Getting more traffic to your website from organic search can be done in three ways.
You can either:
- Rank higher for existing keywords
- Rank for more keywords
- Get more clicks
The SEO techniques below all help you do one or more of those things.
Competition makes life harder, but your competitors can also be a source of topic ideas.
To find your competitors’ most trafficked pages, you can use the Top pages report in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer.
For example, if we plug a competitor of ours into the tool, we see its guide to Magento SEO gets a fair amount of search traffic.
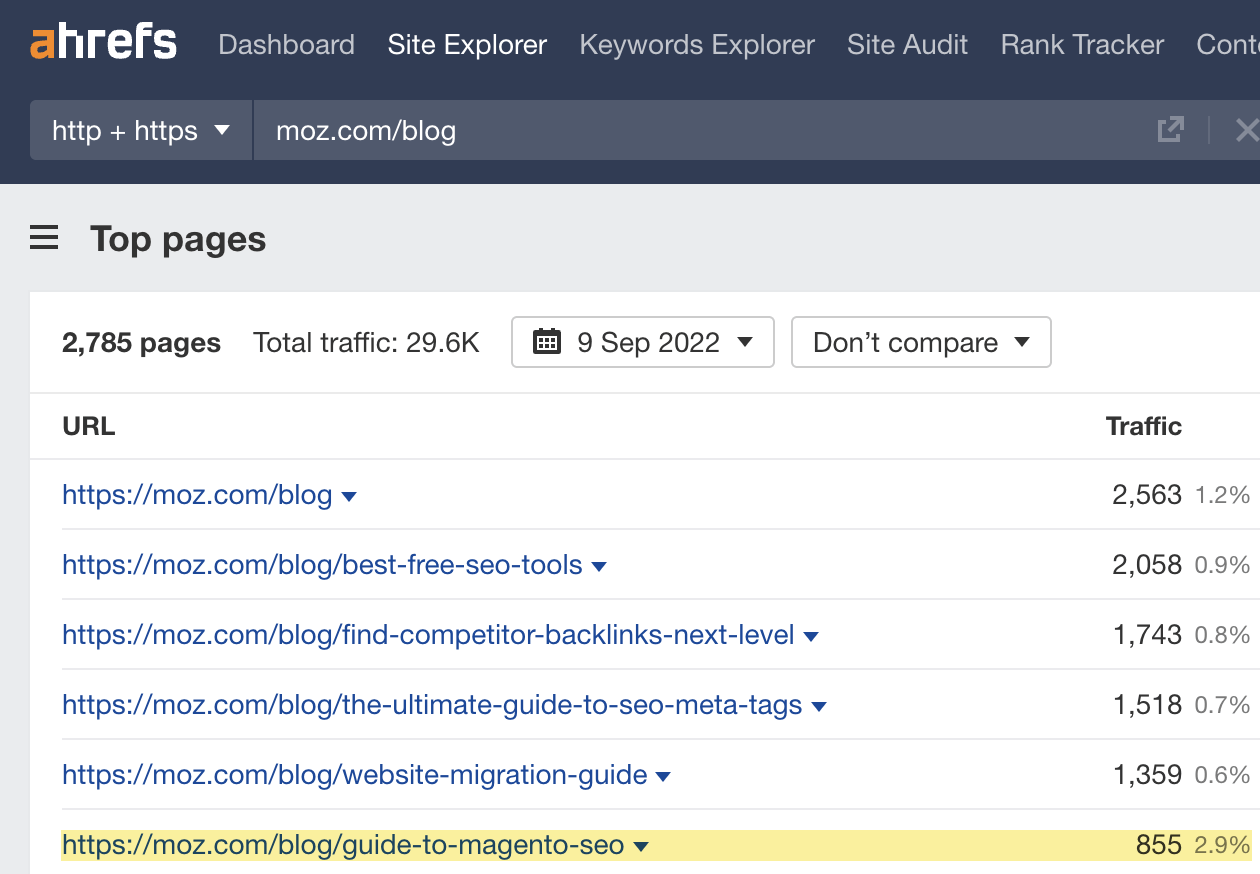
We haven’t yet covered this topic ourselves, but it looks like it could be worth doing so.
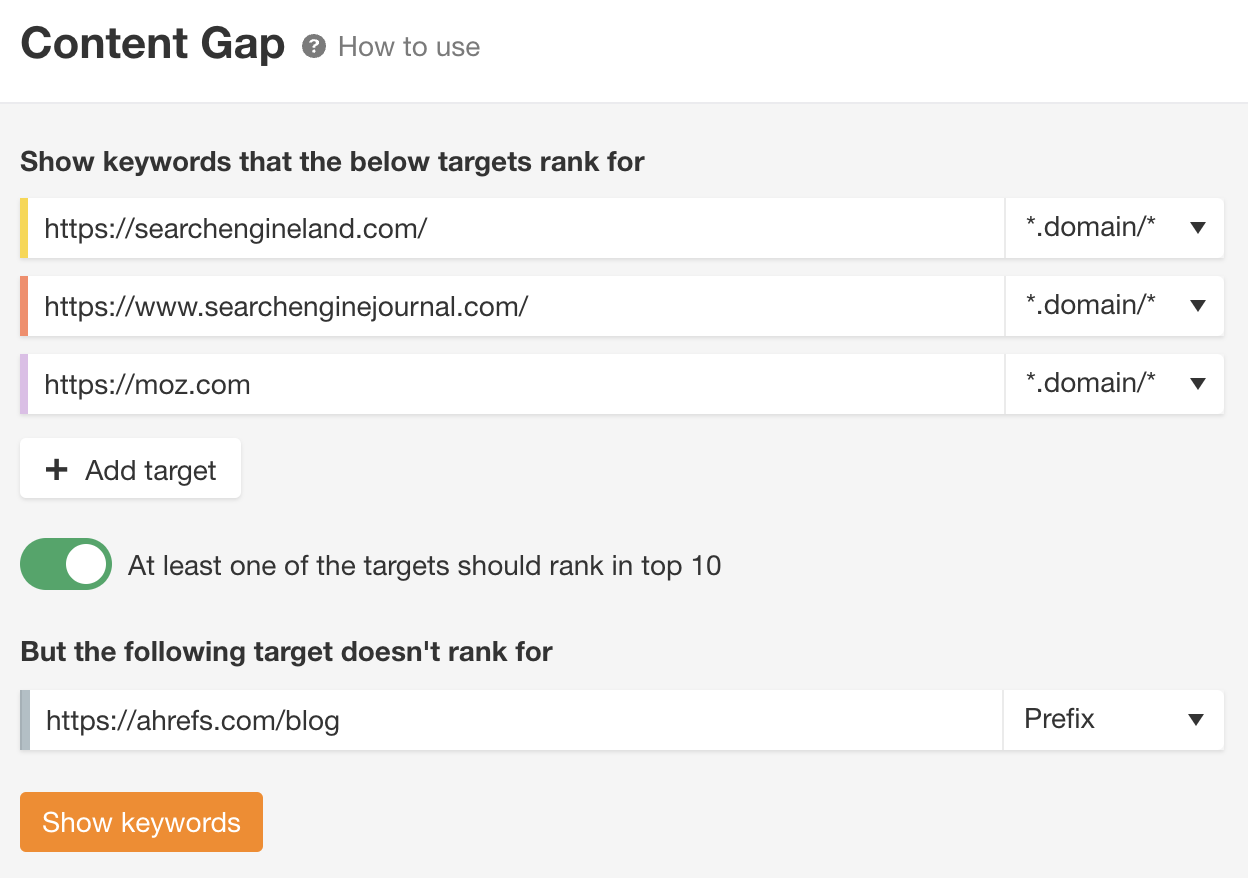
You can also use the Content Gap report in Site Explorer to find keywords your competitors rank for that you don’t.
Here’s the process:
- Enter your domain into Site Explorer
- Go to the Content Gap report
- Enter a handful of competitors
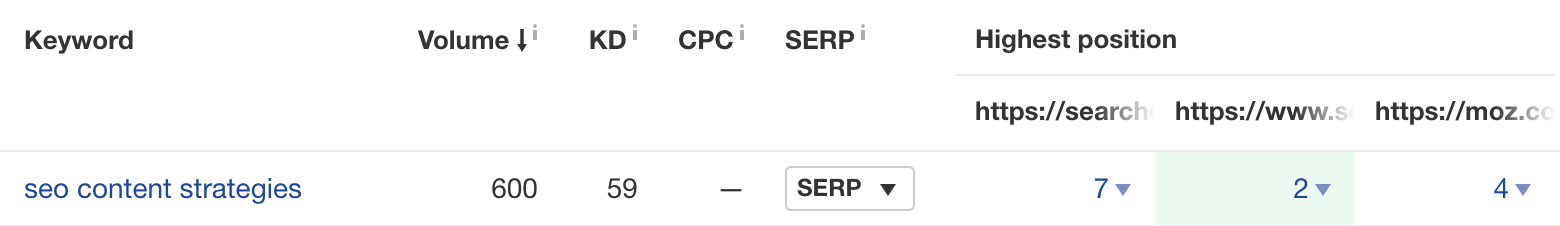
For example, SEJ, SEL, and Moz all rank in the top 10 for “seo content strategies,” but we don’t because we haven’t covered this topic. So it’s probably worth adding to our content calendar.
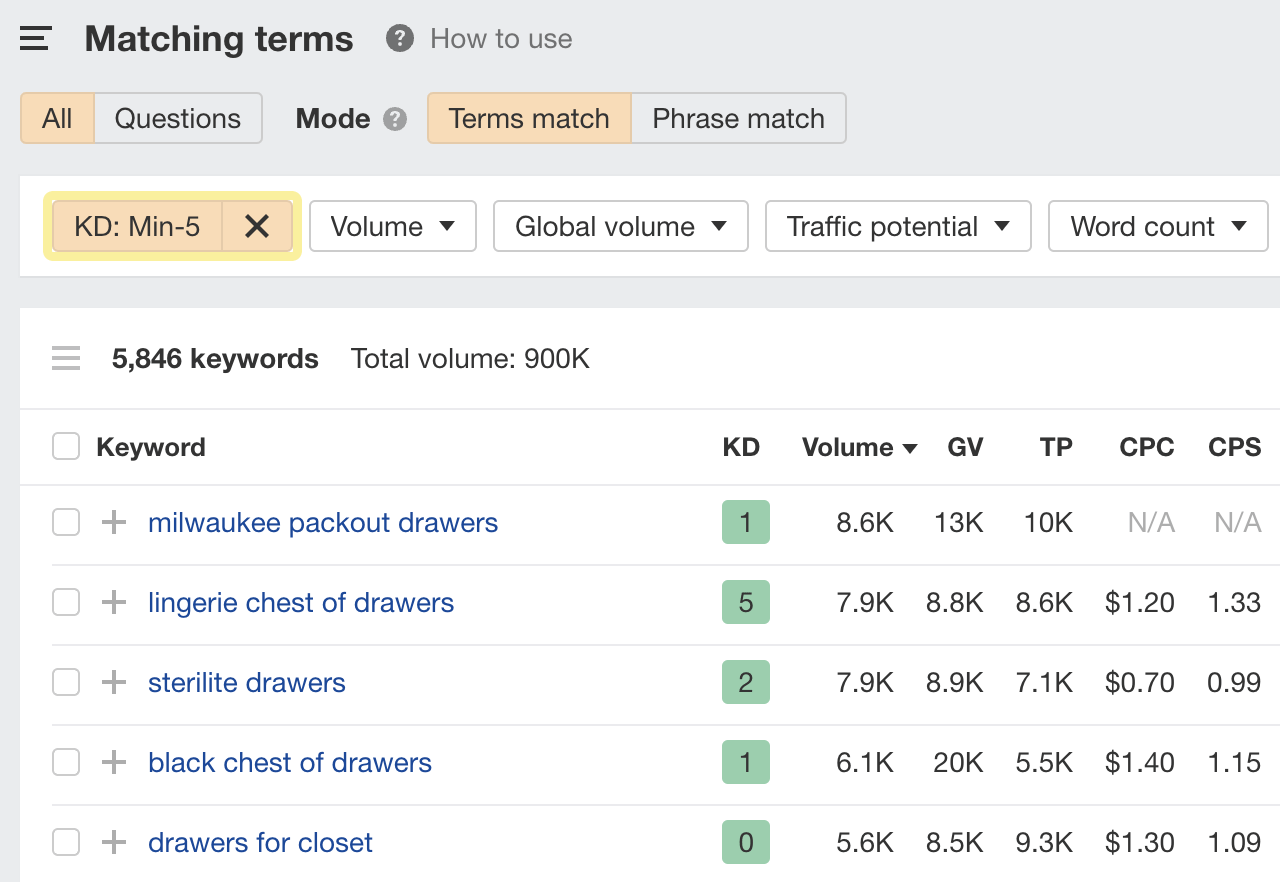
It’s worth prioritizing low-difficulty topics if your site is new because you’ll probably struggle to rank for competitive topics out the gate.
You can find these with a keyword research tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer. Just search for keyword ideas then filter for those with low Keyword Difficulty (KD) scores.
Old content needs updating periodically because rankings don’t last forever, especially if you’re targeting time-sensitive topics.
For example, here’s the estimated organic traffic to our list of top Google searches over time:
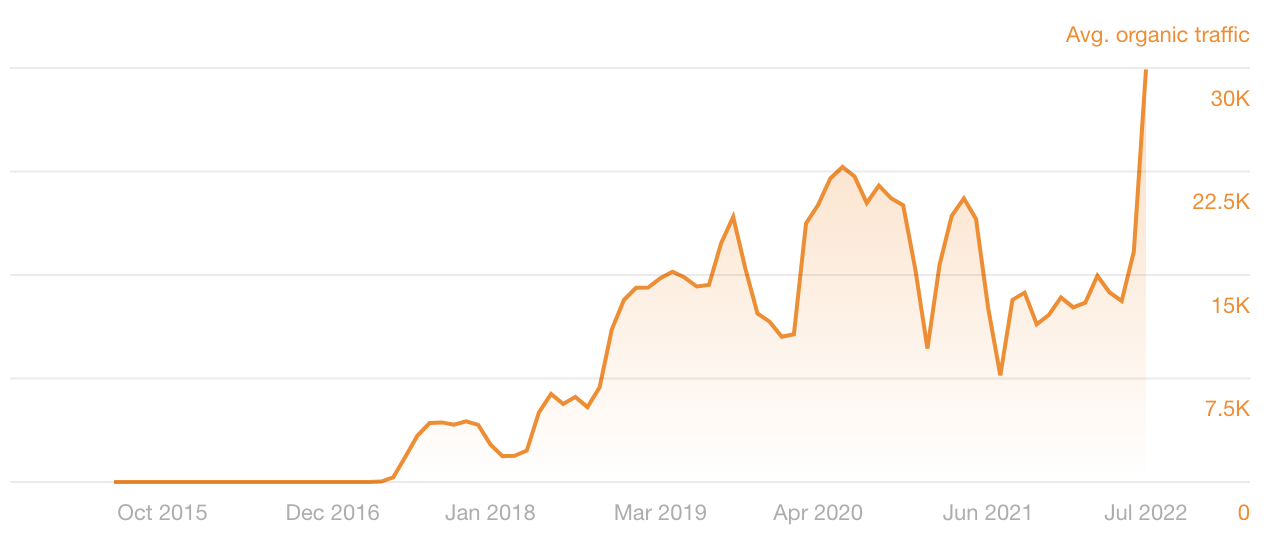
Each dip occurred when the content lost its freshness. Searchers wanted an up-to-date list of the top Google searches, but ours was old. That’s why rankings tanked.
Each spike occurred when we updated the content.
You can find pages on your site that may be due for a refresh in Site Explorer. Just plug in your site, go to the Top pages report, set the comparison mode to “Previous year,” sort the report by traffic change from low to high, and look for topics where freshness may be the issue.
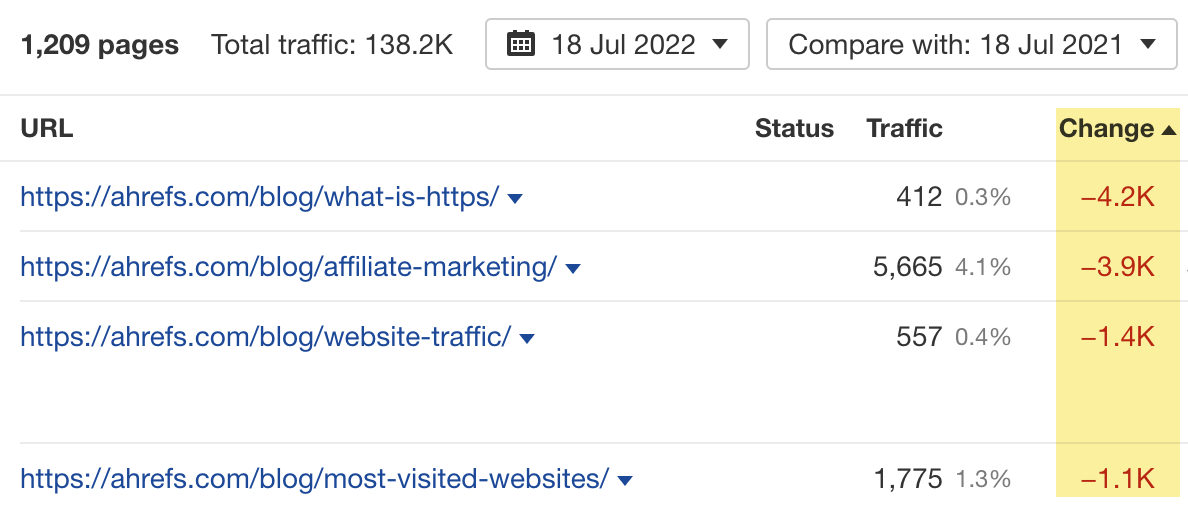
If you’re a WordPress user, you can find pages that no longer perform well by running a free content audit using the Ahrefs SEO plugin.
Our study found that if a page ranks #1 for a keyword, it ranks for almost 1,000 more keywords in the top 10 on average.
Many of these keywords will be different ways of searching for the same thing. But some will likely represent subtopics you’ve covered in your content.
For example, our guide to submitting your website to Google ranks in the top 10 for “submit url to google.”
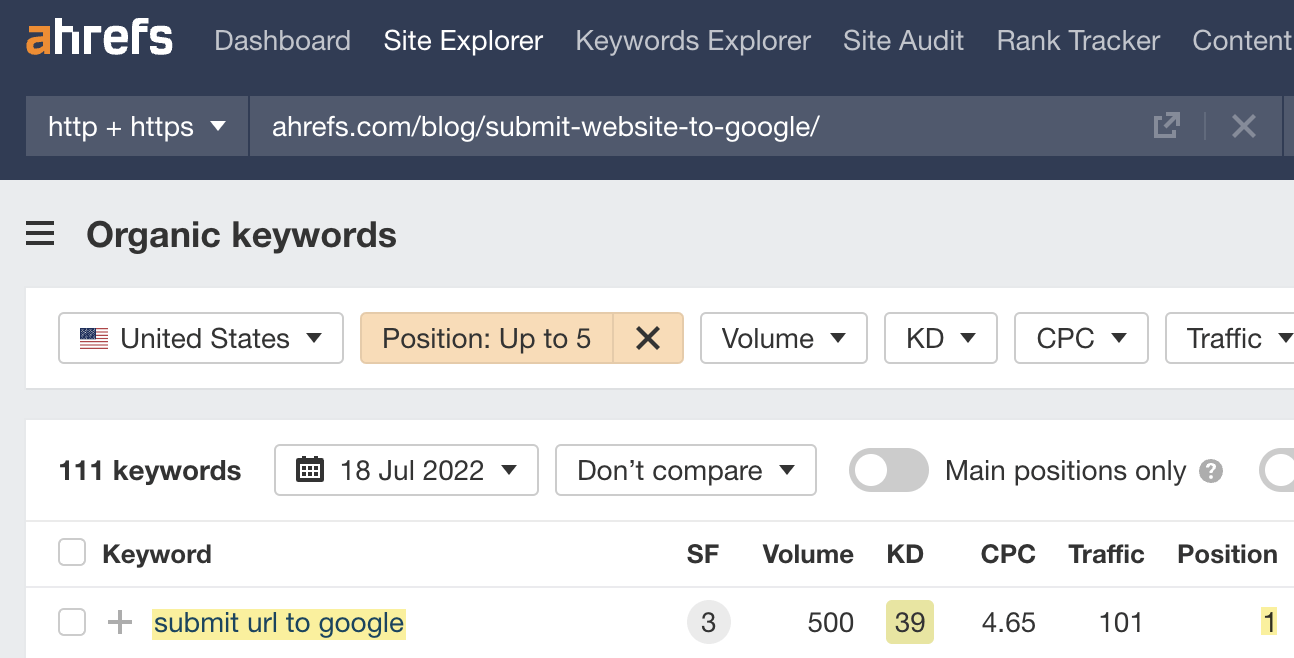
That happens because we’ve covered this subtopic in the post.

However, we have plenty of posts that almost certainly miss important subtopics. If we can find these and fill the gaps, our page can likely rank for related keywords and get more traffic.
Here’s a simple way to find content gaps:
- Enter one of your page’s URLs into Site Explorer
- Go to the Content Gap report
- Paste in a few top-ranking URLs for your main keyword
- Sift through the keywords for content gaps
For example, HubSpot and Neil Patel rank in the top 10 for “what are guest posts,” but we don’t.
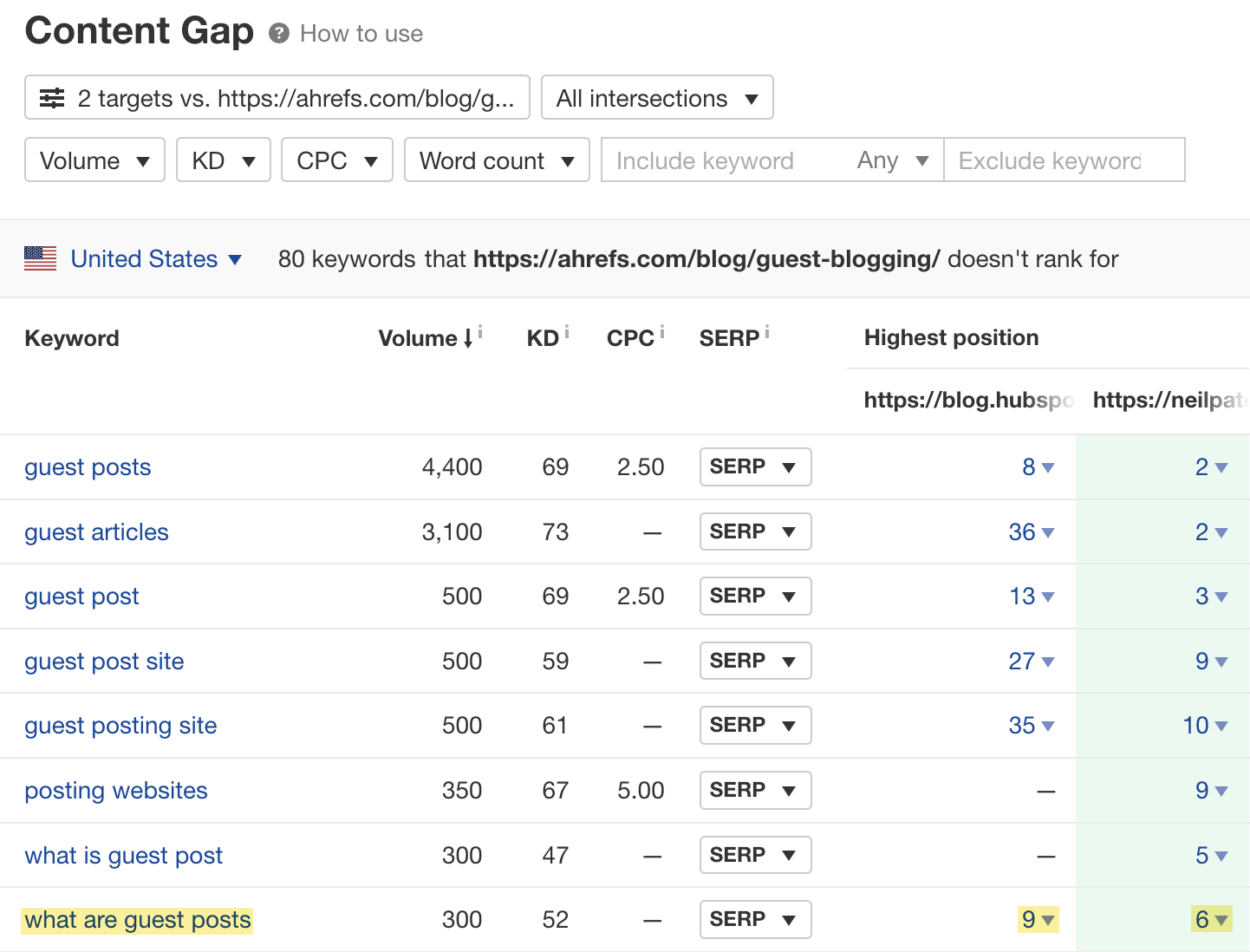
This happens because we didn’t cover that subtopic in our guest posting guide, whereas they did.
Not only could covering the topic in more depth help us rank for more long-tail keywords, but it could also serve the user better with information they might want.
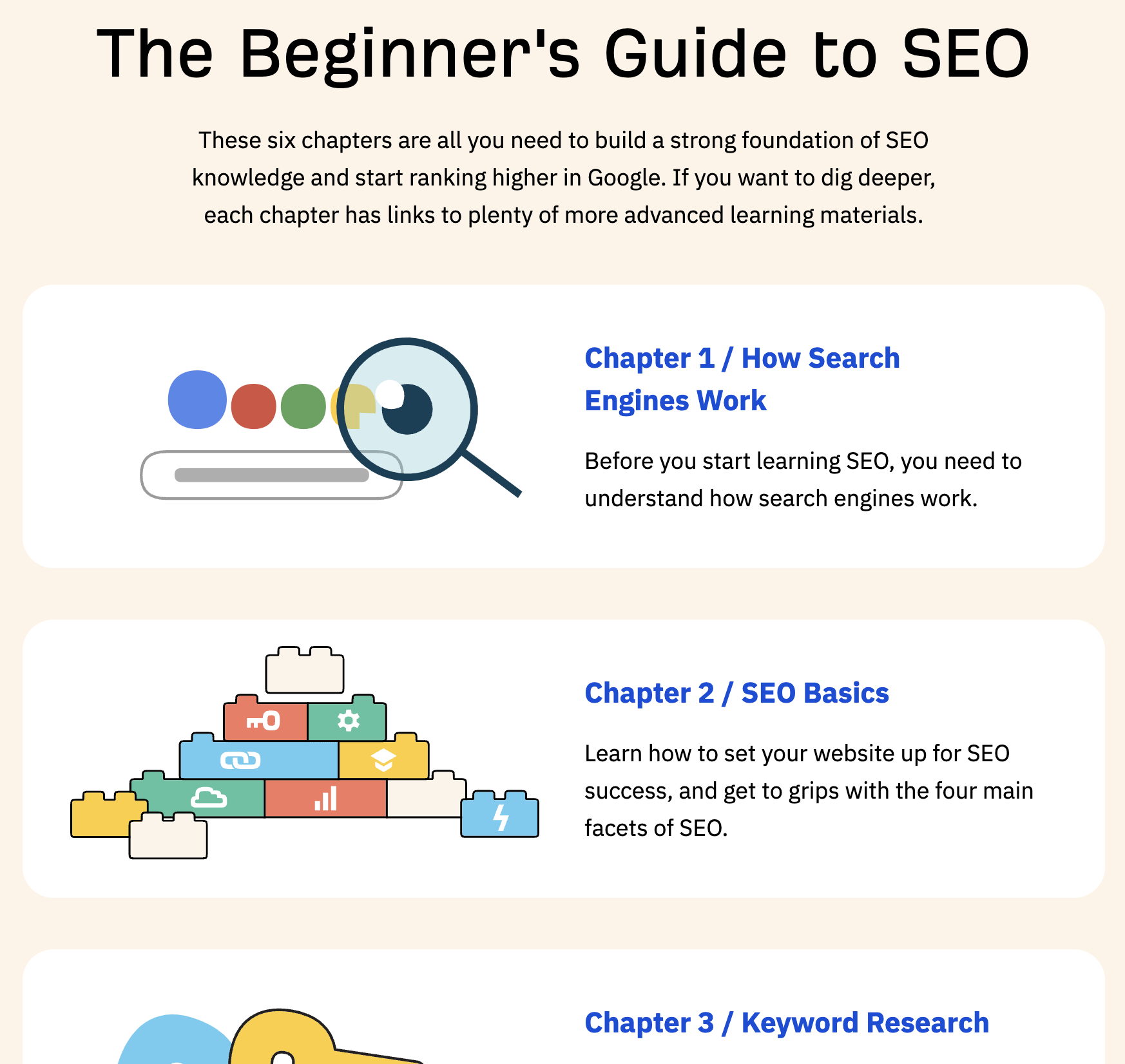
Content hubs are interlinked collections of content about a topic.
For example, our beginner’s guide to SEO is a content hub. It has a pillar page about SEO that links to and from subpages about how search engines work, SEO basics, keyword research, etc.
The main benefit of content hubs is that link equity flows to and from all the pages in the hub via internal links. In other words, if one of your subpages gets lots of backlinks, they all get stronger and potentially rank higher.
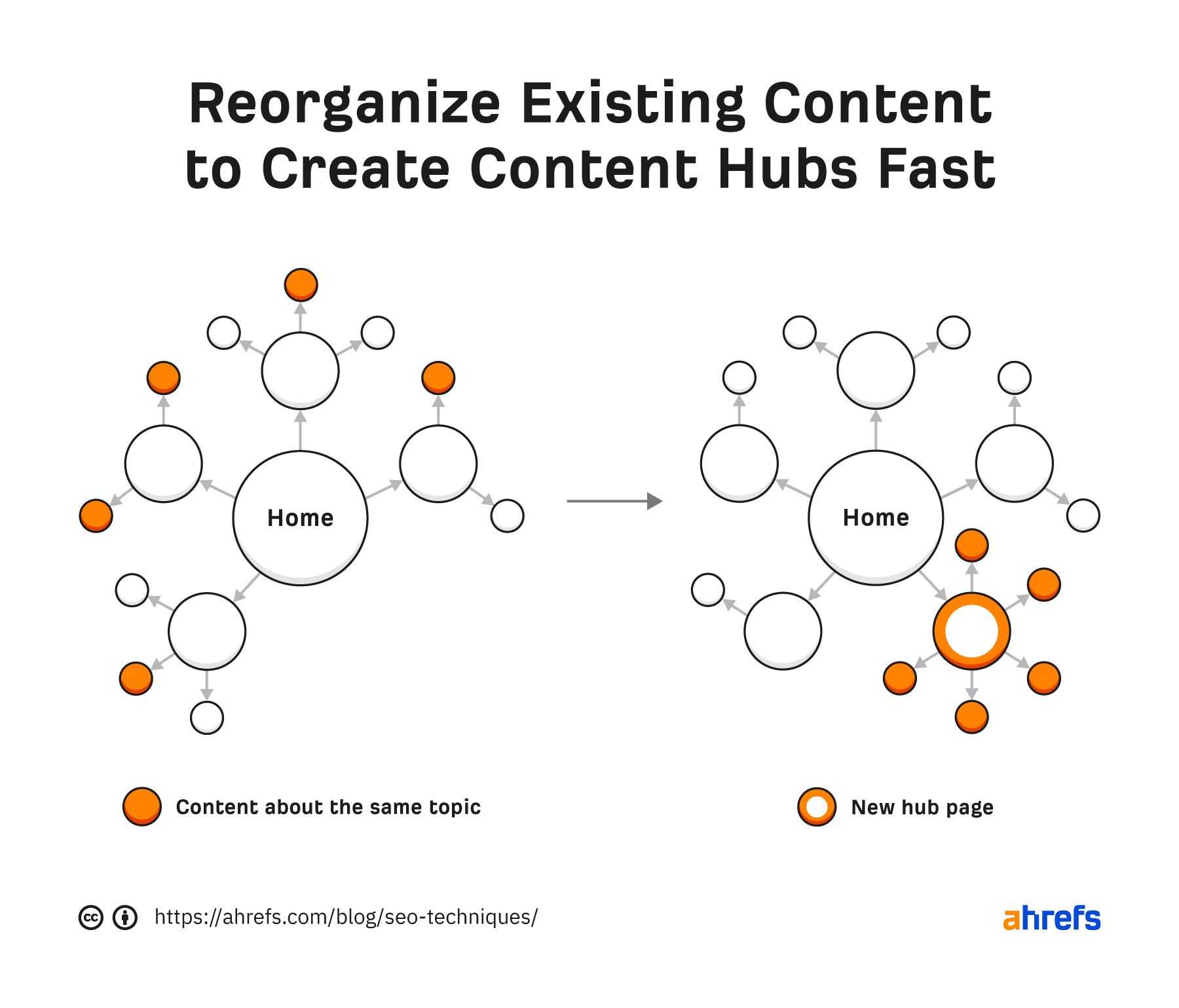
If you already have content on your website, the easiest way to create a content hub is to reorganize related pages around a new “hub” page.
If you want to create a new content hub, one of the easiest ways to find topics is to look at your competitors’ top subfolders.
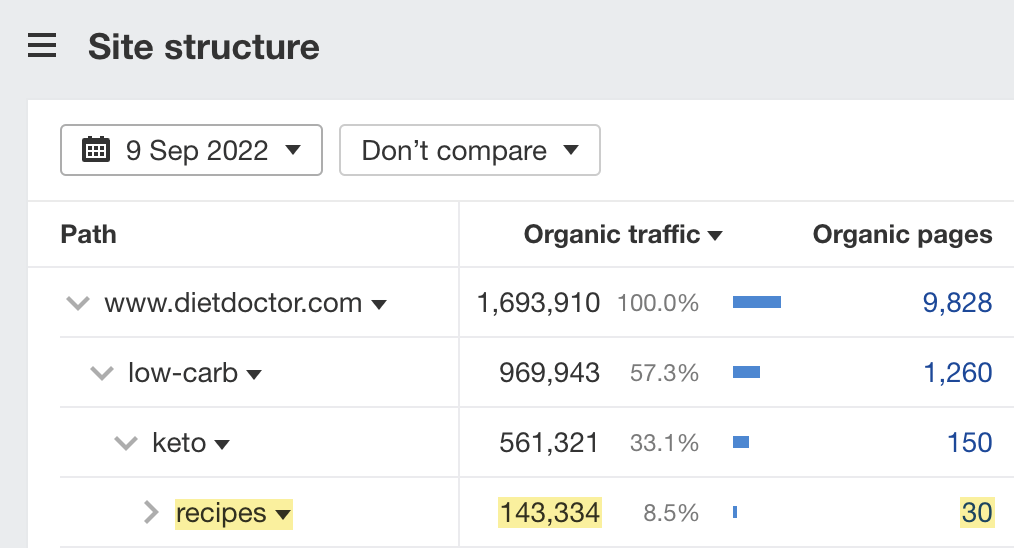
For example, let’s plug DietDoctor into Site Explorer and go to the Site structure report. We see 30 pages under the /low-carb/keto/recipes subfolder that get an estimated 143K monthly search visits in total.
If we click the number of pages, we see all the pages under that URL structure along with their estimated traffic and top keyword.
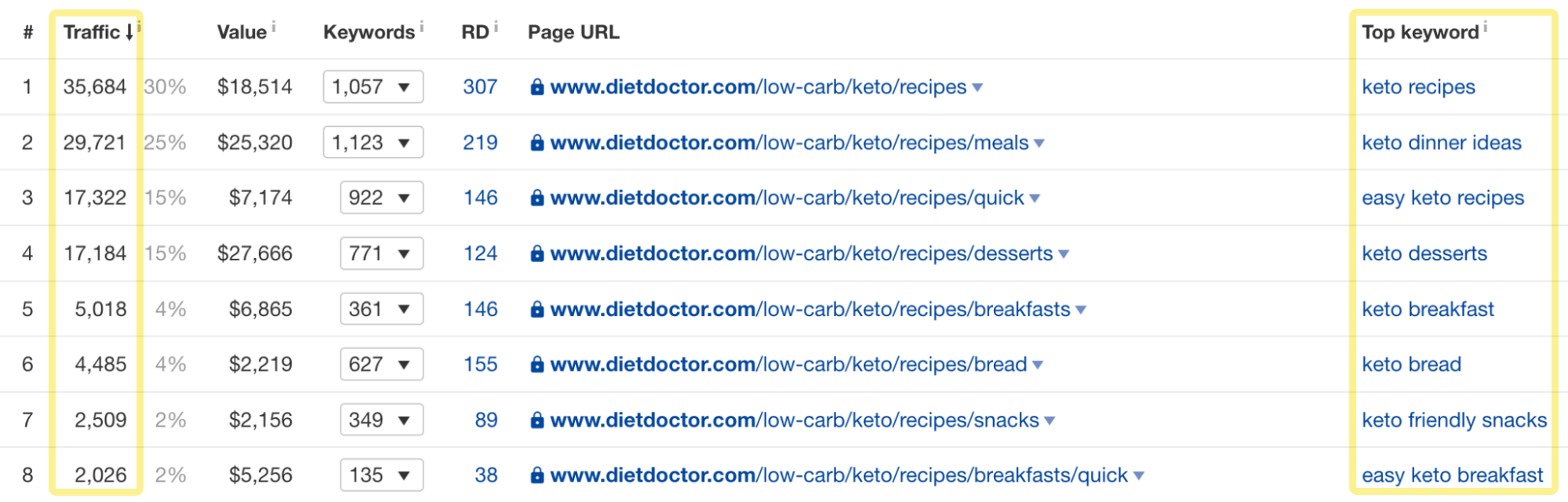
Many of these topics will make sense for a content hub.
Learn more: Content Hubs for SEO: How to Get More Traffic and Links With Topic Clusters
Backlinks are one of Google’s top ranking factors, but getting high-quality ones is easier said than done. It’s arguably one of the most challenging parts of SEO.
For that reason, before you start trying to build more backlinks to a page, it’s worth checking whether this is likely to help.
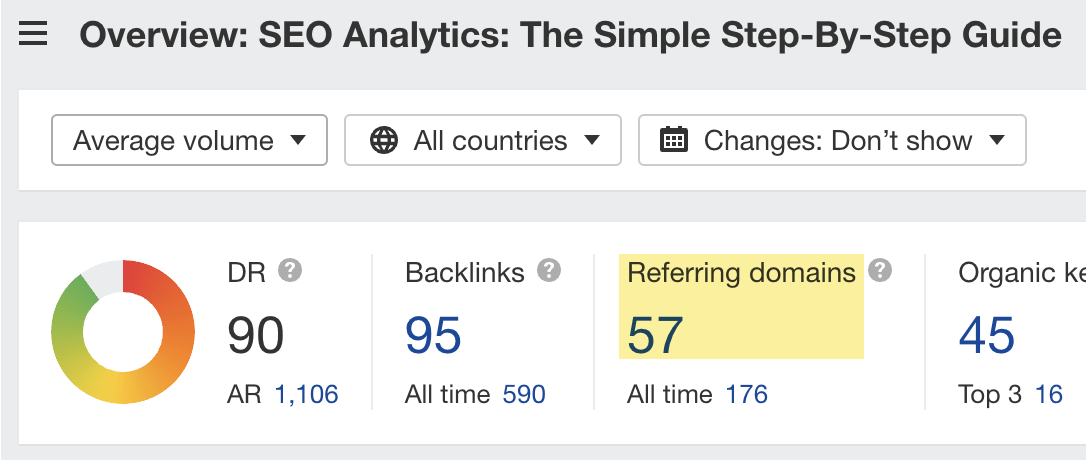
For example, if you plug our guide to SEO analytics into Site Explorer, you see it has backlinks from 57 referring domains (websites):
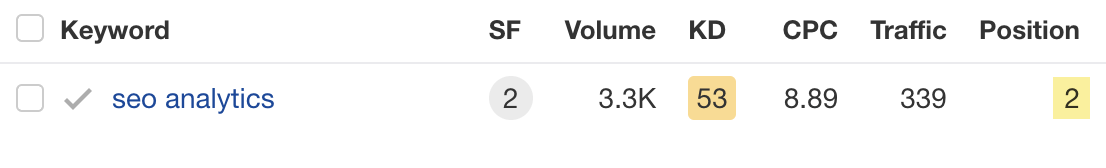
This page currently ranks #2 for its main target keyword:
But if you check the top-ranking pages for that keyword in Keywords Explorer, you see that the page outranking us has significantly fewer referring domains.
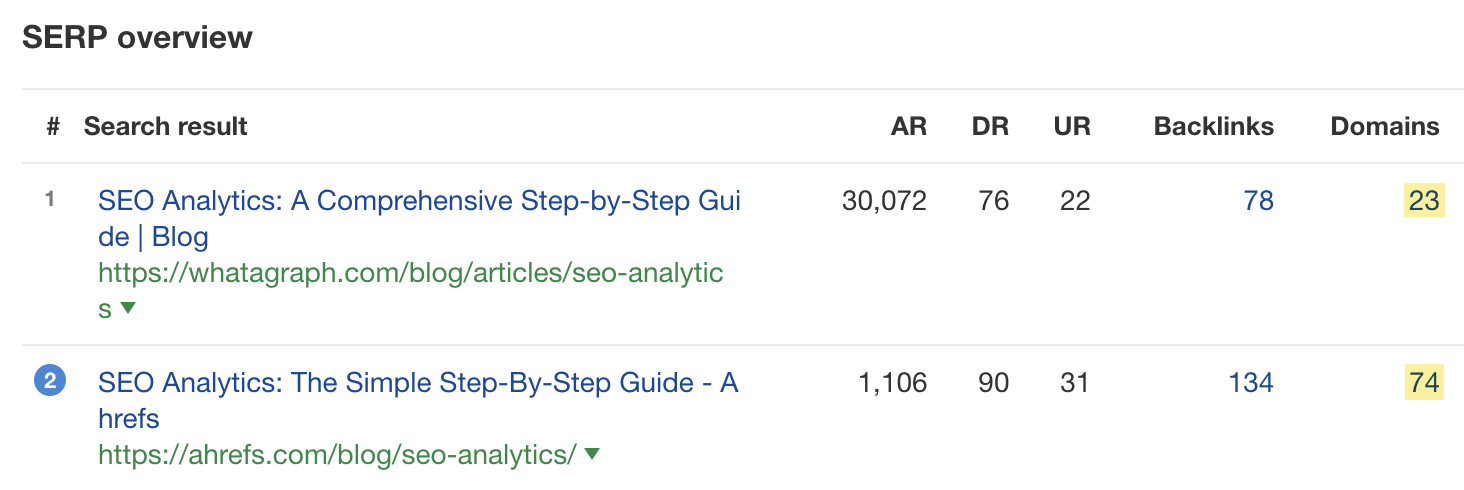
These numbers don’t consider backlink quality, so it could be the case that the top-ranking page outranks us because it has more high-quality backlinks. But generally speaking, it doesn’t look like a lack of backlinks is the issue.
On the other hand, if you look at the SERP for “what is seo,” you see that our page has significantly fewer backlinks than those outranking us.
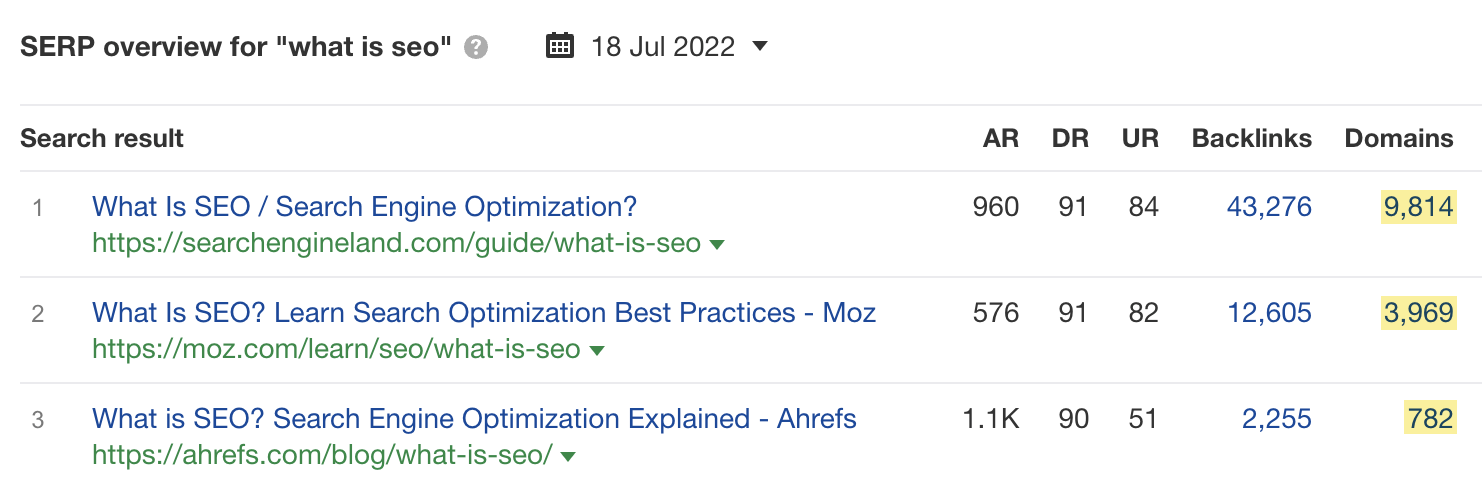
Building more backlinks is probably the way to go here.
Internal links are links from one page on your website to another.
Like backlinks, they transfer “link equity” from page to page. Unlike backlinks, you have complete control over where and how you internally link on your website. That’s why a popular SEO technique is to point more internal links at pages that need a boost.
To find these pages, plug your domain into Site Explorer, go to the Organic keywords report, and filter for keyword rankings between 2–10.
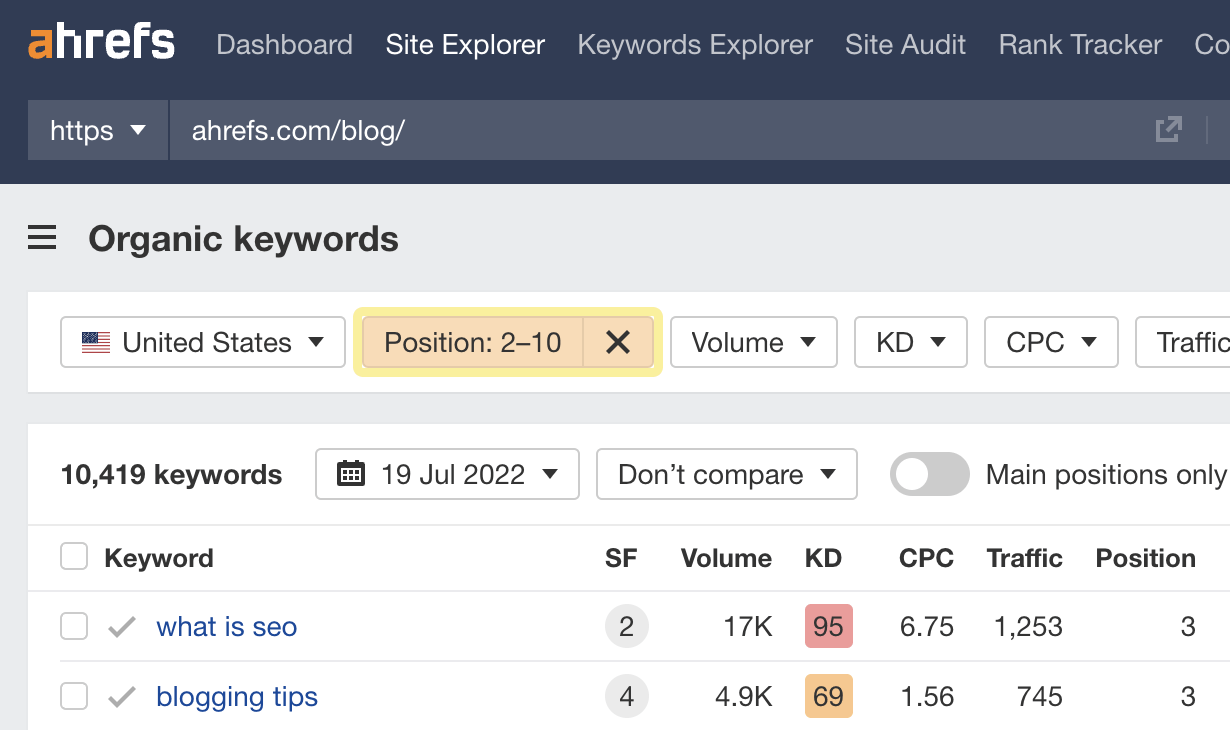
You can then sift through this report for your main target keywords.
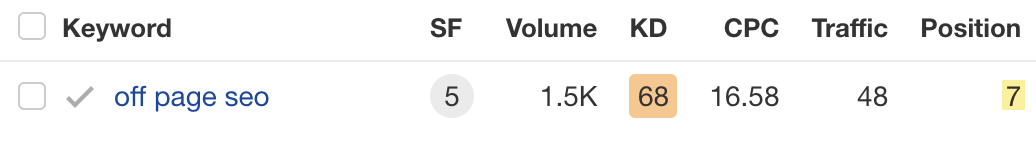
For example, we rank #7 for “off page seo.”
To find relevant and contextual internal link opportunities for this page, we can add it to the target page filter in the Link opportunities report in Ahrefs’ Site Audit.
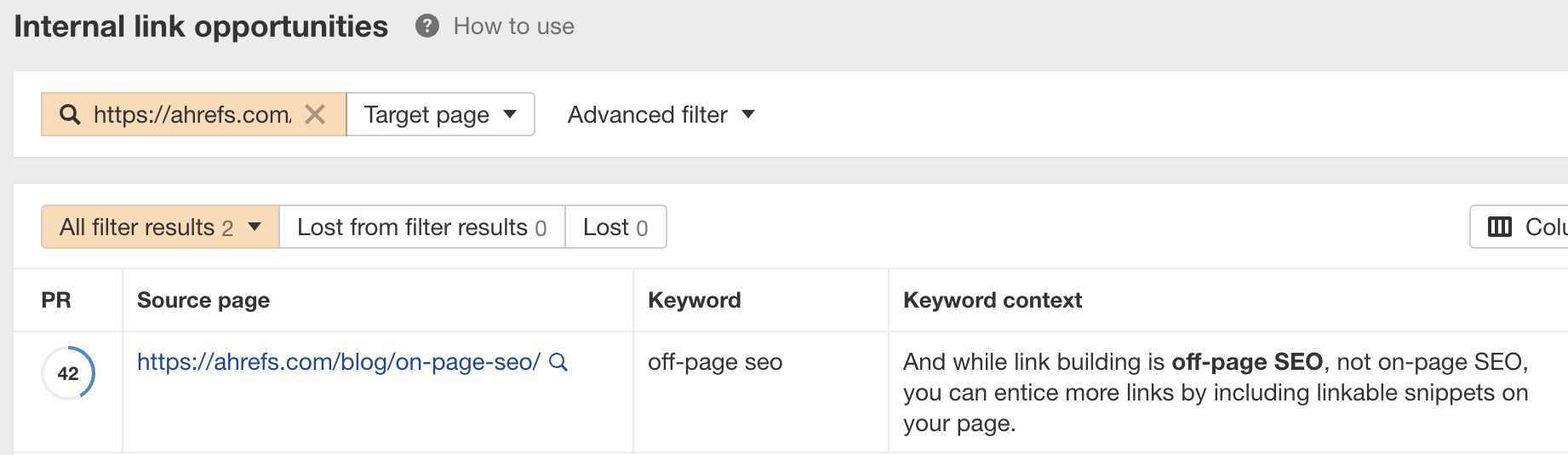
In this example, the report suggests we internally link a contextual mention of “off-page seo” in our on-page SEO guide.
Learn more: Internal Links for SEO: An Actionable Guide
Broken backlinks are a common problem because people often delete or move pages over time. Unless you redirect these pages to their new URLs, any backlinks pointing to the old ones will effectively point to nowhere.
Here’s how to find broken pages with backlinks on your site:
- Paste your domain into Site Explorer
- Go to the Best by links report
- Add a “404 not found” filter
- Sort the report by referring domains from high to low
For example, we have backlinks from 57 referring domains pointing to the old URL for our SEO Toolbar.

Given that our “SEO toolbar” page still exists, we can reclaim those backlinks by redirecting the old URL to the new one.
Learn more: How to Find and Fix Broken Links
Ranking high on Google is only part of the battle. You also need to entice searchers to click on your result.
Here are a couple of ways to do this:
- Write a compelling title tag and meta description
- Add schema markup for rich snippet eligibility
Google often shows title tags and meta descriptions in the search results, so making them as compelling as possible without creating clickbait is important.
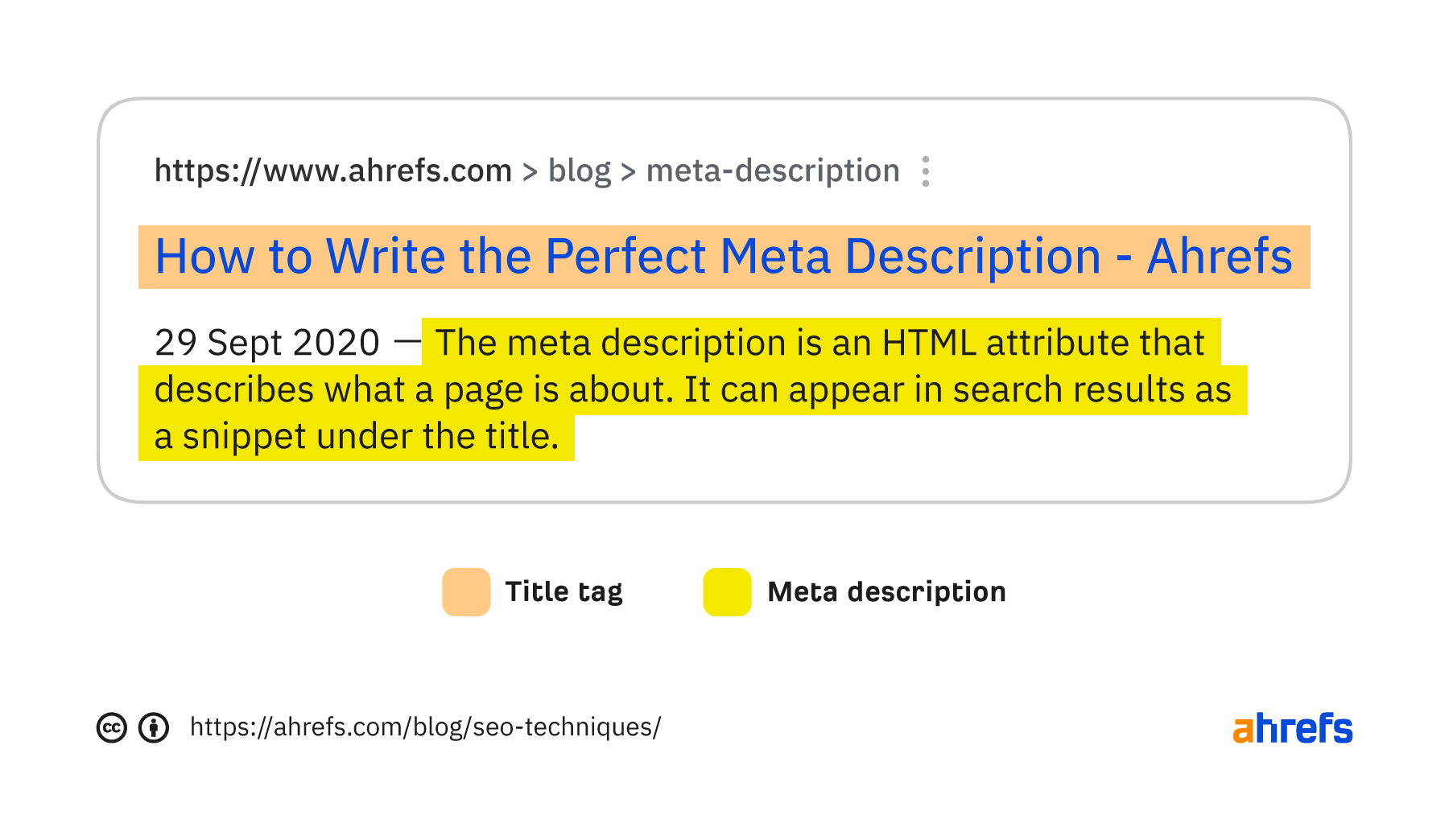
Here are a few tips:
- Match search intent
- Avoid truncation (use a free SERP snippet optimizer like this one to check)
- Address the searcher directly
- Include your main keyword
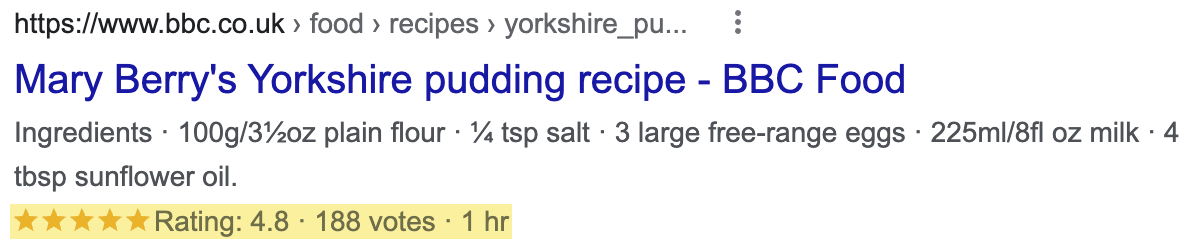
You can also use schema markup to make pages eligible for rich snippets. This is where Google shows additional information below the search snippet, such as review ratings and FAQs.
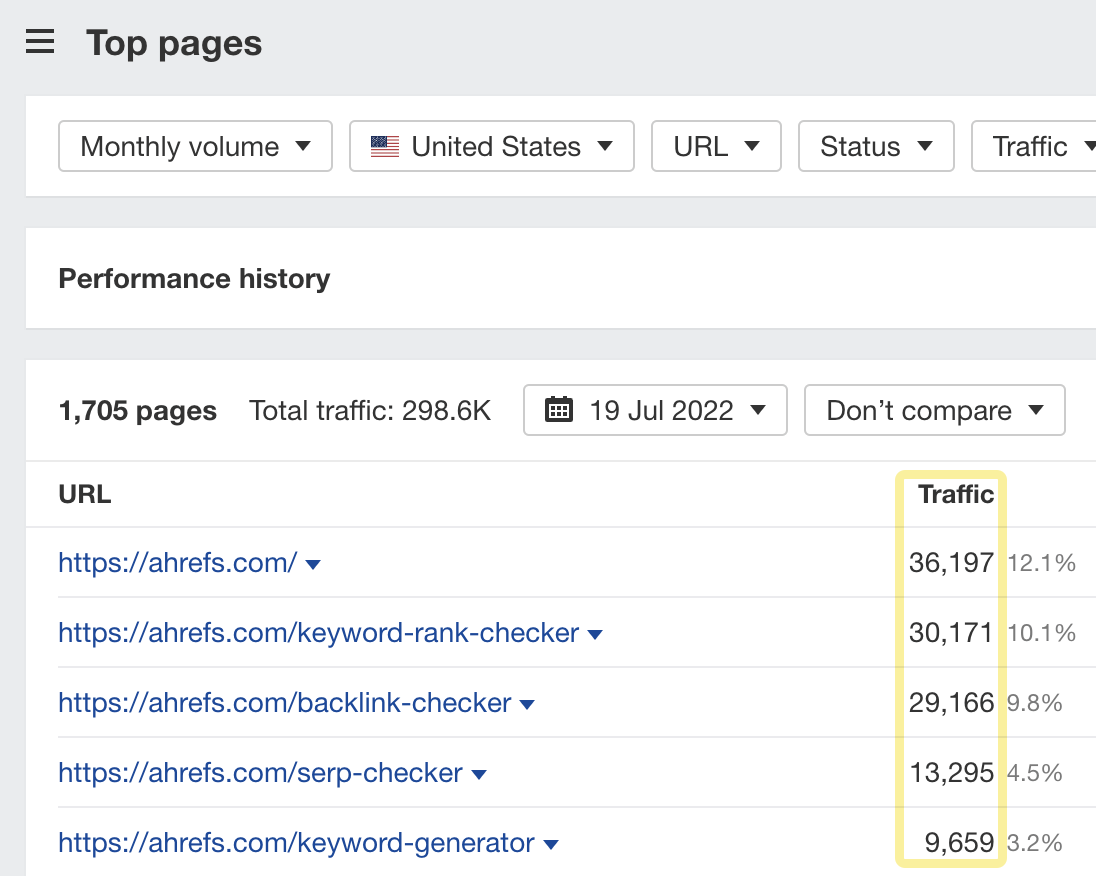
Given that these optimizations take time, it’s worth prioritizing pages with the most search traffic. You can find these in Google Search Console or get an estimate using the Top pages report in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer.
Featured snippets are short answers that show in some search results. Google pulls them from one of the top-ranking pages.
You can effectively shortcut your way to the top of Google by winning featured snippets. But first, you need to find the best opportunities.
Here’s how to do it:
- Enter your domain into Site Explorer
- Go to the Organic keywords report
- Filter for top 10 rankings
- Filter for SERPs with featured snippets where you don’t rank
You should now see all the keywords you rank for in the top 10, where Google shows a featured snippet from another result.
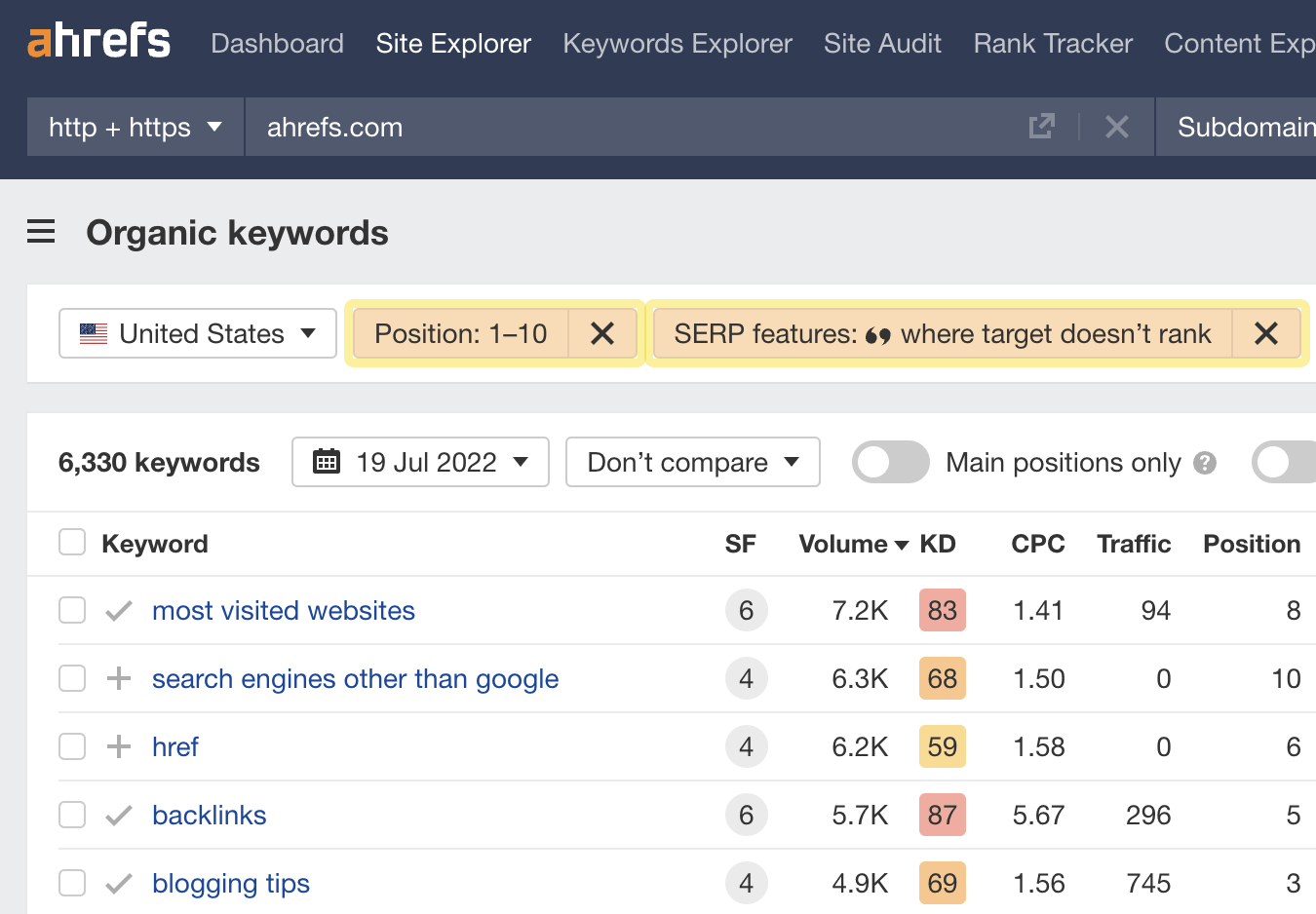
For example, we rank #2 for “google operators,” but Google pulls the featured snippet from another page.
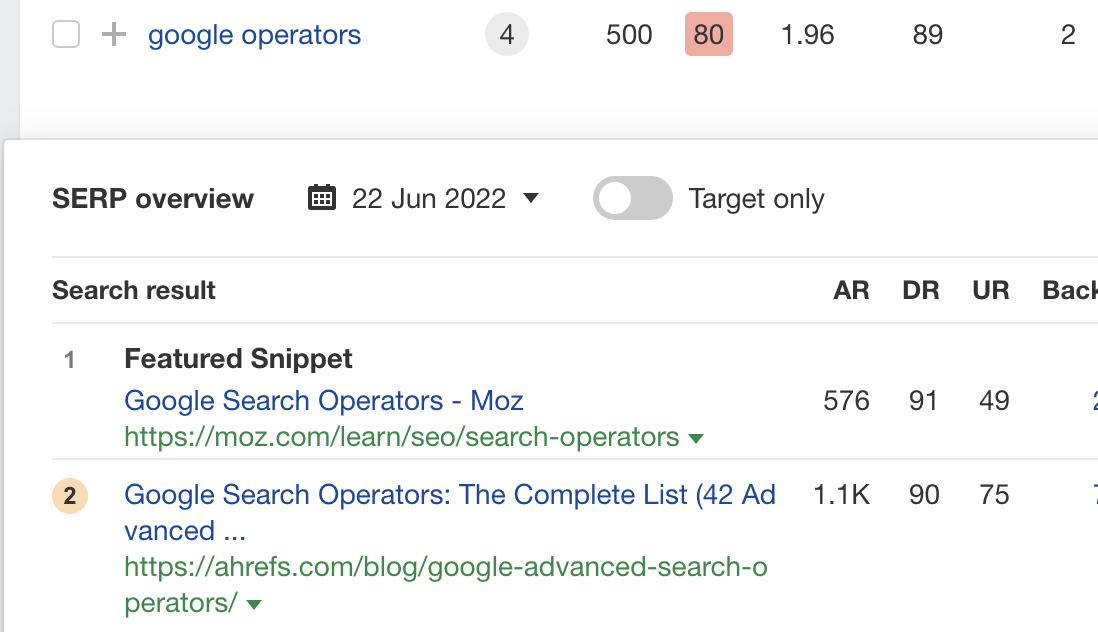
There’s no exact science to winning featured snippets, but you’re unlikely to do so unless your page has the information Google wants to see.
For example, it’s clear that Google wants a short definition here, but our page doesn’t have one.
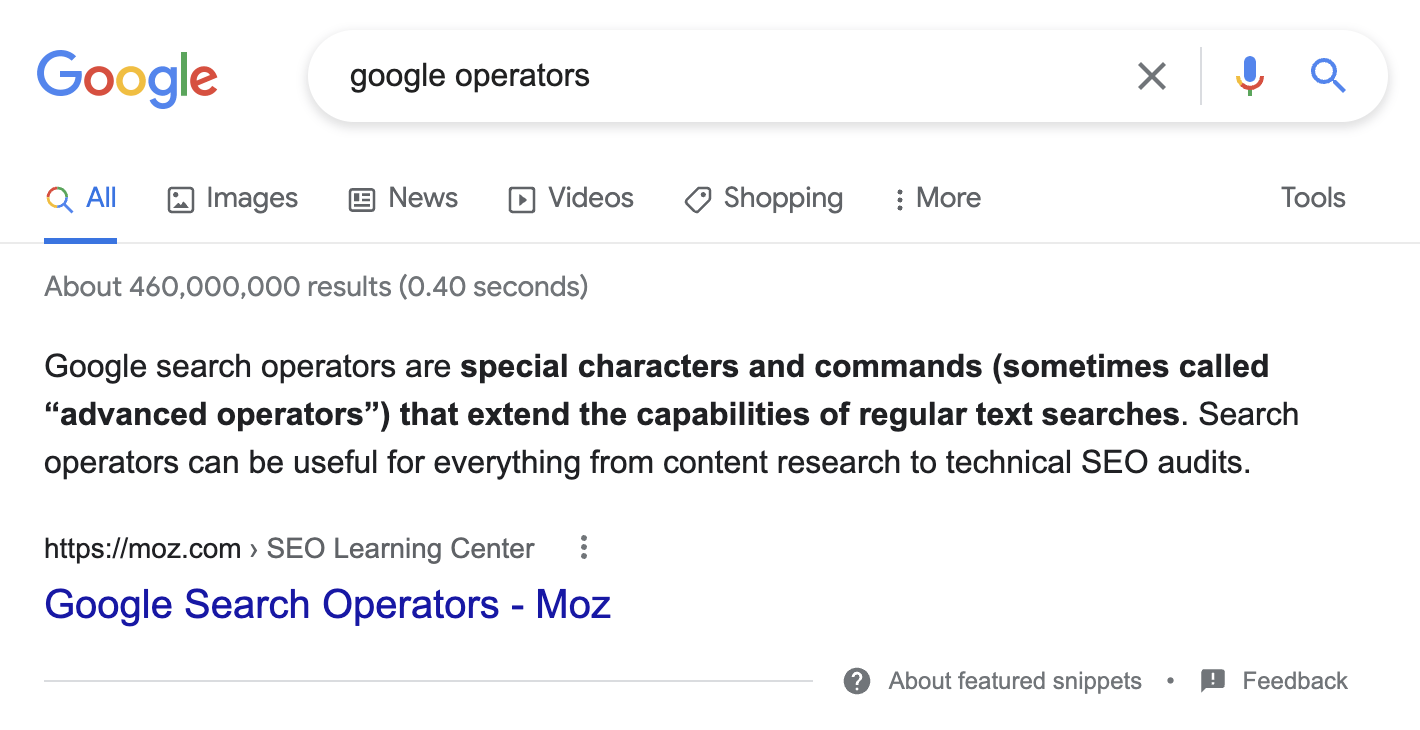
While adding one to our page doesn’t guarantee Google will choose us for the featured snippet, it will improve our chances.
Final thoughts
Getting more search traffic to your website is about ranking higher for existing keywords, ranking for more keywords, or getting more clicks. There are plenty of SEO techniques you can use to do that. These are just a few of them.
If you want more, read our list of SEO tips.
Got questions? Ping me on Twitter.
