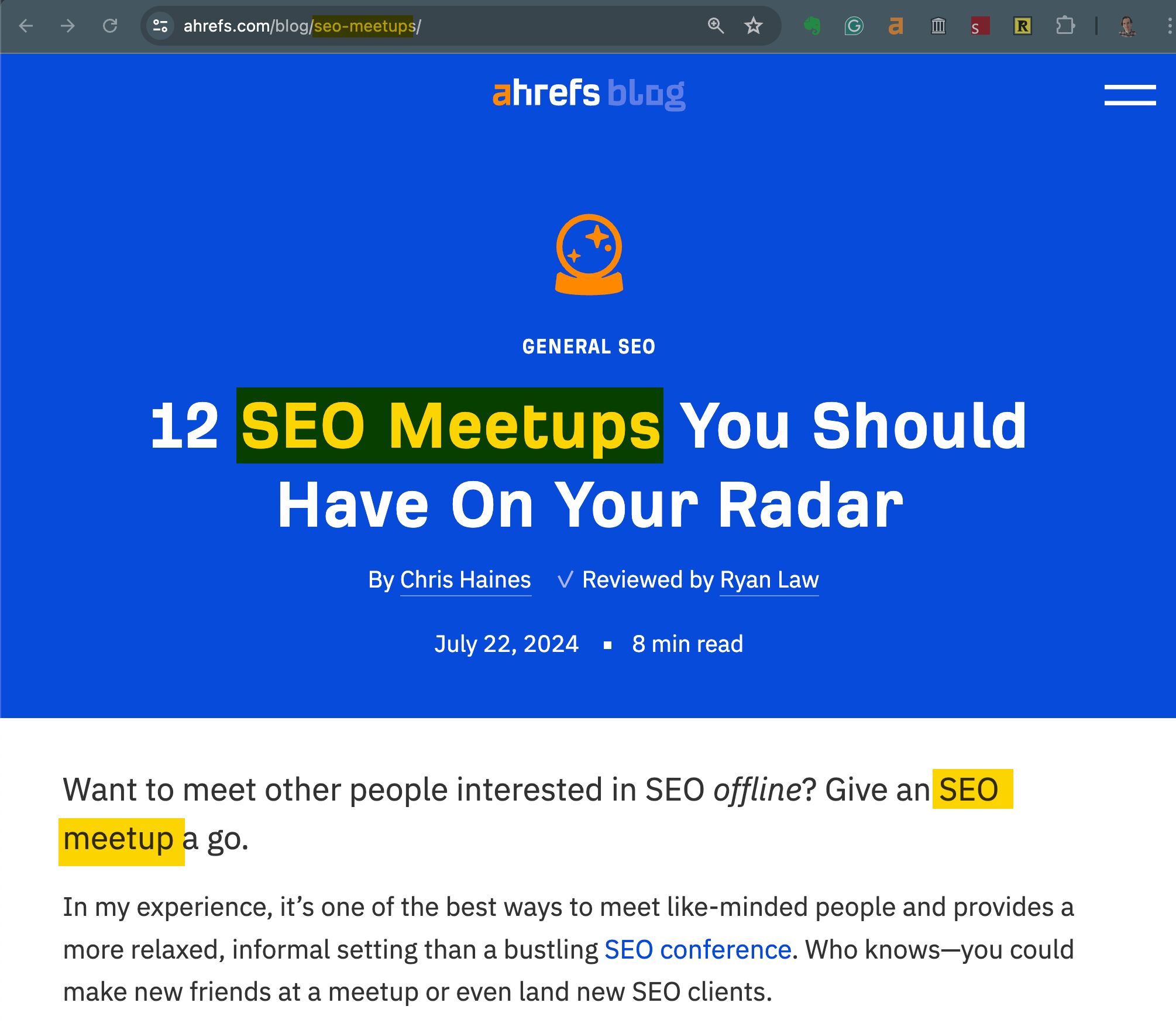

In other words, Google is looking for the most direct, straightforward type of relevance. Both a poem and a Wikpedia article can be about a topic like love. But the kind of relevance that you need to achieve in content is the latter type.
Keep in mind that in any text that you want to rank, however creative or unique you want it to be, Google will likely look at these places.
3. Include secondary keywords and frequently mentioned phrases
This step refers to words and phrases that naturally fit into the text. Once you identify them, it feels obvious. For example, if your primary keyword is ‘running shoes,’ related phrases could include ‘breathable material,’ ‘arch support,’ and ‘lightweight design.
You can manually look for commonalities among top-ranking pages or even brainstorm these words. But the quickest and most reliable way is to use an SEO tool that allows you to look specifically for those keywords.
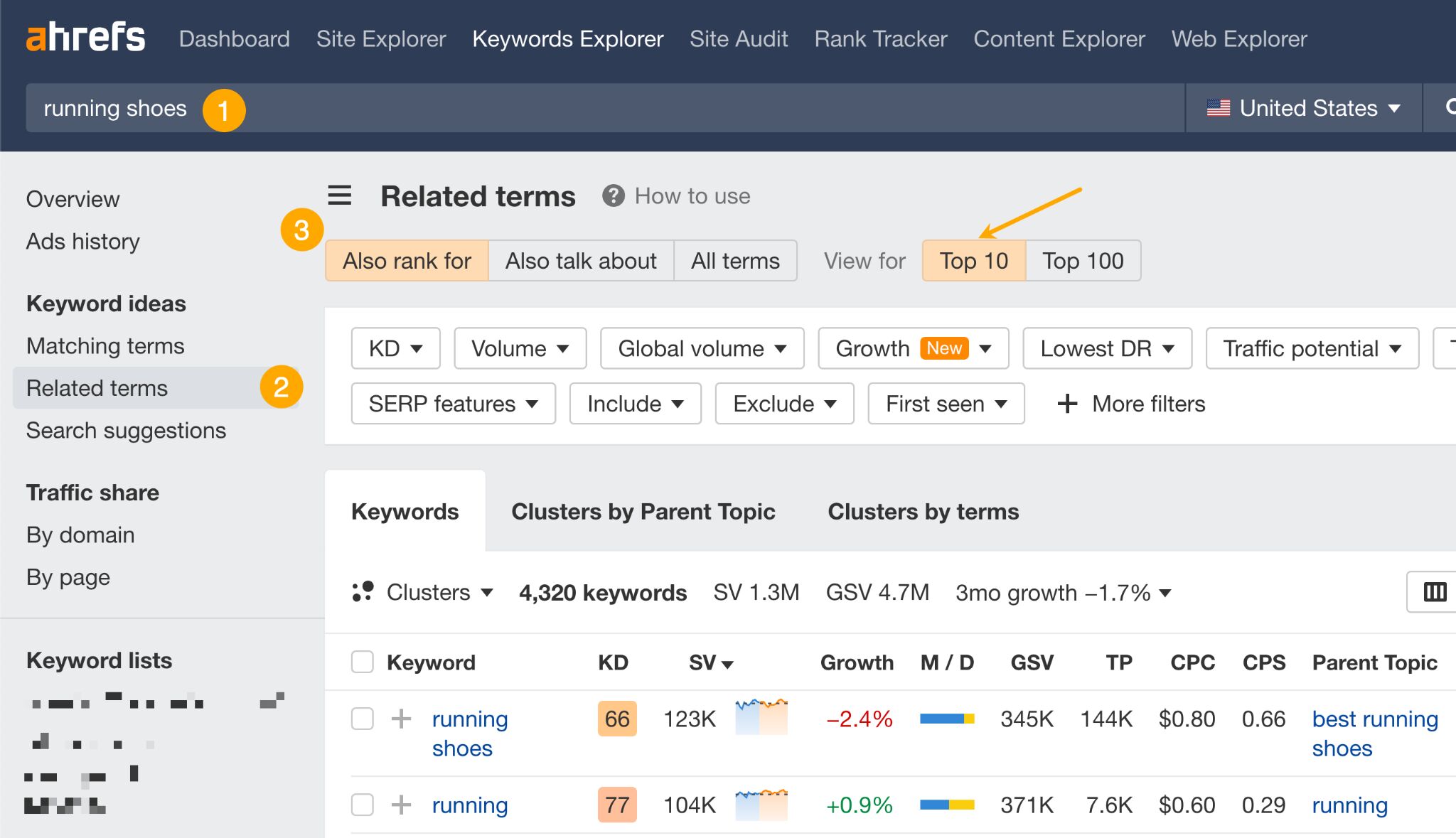
Here’s how it looks in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer:
- Enter your target keyword.
- Go to the Related terms report.
- Choose Also rank for for secondary keywords and Also talk about for frequently mentioned phrases. You’ll likely get the best results in the Top 10 mode.

4. Align with the content structure of top-ranking pages
Content structure is about serving the most relevant need-to-know information first and goo-to-know information last.
The key to understanding what is need-to-know and what is good-to-know is to look for hints in the content that already ranks; these have already nailed keyword relevance.
For example, if you’re creating content about “beginner’s guide to investing” you’ll want to start with the most essential, need-to-know information, such as “What is investing?” and “Why should you start investing?”. Opening with key takeaways, as Nerdwallet does in the example below, wouldn’t be a bad idea, either.


The structure is also about the comprehensiveness of your content. In other words, it’s about covering the topic in full and how much focus you’ll give to each subtopic.
Again, you can look at pages manually or streamline the process with an SEO tool. In Ahrefs, you can find a tool called Content Grader that scores content based on the topics mentioned and how well they are explained.
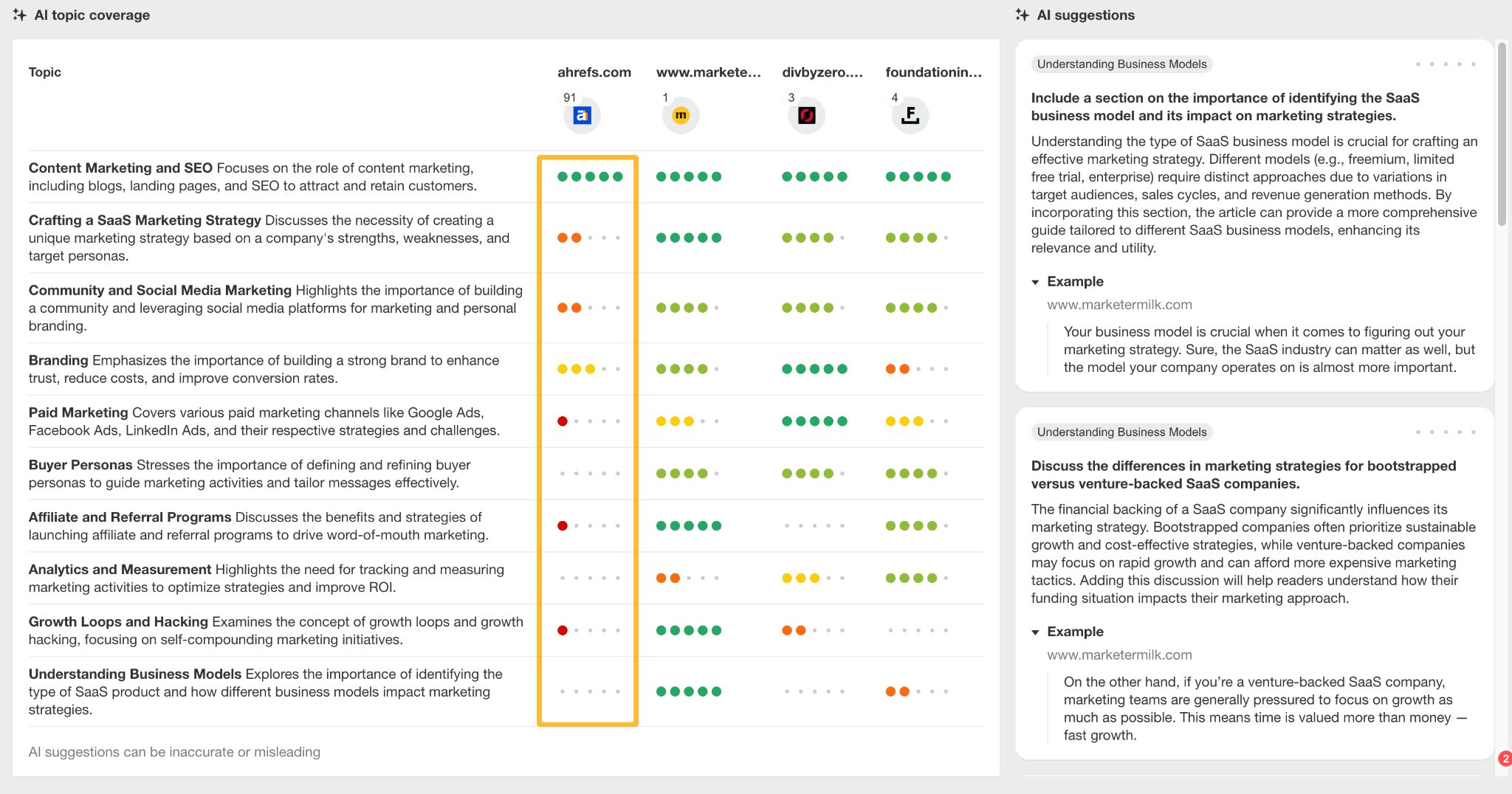

If you’re working on a new piece of content, you can use Content Grader to aid your outlining process. You can also use it to optimize existing content; it will help close the content gap.
Finally, structure is also about what media you include on a page. Google claims to take into account the presence of images or videos that could support content’s relevance:
Just think: when you search for ‘dogs’, you likely don’t want a page with the word ‘dogs’ on it hundreds of times. With that in mind, algorithms assess if a page contains other relevant content beyond the keyword ‘dogs’ – such as pictures of dogs, videos or even a list of breeds.
Tip
Remember to add descriptive alt text to your images. It will help Google understand what the image is about and how it relates to the entire text. So this might help you rank in Google Image Search, too.
Google has some helpful, easy to follow tips on how to write good alt text here.
5. Look for hints in the SERPs
Apart from what we’ve discussed so far, you may find additional clues on search engine results pages.
For example, meta descriptions are often overlooked in SEO because they’re not a direct ranking factor. However, since Google rewrites meta descriptions around 60% of the time, they can provide valuable insights into what Google and searchers find most important about a page.
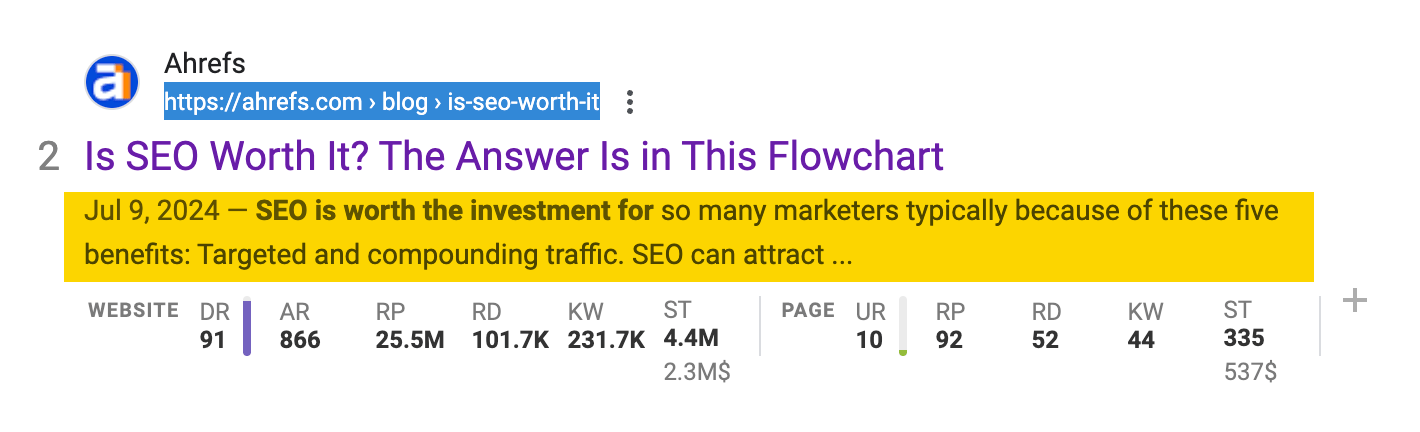
I used the information from meta descriptions to rank #2 for the keyword “is seo worth it” and increase traffic to the post (#1 being Reddit…).
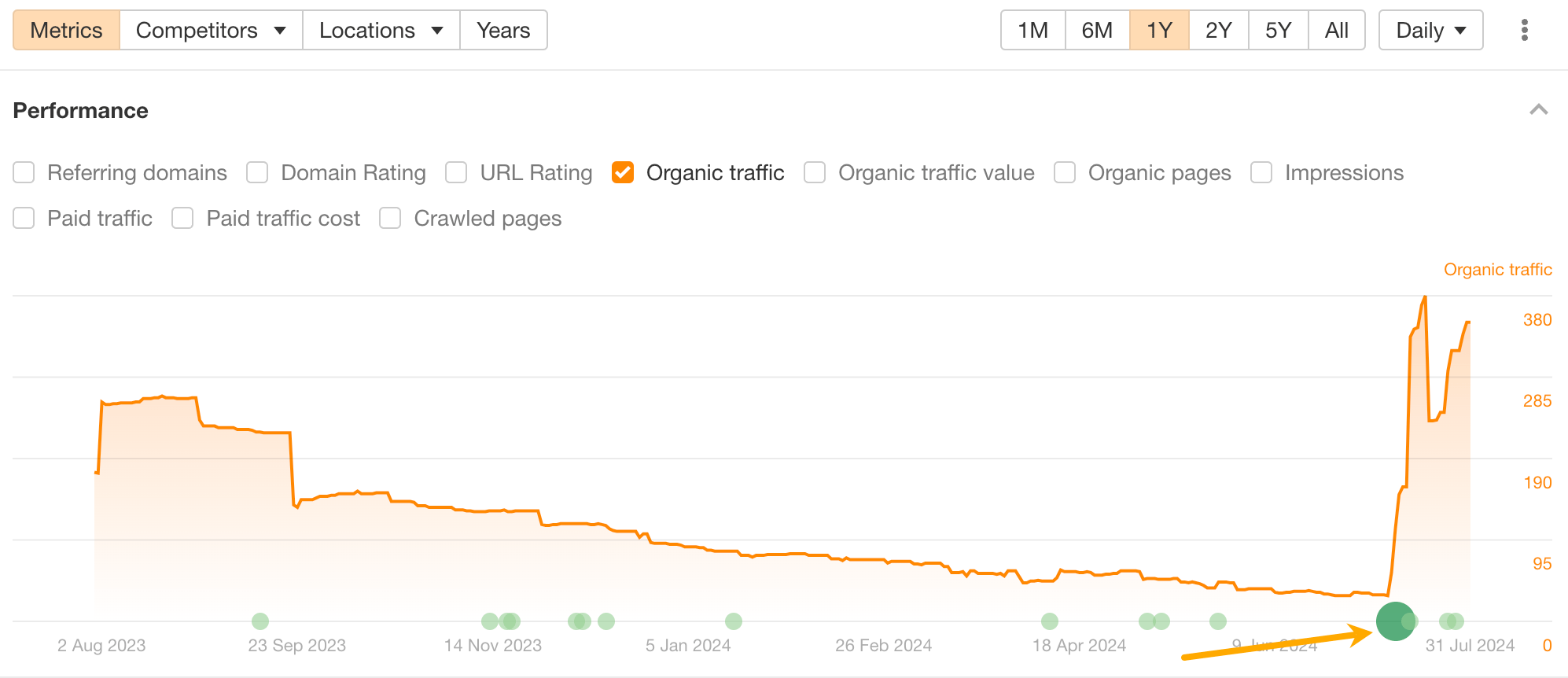

I noticed that Google favors a quick and direct response to the question (they even highlight the most direct answer—“yes”), so I added that to the intro.
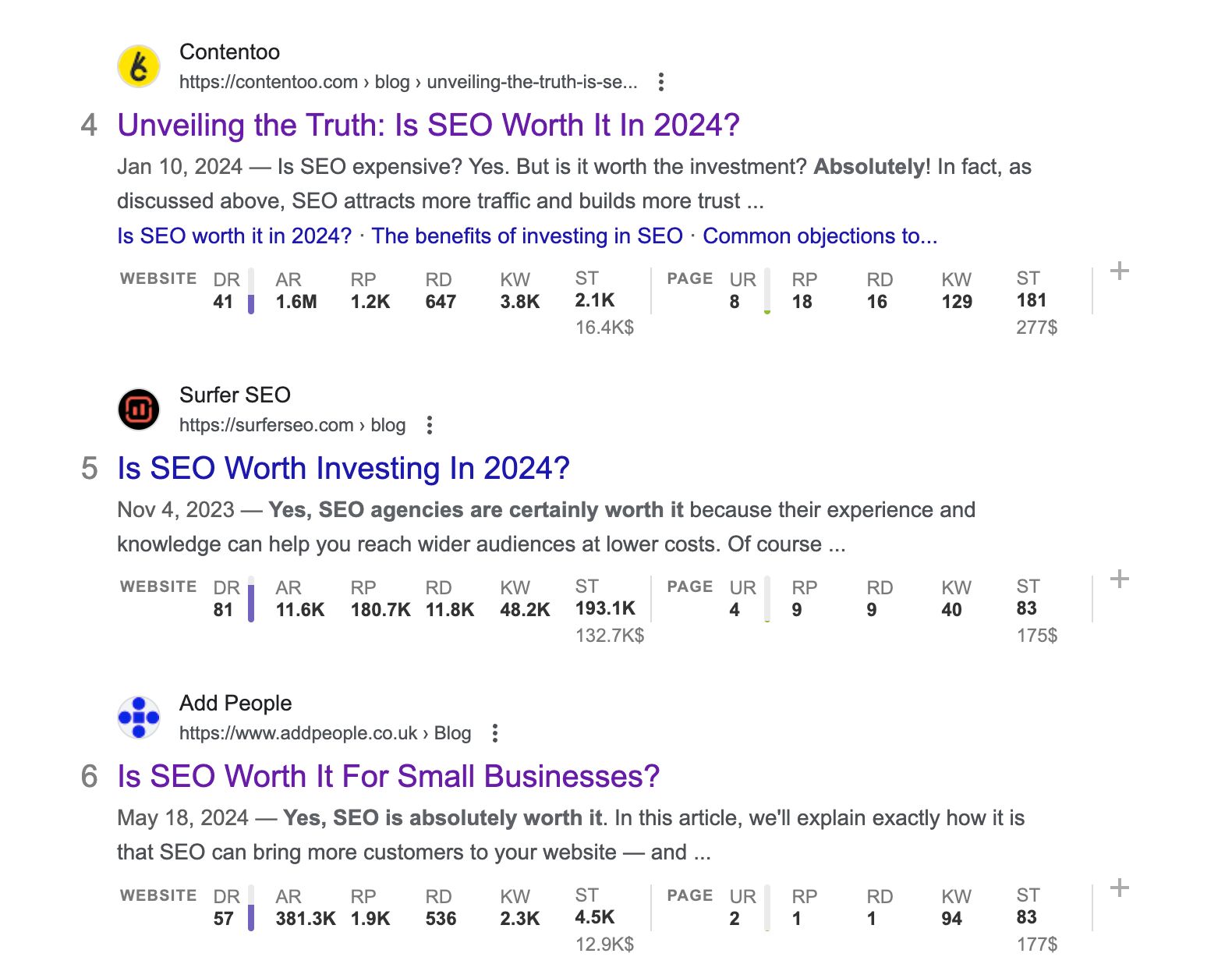

Moreover, Google also rewrote my original meta description to put the new direct answer in front of the searcher.



You can find similar hints in these SERP features:
- Featured snippets.
- “People Also Ask” box.
- “Things to know” box.
- Images shown on top of the SERP.
6. Add relevant internal links
As you may already know, internal links are hyperlinks between pages on your site. Not only they help Google understand the linked page is about but also they aid the flow of link equity, helping interilnked pages rank higher.
Here’s a tip for adding internal links as you write. Use the “inurl” search operator to find other places on your site where you mention a particular word or phrase. To illustrate, here’s what I would type into Google’s search bar if I wanted to find mentions of the phrase “content marketing”:
inurl:ahrefs.com "content marketing"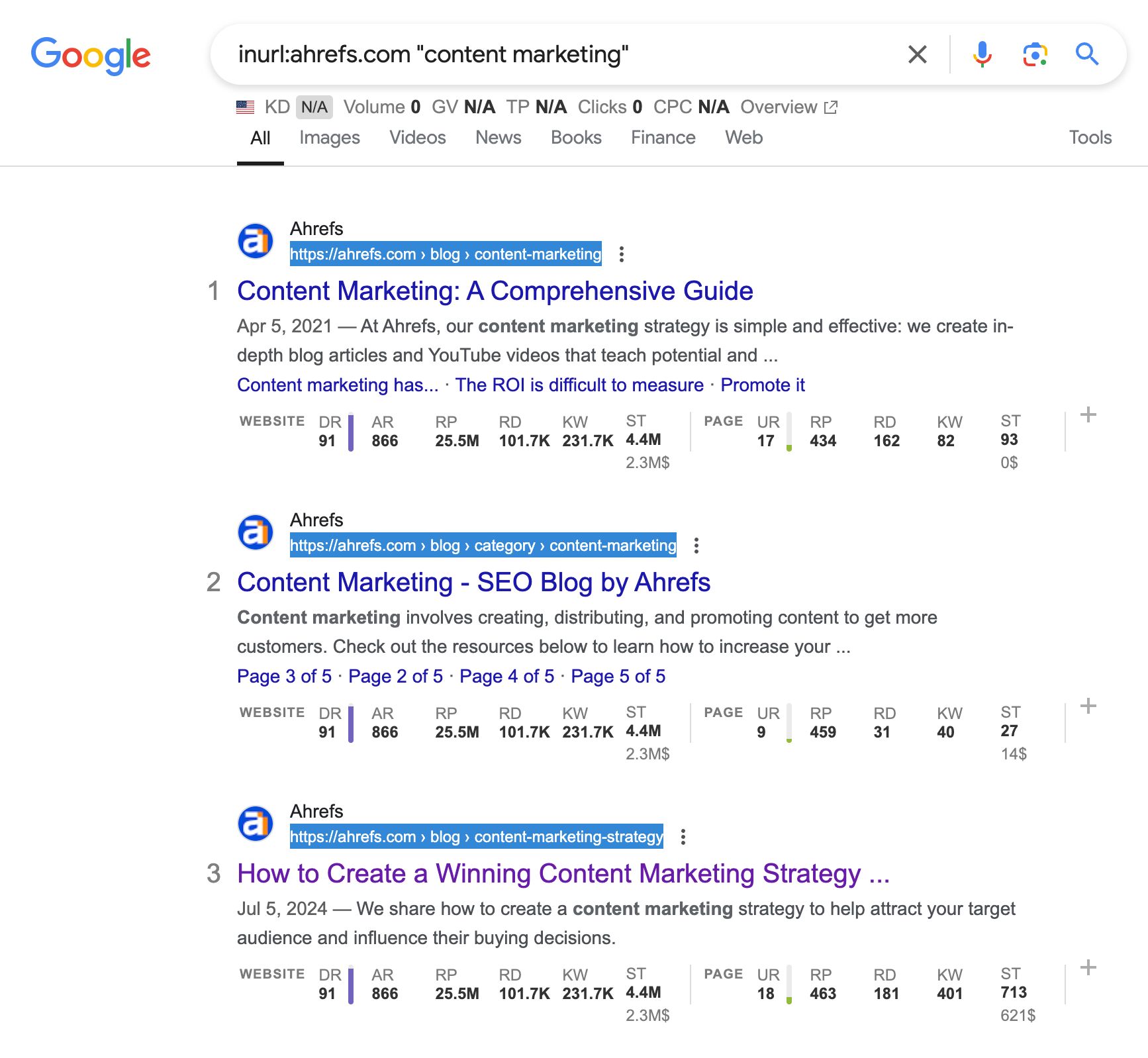

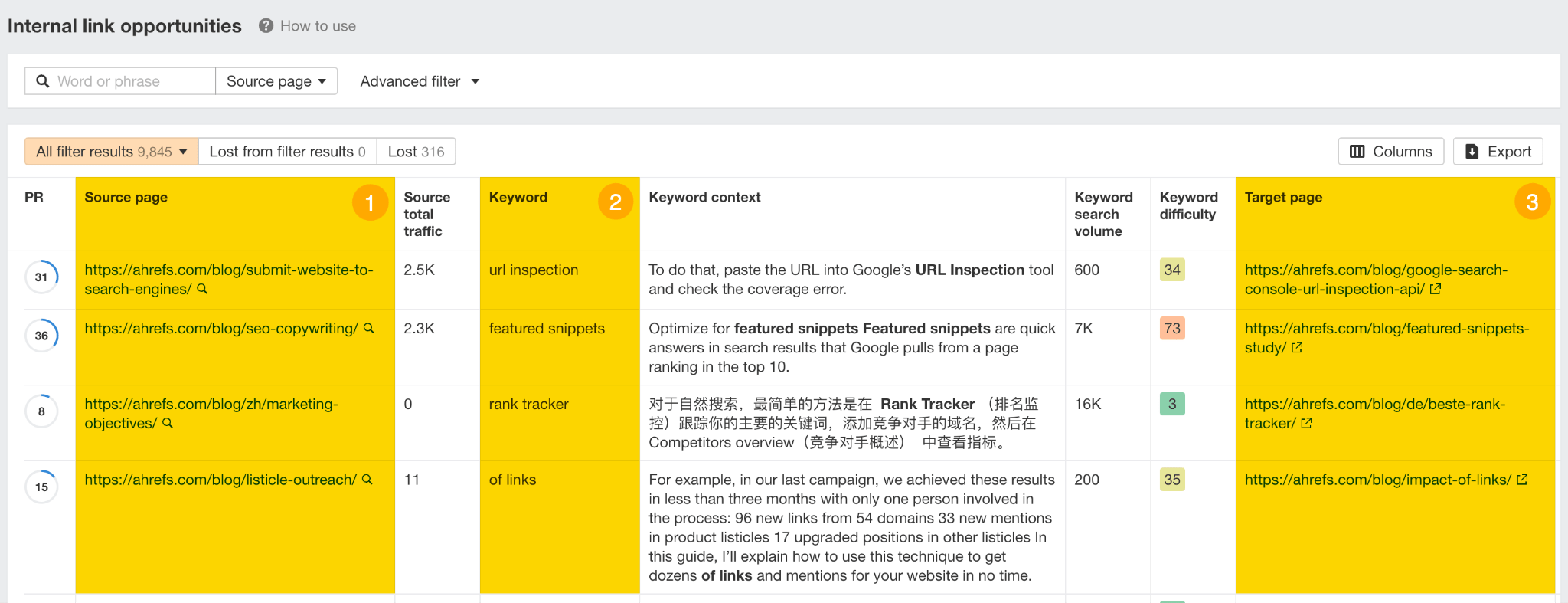
As for adding internal links to your existing content, you can streamline the process with Internal link opportunities tool in Ahrefs’ Site Audit. It takes the top 10 keywords (by traffic) for each crawled page, then looks for mentions of those on your other crawled pages.
It will tell you where to link from, where to link to, and which word/phrase to link.

7. Aim for relevant backlinks
Relevant backlinks mean links from other sites that mention your target keyword or a similar phrase in the anchor text or surrounding text.
In a short video on how Google Search works (below), Google’s Matt Cutts explains that a document can become relevant to a query by having that query included in its backlinks. Paraphrasing his explanation, backlinks containing the target query can enhance the relevance of a webpage in search results.
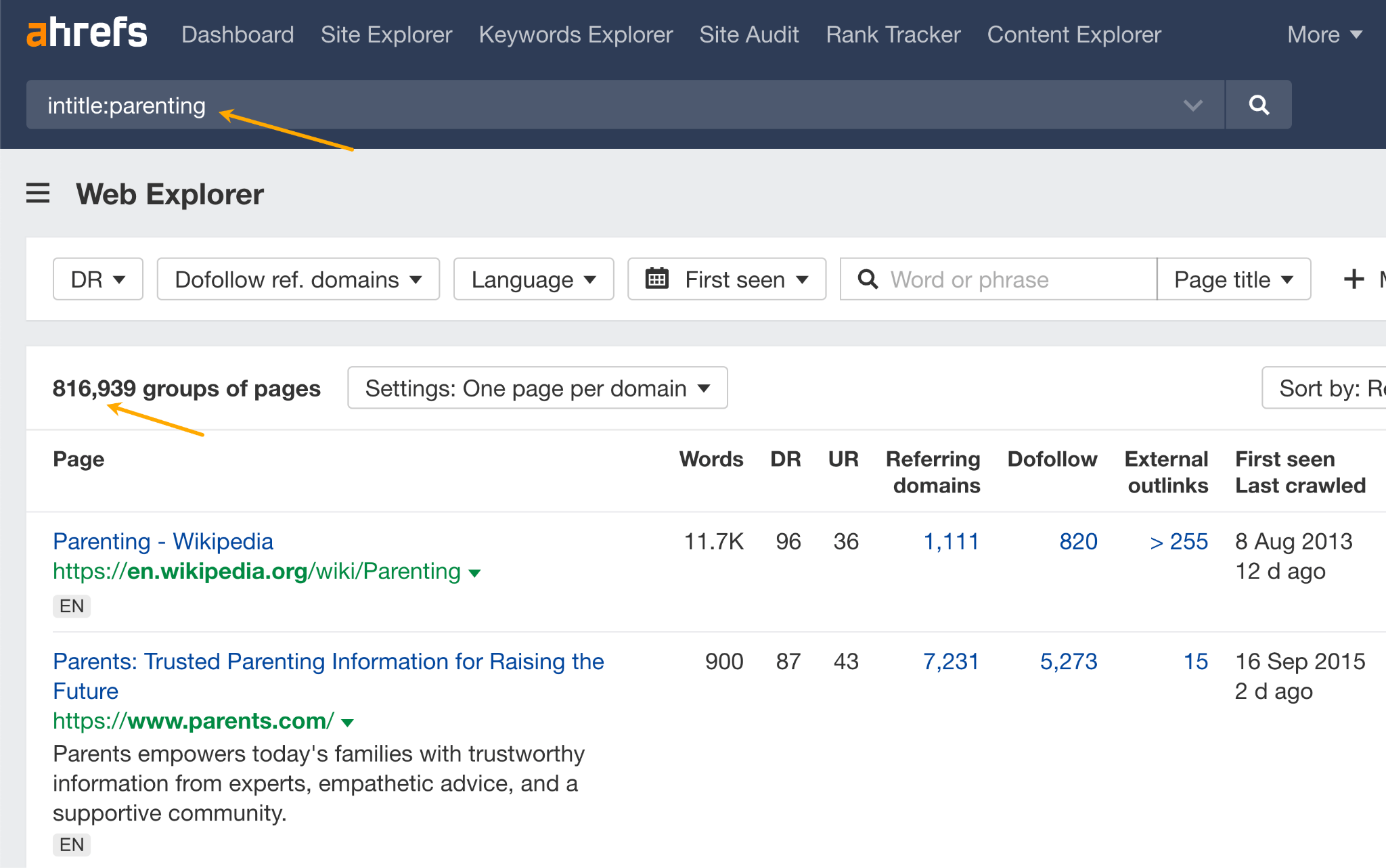
You can use Ahrefs’ Web Explorer to find and vet pages that already use your target keyword as link anchors and try to win over those links. Just type “outlinkanchor:[your keyword]” in the search bar.

There is also a possibility that backlinks coming from pages or sites on the same topic (or closely related) can increase relevance — some SEOs believe so. Mentions of such a system come from Google’s Reasonable Surfer patent, research on topic-sensitive PageRank. Moreover, irrelevant links were supposedly the target of the Google Penguin update.
However, at this point Google erased the only official mention of this I could find.
In 2021 Google said this:
If other prominent websites on the subject link to the page, that’s a good sign that the information is of high quality.
But then, they erased a few words, giving a whole different meaning to that sentence:
For example, one of several factors we use to help determine this is understanding if other prominent websites link or refer to the content.
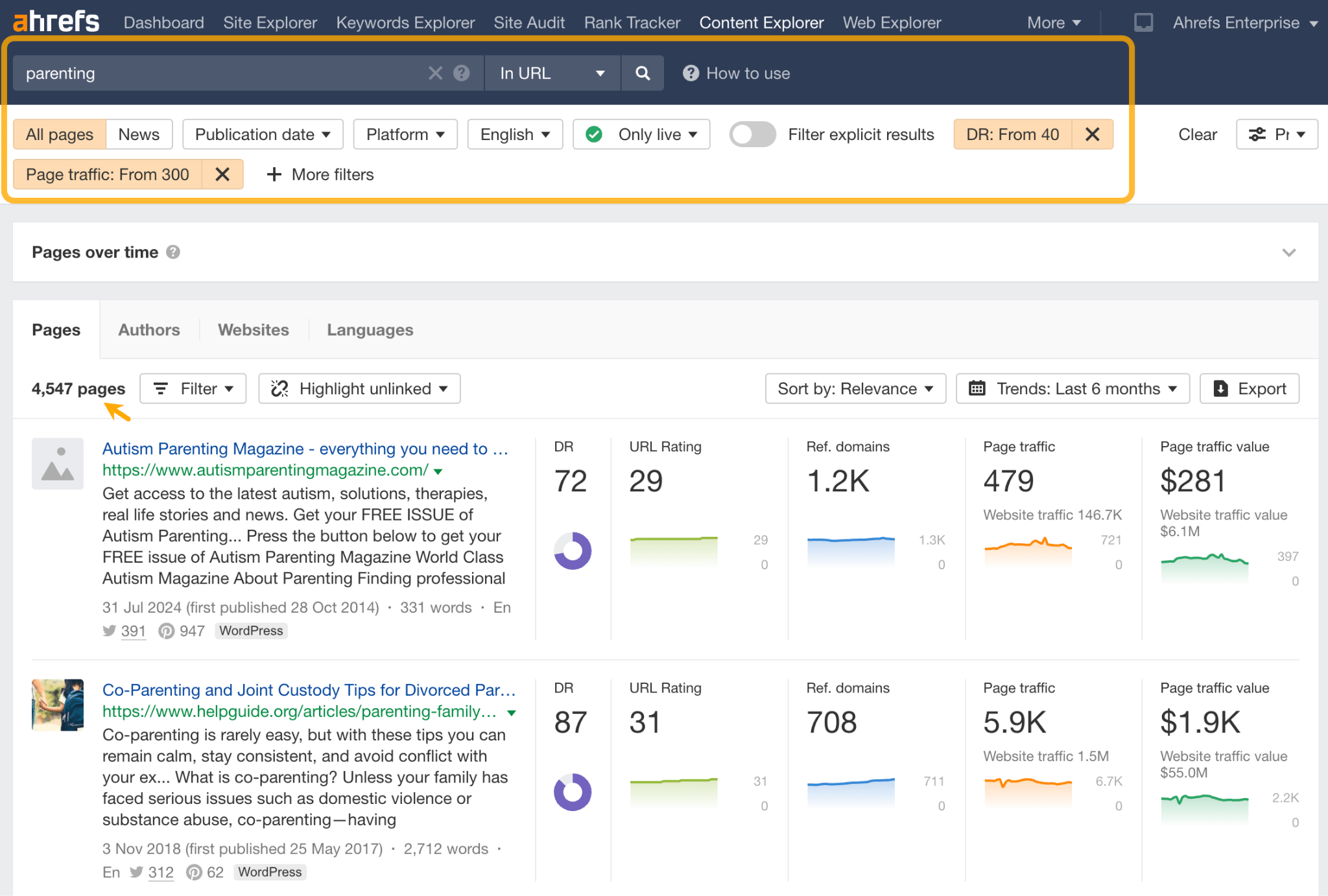
If you want to see if these kinds of links work for you, you can find them and vet them using either Ahrefs’ Web Explorer or Content Explorer.

You can aim for topically relevant backlinks but make sure you don’t over-optimize your link profile. If most of your backlinks include the same anchor, it may signal link manipulation to Google.
Final thoughts
The goal of achieving high keyword relevance is to improve your organic rankings. But it’s sometimes hard to draw the line between all the different systems that Google uses for ranking. Backlinks are a great example of that. They play a role in determining relevance but authority as well.
For this reason, content optimization tools can be useful in creating relevant content, but they don’t guarantee high rankings. A high content score doesn’t always mean your page will rank well (read our study), and sometimes you can rank high even with a low score.
So, it’s best to treat SEO as a holistic process. Do what you need to do to achieve high relevance, then check all the other boxes, such as technical SEO, EEAT, and link building.
