Here’s what we recommend: pick just one primary keyword and enough secondary keywords to cover a given topic in full.
In the rest of the article, I’ll explain why and how.
Going forward, we’ll differentiate between two kinds of keywords.
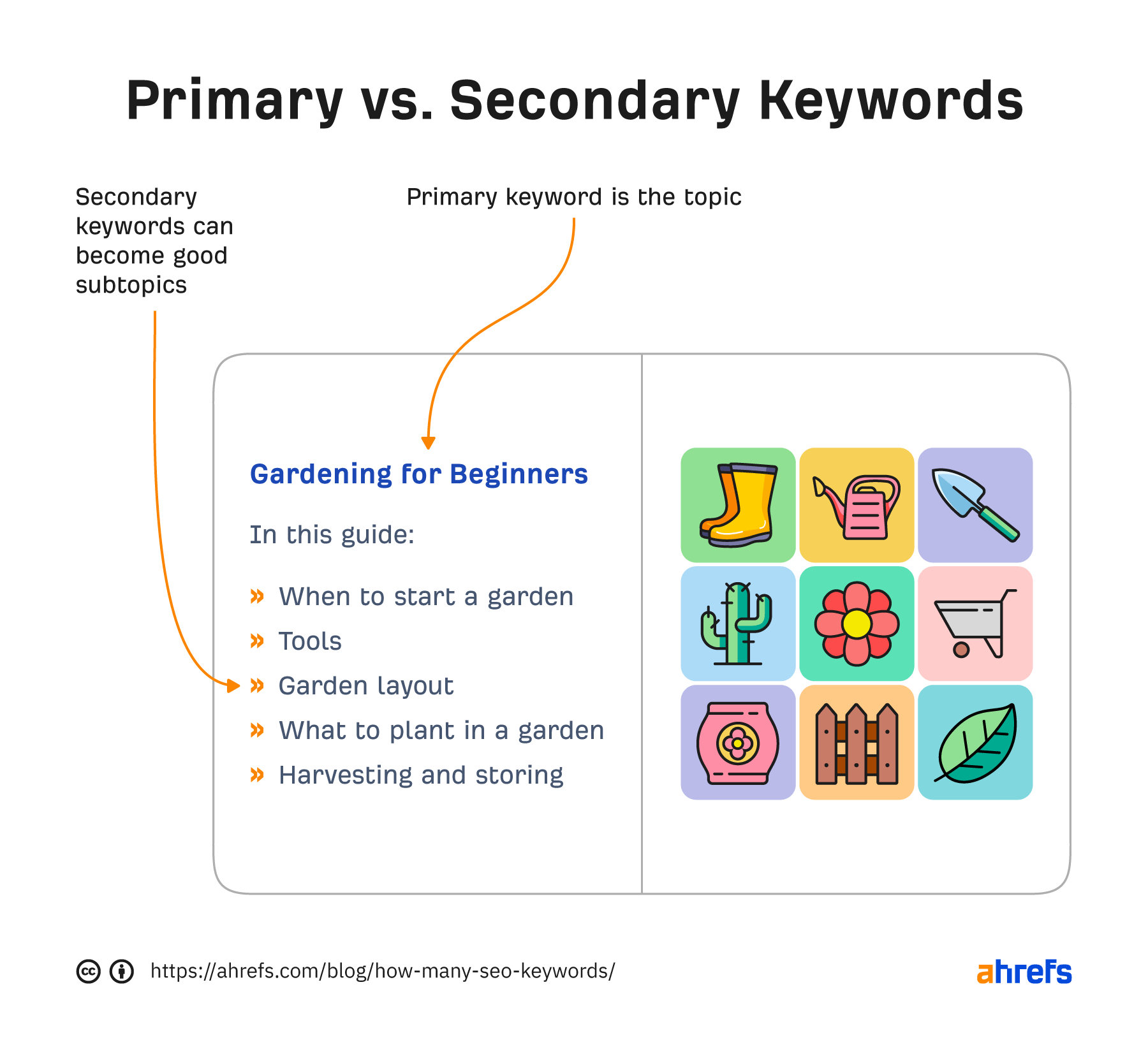
The primary keyword, also called the target keyword, is the main topic of a page. It’s also the single keyword to optimize a page for.
Secondary keywords are any keywords closely related to the primary keyword that you’re targeting with your page.
Synonyms, subtopics, and long-tail keyword variations can be considered secondary keywords. But the best use of secondary keywords for SEO is as relevant subtopics—this is what I’ll focus on in this article.
So to sum up the difference, if the primary keyword is the topic of the book, you can use secondary keywords as subtopics.
There are at least three reasons why.
Reason 1. Any page needs one clearly defined topic
Sounds quite obvious, but a satisfactory explanation of this idea can become complicated quite quickly. It’s probably best if we look at this from a user experience perspective.
Since people look for specific things online, it won’t be the best idea to make them look for those things on pages about multiple things or even worse—everything. So a single page targeting multiple topics will not be that useful.
And since Google exists to help people find specific things, it will likely show a page with a specific focus, i.e., the most relevant one, rather than a page that tries to rank for multiple different topics simultaneously.
Reason 2. Google is good at catching close variations and misspellings
Have you noticed what happens when you misspell something in Google?
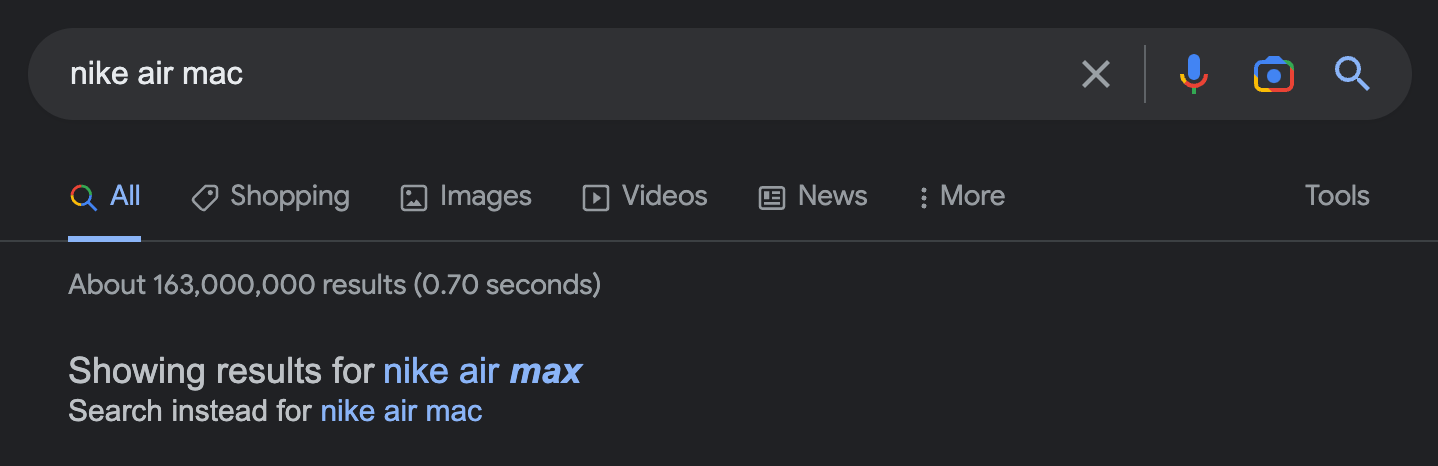
Google will correct you like a grammar teacher because you likely had something else in mind when typing that search term.
But what about close variations and synonyms?
Same thing. Google will rank your page for keywords with the same meaning and intent without you having to target every single variation intentionally. It knows that people search for the same thing in different ways.
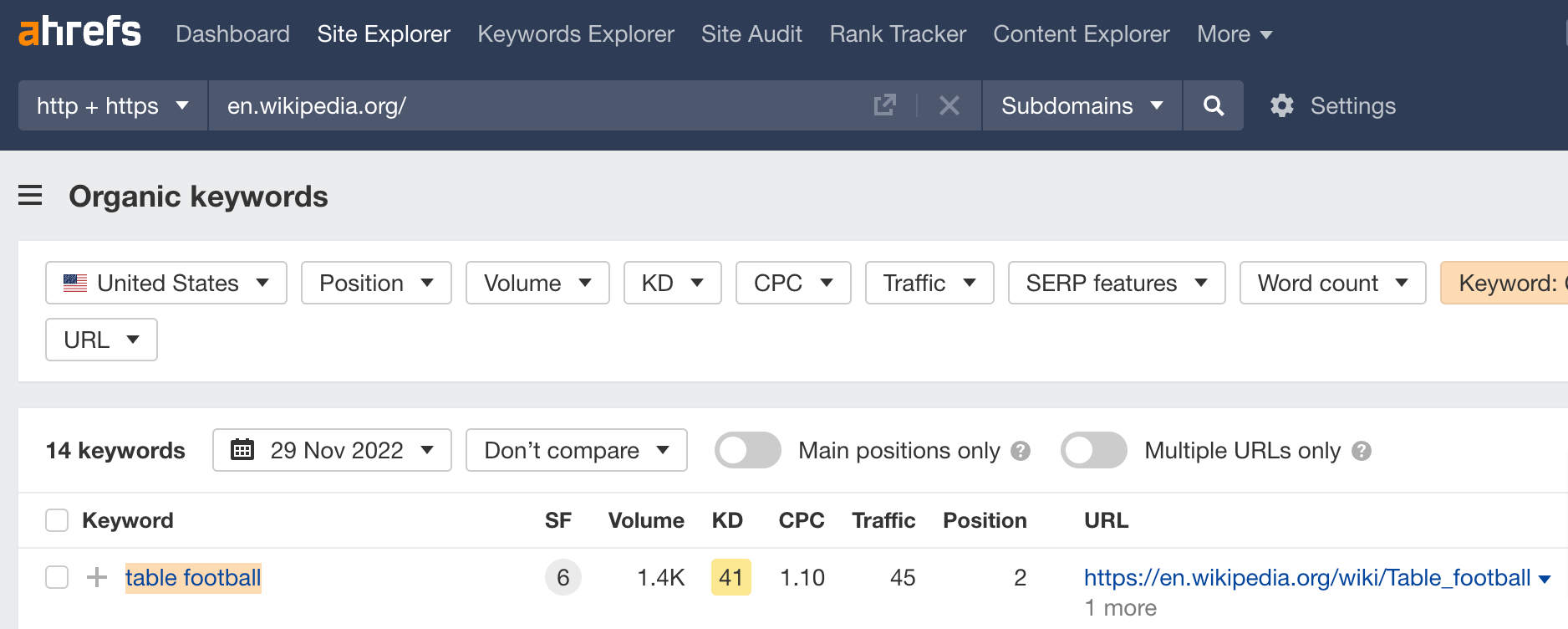
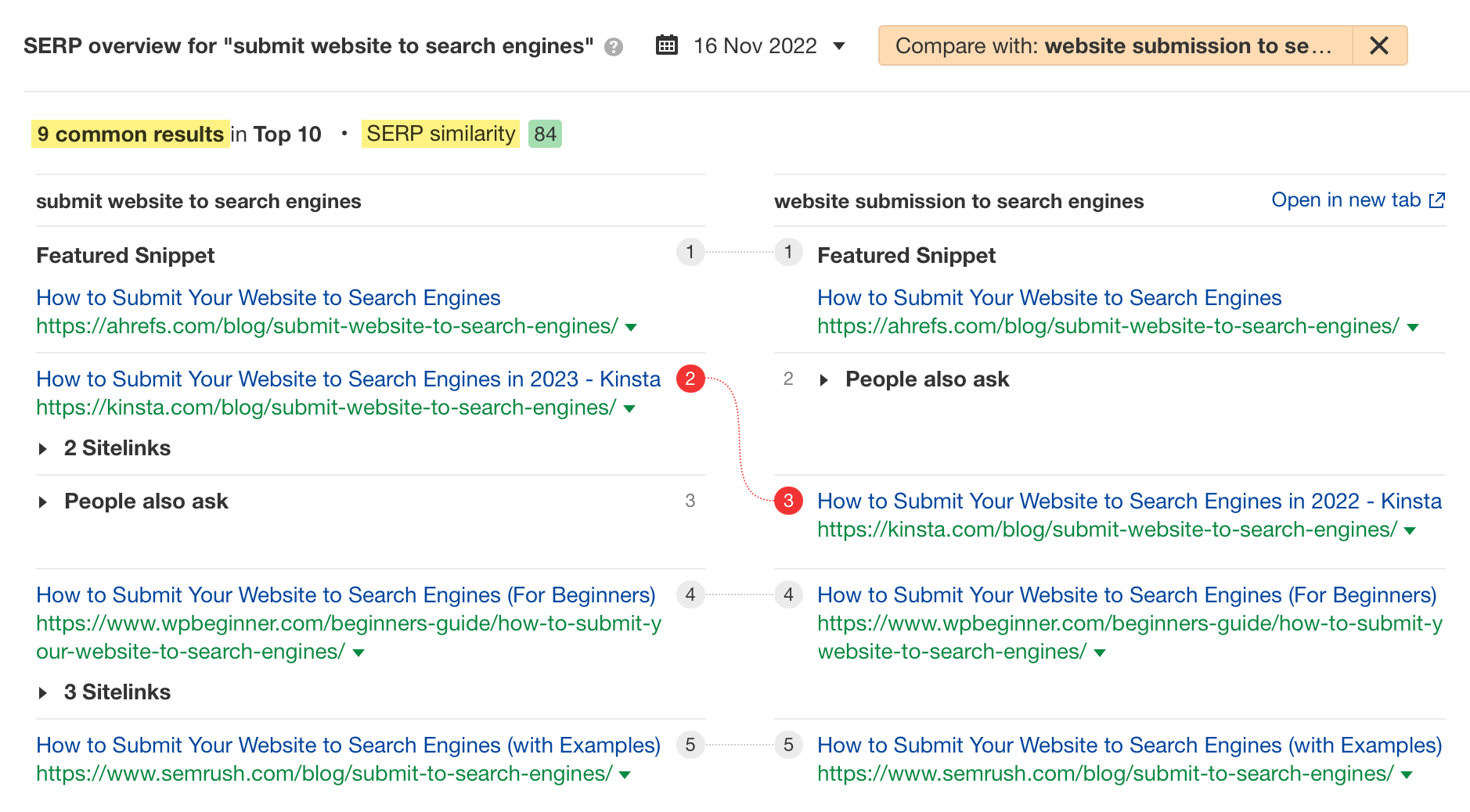
To illustrate, let’s compare “submit website to search engines” and “website submission to search engines.” The SERP comparison in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer tells us these two keywords have almost the same results.
Reason 3. You can rank for hundreds of keywords if you optimize for one
According to our study, the average #1 ranking page will also rank in the top 10 for nearly 1,000 other relevant keywords.
This doesn’t apply only to keywords with large volumes. The pattern remains the same even for less popular keywords.
Case in point: Our article on seo basics was optimized for a single keyword with 1,400 monthly searches. The article now ranks for 463 keywords, out of which 156 are in the top 10.
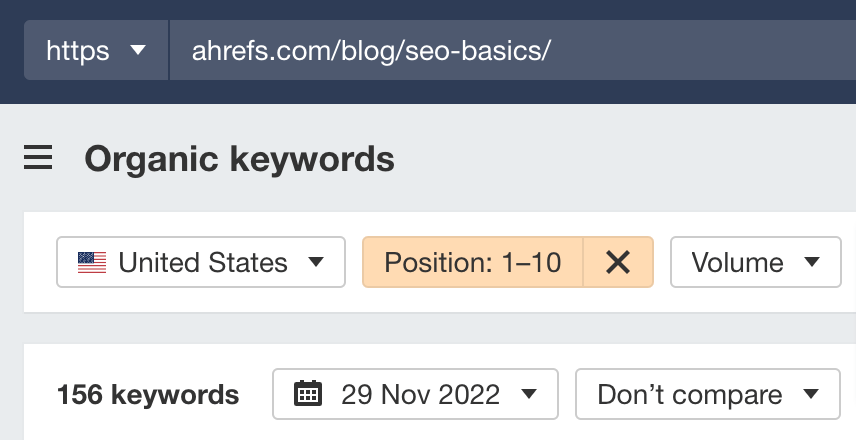
Some of those keywords don’t sound like close variations at first:
- “seo basics”
- “how to use seo”
- “beginner’s guide to seo”
- “getting started with seo”
- “search engine optimization how to”
- “seo knowledge”
- “seo fundamentals”
Yet, in Google’s eyes, they can be “served” by the same or similar pages.
The best part here is that all of the keywords bring traffic independently. As a result, that article optimized for a keyword with a volume of 1,400 monthly searches in the U.S. generates an estimated 8,600 visits every month.
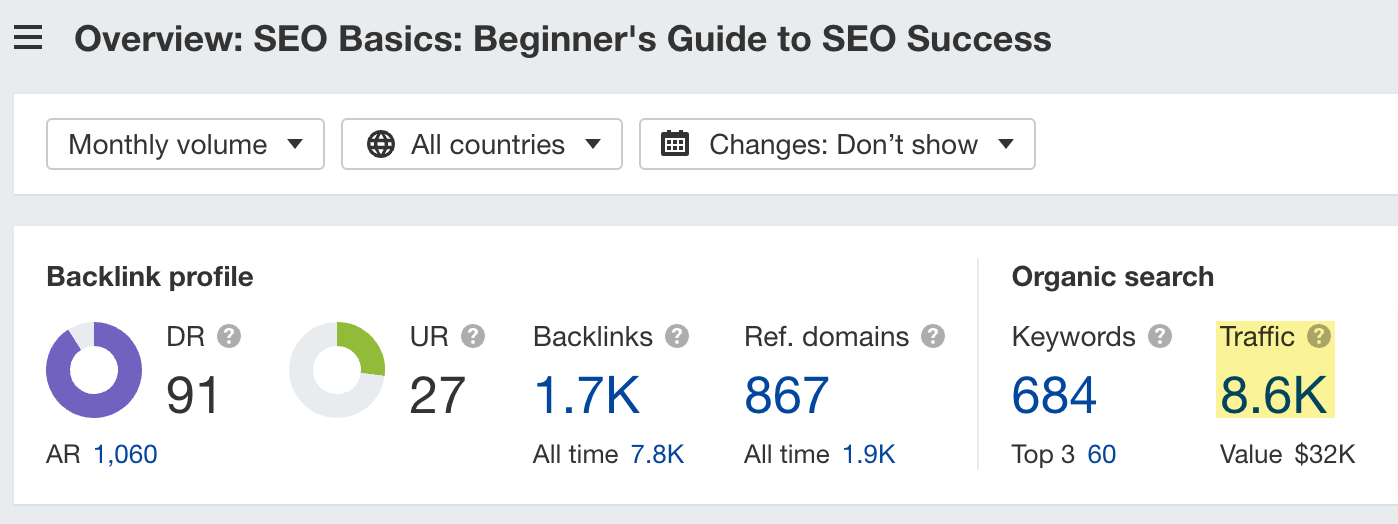
So while targeting not multiple but a single primary keyword is the best tactic, you will get the best results if you incorporate multiple secondary keywords.
In short, to cover a topic in full, you need relevant subtopics. And one of the best ways to find relevant subtopics is through secondary keywords.
Imagine that Google is a huge bookstore, and you walk in to get the best beginner’s guide to gardening. You’d surely appreciate it if the shop assistant showed you a guide that explained all the basics in layperson’s terms that other people seemed to be satisfied with. Why would you even look at other guides?
In an overly simplified analogy, that’s how Google works. The system understands what the searcher may be after and tries to serve the most helpful result while keeping other options in the back.
Let’s look at some practical ways to find both primary and secondary keywords at scale.
How to find primary keywords
Use these methods to find the main topic for your content.
Method 1. Use a keyword research tool
One of the best ways to find a good keyword to target is to use a keyword research tool. One that not only uncovers keyword ideas but also provides actionable SEO metrics.
Here’s how to find a good primary keyword with Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer.
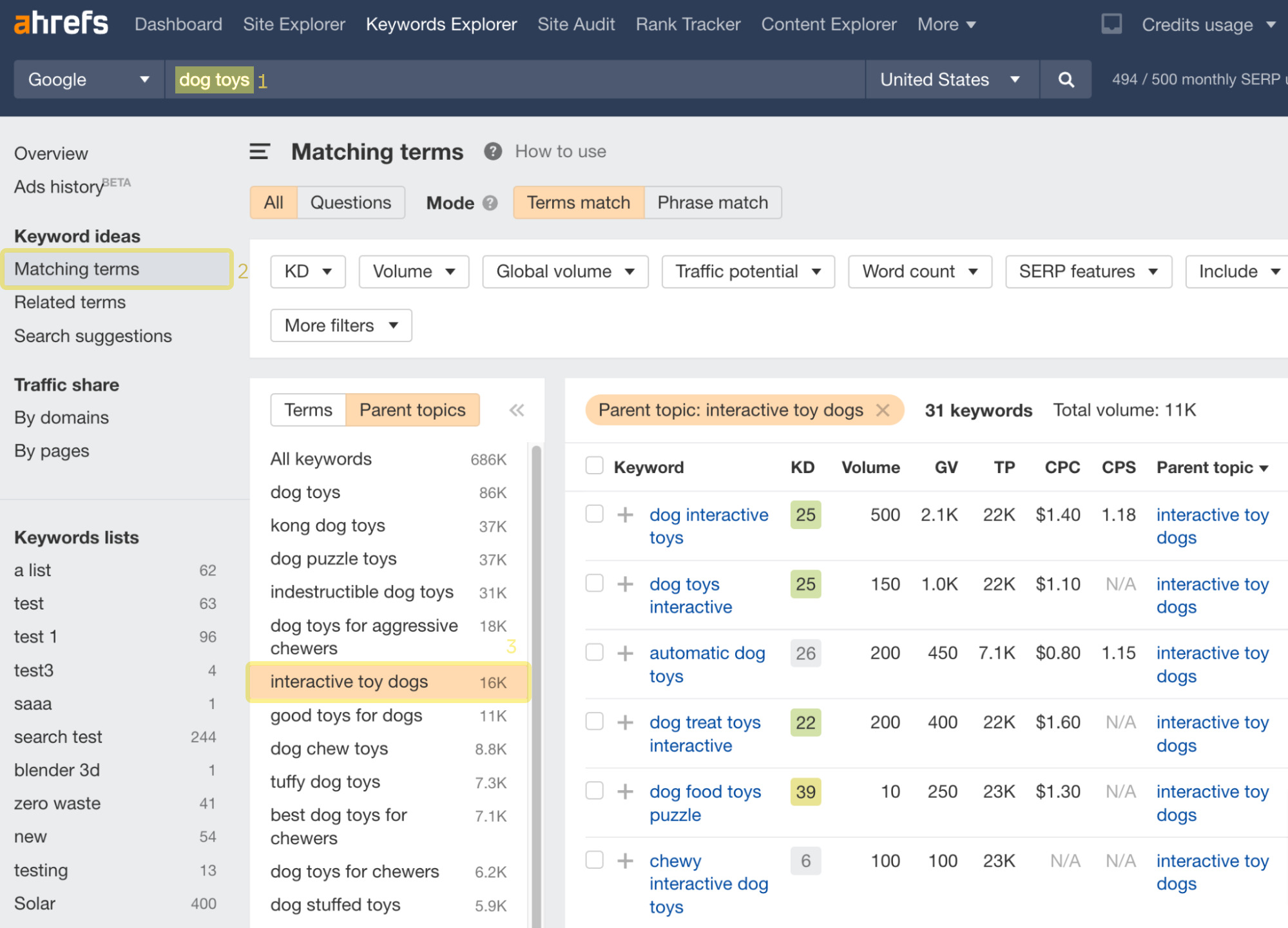
Let’s say you run a website with pet supplies, and you think dog toys may be a good topic for your visitors. You can:
- Enter your seed keyword (“dog toys”). You can also use multiple seed keywords.
- Go to the Matching terms report.
- Browse through Parent Topics on the left-hand side. When you find an interesting topic, click on it to see the keywords that fall under the same keyword group.
- Pick the keyword while weighing in Keyword Difficulty (KD), Traffic Potential (TP), and what makes the most sense for your website (you can learn more about choosing the right keywords in this guide).
Method 2. Find common topics in any niche
Use a content gap analysis tool like Ahrefs’ Content Gap tool to find topics often covered within a niche. It’s a helpful technique if you’re entering a niche you don’t know much about.
Here’s what to do:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Open Content Gap tool
- Enter URLs of websites with similar content, and make sure the last input field is clear
- Hit Show keywords
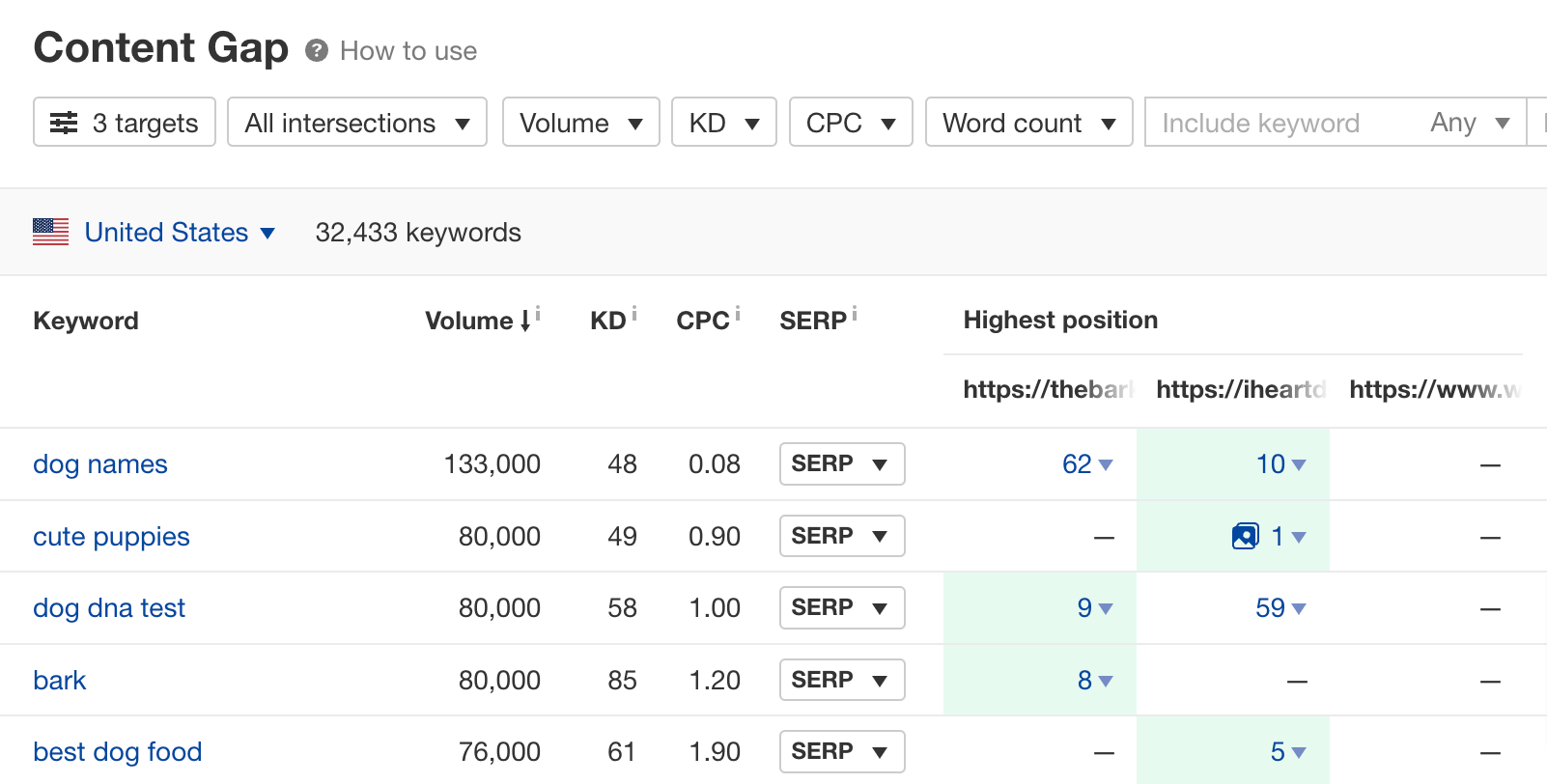
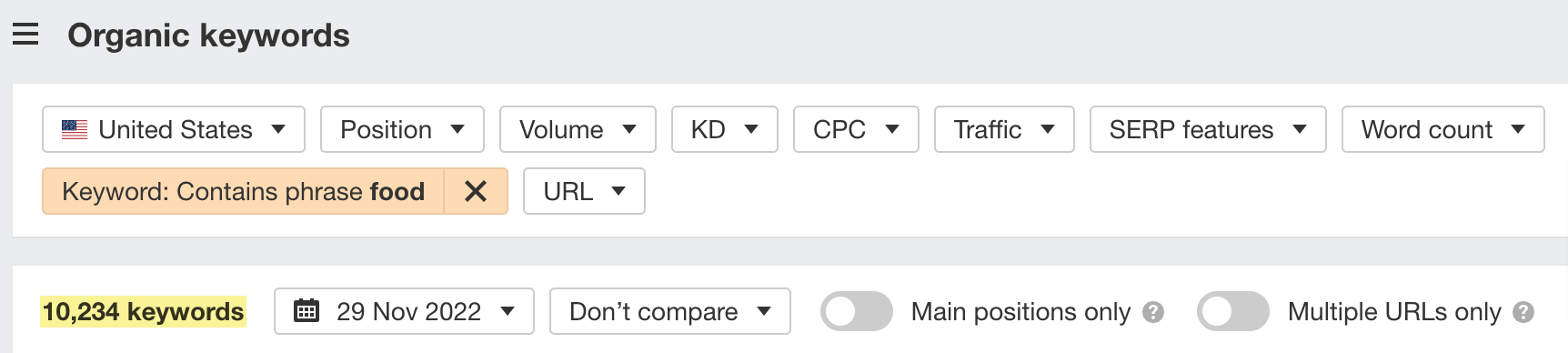
You can also use filters to refine your list. For example, show only the most common keywords (Intersect filter) with a minimum volume of 100 and a maximum Keyword Difficulty (KD) of 20.

Method 3. Analyze keywords of your competitors
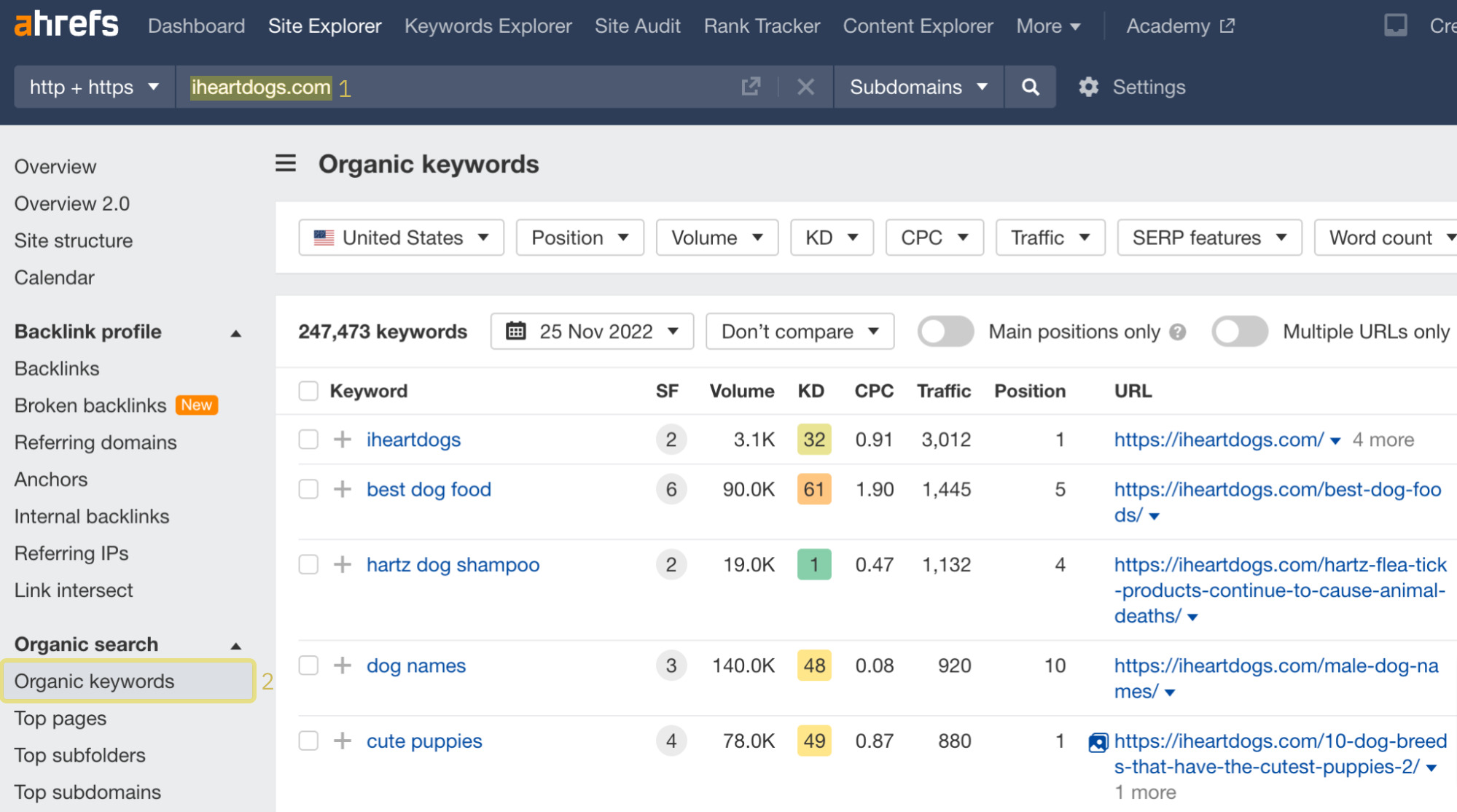
This method will show the keywords that your competitor ranks for (or any other site you wish to analyze). Based on that, you can pick keywords that could make a good fit for your website too. Here’s a rundown of the process using Site Explorer. You can:
- Enter your competitor’s website address.
- Go to the Organic keywords report.
- Refine the list of keywords to your heart’s content. For example, you may want to uncover keywords that include a particular word or phrase.
How to find secondary keywords
Use these methods to find relevant subtopics for your content.
Method 1. Find secondary keywords of the top-ranking pages
Once you uncover secondary keywords of the top-ranking content, you’ll have a good idea of the subtopics to include in your content.
Here’s how to find them with Keywords Explorer:
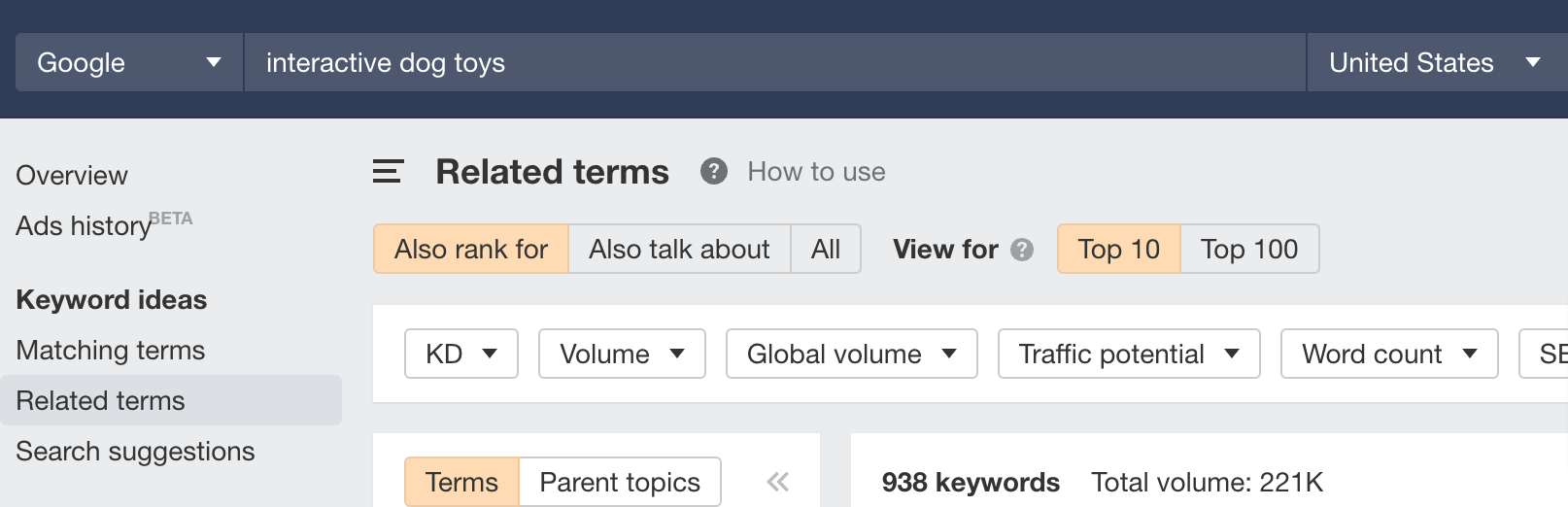
- Enter a topic you want to analyze, preferably a primary keyword you want to target
- Go to the Related terms report
- Set the toggles to Also rank for and Top 10
- Look at the results and pick keywords that sound like good subtopics for your page
Recommendation
Google tries to avoid ranking content that brings nothing new to the table.

So use competitor analysis wisely. Get an understanding of the kind of information necessary to meet searchers’ expectations but make sure to add something unique (your own research, a unique perspective, more up-to-date data, etc.).
Method 2: Find missing keywords with Content Gap
This last method should be used to boost your existing content. It allows you to find subtopics you may be missing by uncovering relevant keywords you don’t rank for.
We’ll use Ahrefs’ Content Gap tool again. But this time, we’ll insert a page in the last input to compare it with others.
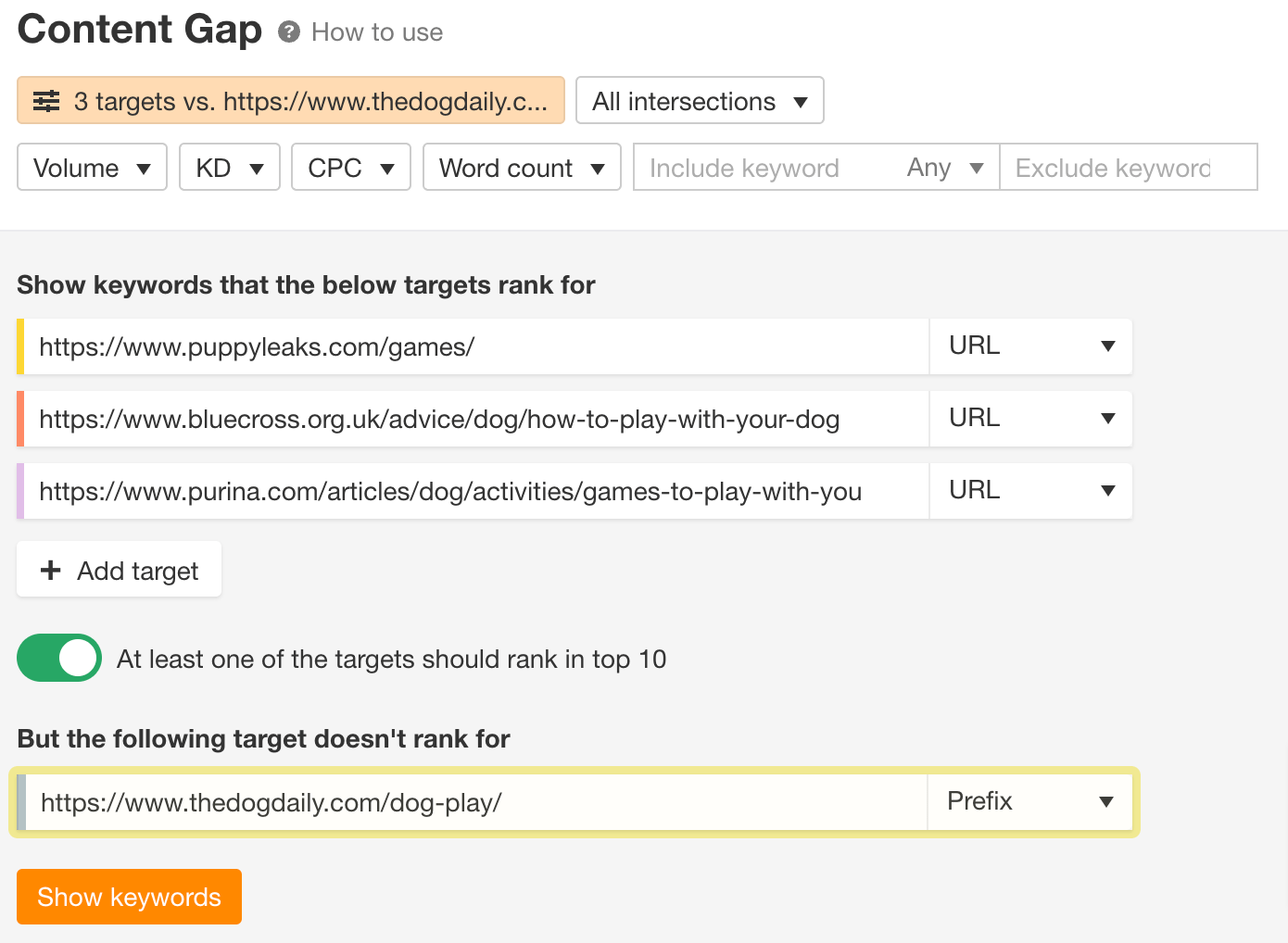
For example, comparing pages about playing with dogs, we see that the authors of the compared page can consider adding a section about games to play with puppies.
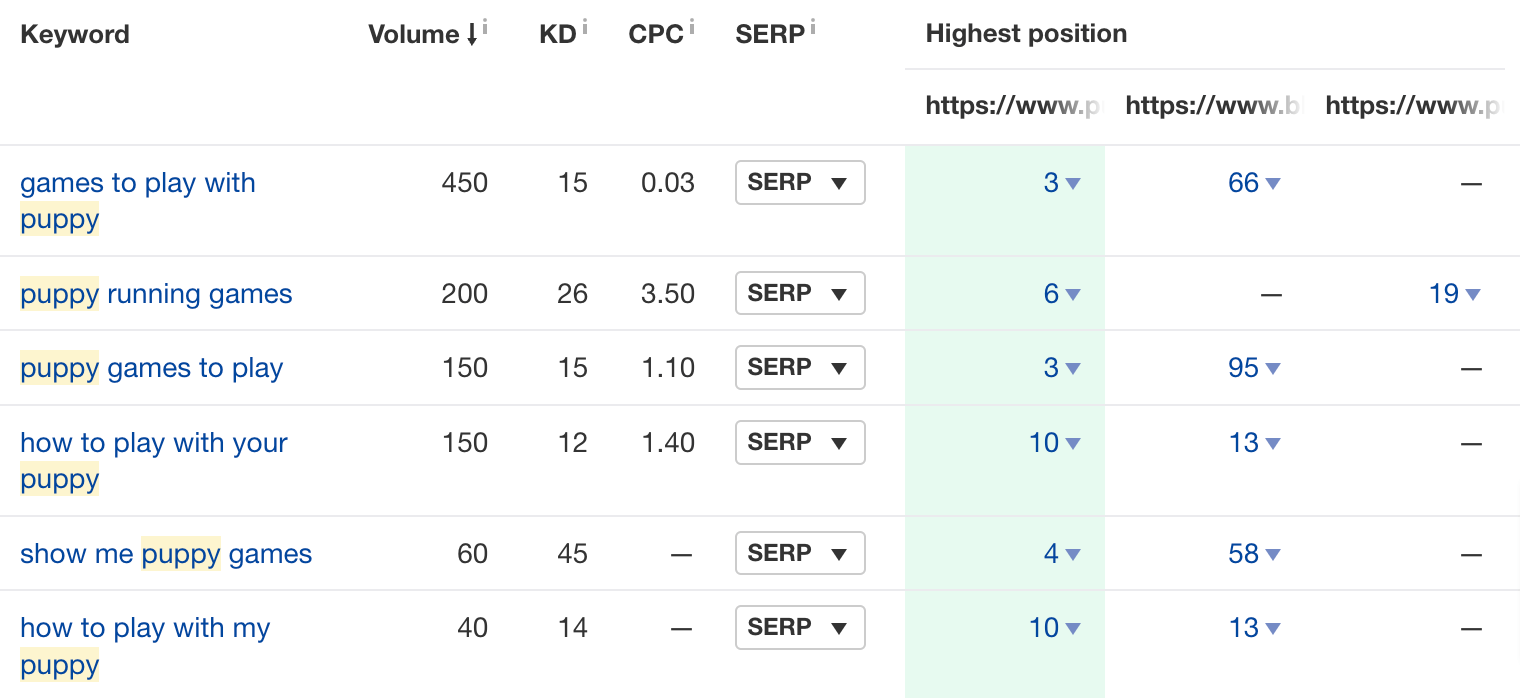
If you want to target a keyword for SEO effectively, it’s essential to know how to use your primary and secondary keywords inside the content. Here’s a quick overview.
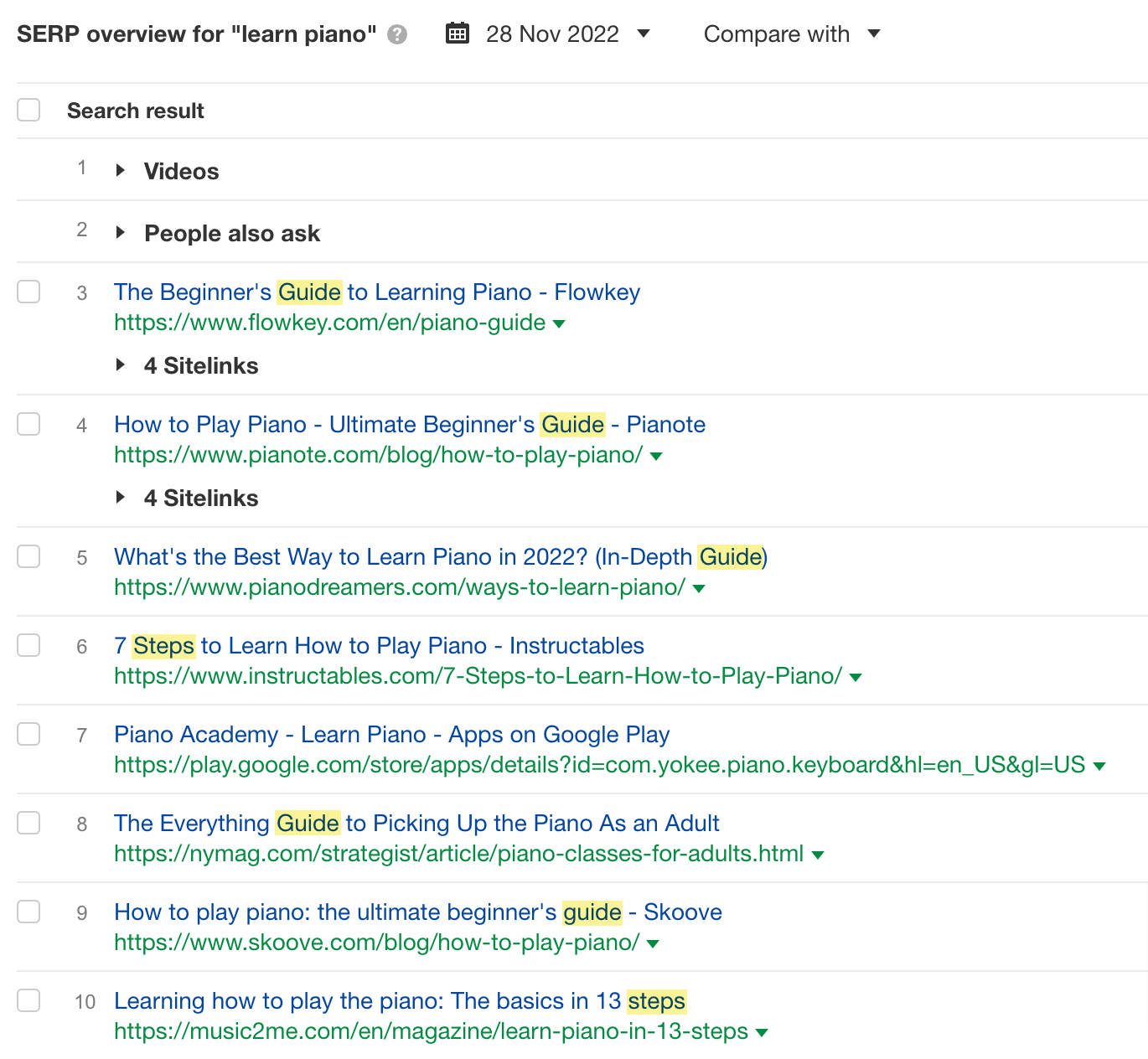
What’s most important is your primary keyword should determine the search intent, which is a fundamental aspect of search engine optimization. To get the search intent right, plug in your primary keyword into Google, look at the top-ranking pages, and identify:
- Dominating content type – Popular types: video, article, landing page, product page.
- Dominating content format – Popular formats: reviews, comparisons, listicles, how-to guides, and opinion-based articles.
- Relevant content angles – This refers to the unique selling point of the top-ranking pages. For instance, “best,” “free,” “in 5 minutes,” “for 2023,” etc.
Next, as already mentioned, you need to cover your chosen topic in full. A quick reminder here: Your primary keyword is the topic, while your subtopics can come from relevant secondary keywords.
But not all relevant subtopics will be uncovered by keyword research. It’s always a good idea to look at the structure of top-ranking pages to get an idea of what searchers may be looking for.
To make the job even easier, get our free SEO Toolbar and let it work out the structure for you.

While we’re at using keywords inside the content, let’s address a couple of “don’ts”:
- Don’t stuff your content with keywords – You don’t need to try to mention your keywords as much as possible or aim for some kind of keyword density or statistical importance score.
- Don’t try to “force in” synonyms and closely related keywords (aka LSI keywords) – Google won’t rank your content higher just because you’ve used more words than other pages to describe the same thing.
Finally, it’s a good idea to:
- Insert your target keyword into the title – Title tags help Google understand what the content is about.
- Align the H1 tag with the title – The easiest thing to do here is to make the H1 and title tags identical.
- Use secondary keywords in the H2–H6 headings – But only if it’s natural to the main body of the text. This can help Google understand what your page is about.
- Use the primary keyword in the URL – Not a requirement, just the easiest way to help Google and searchers understand the context of the page.
Those are the basics. If you’re interested in learning more, check out How to Do Keyword Optimization for SEO (3 Steps).
Final thoughts
Let’s recap the article in a handy list of dos and don’ts.

Got questions? Ping me on Twitter or Mastodon.
