It can be alarming if your website’s Google rankings drop suddenly.
But before you make any changes, it’s important to check certain things first.
Google’s algorithm updates are among the most common ways your website’s rankings can be negatively impacted.
Google doesn’t like low-quality or misleading results appearing at the top of its organic search results, so it runs regular algorithm updates to preserve the quality of its search index.
Updates are announced on Google’s status page. So it’s worth checking if any dates align with your website’s ranking drops.
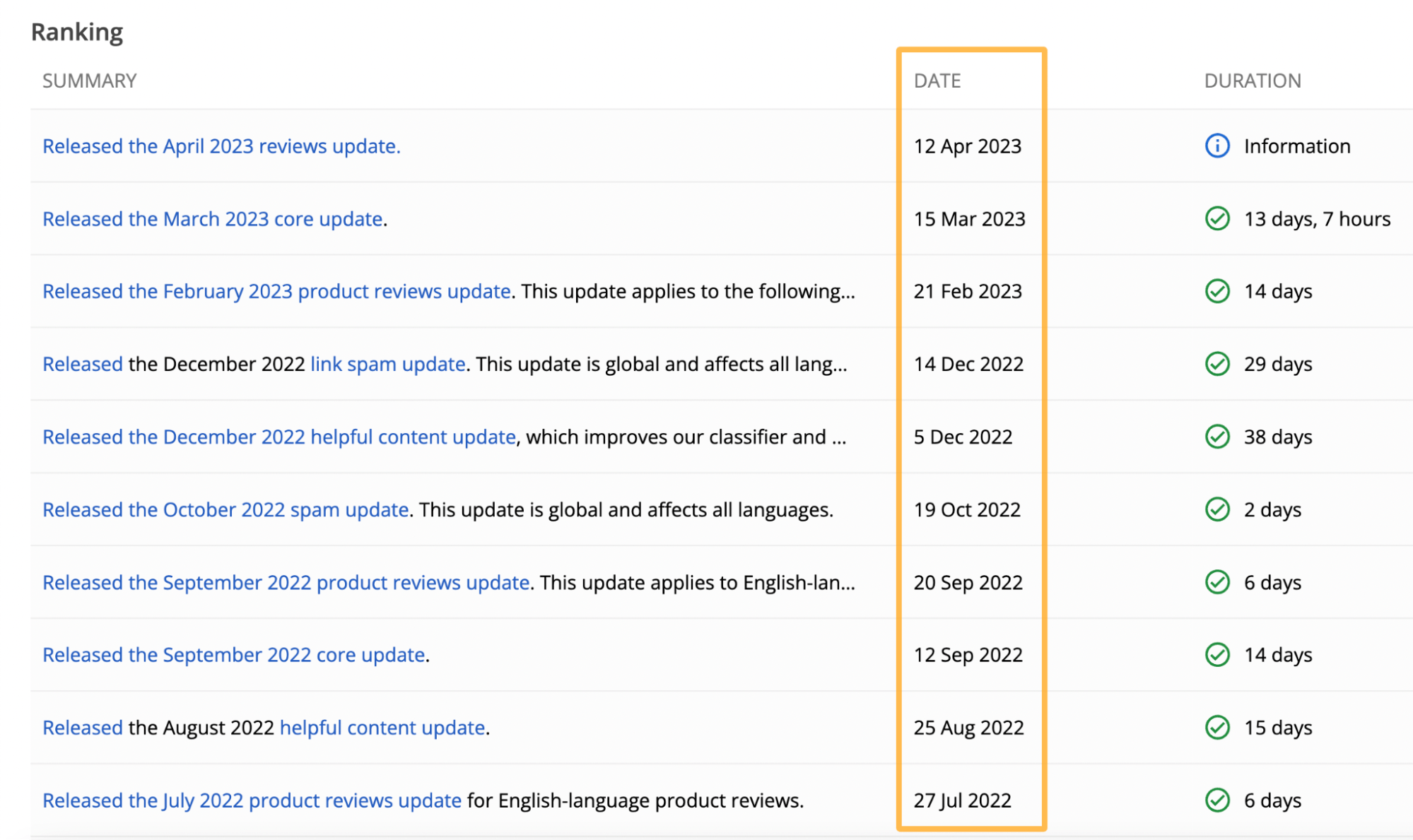
It takes time to align these dates against your organic traffic data, so a faster way to understand the impact is to use a tool like Ahrefs.
To do this, head to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, plug in your domain, and scan the Ⓖ updates at the bottom of the Overview 2.0 organic traffic chart.
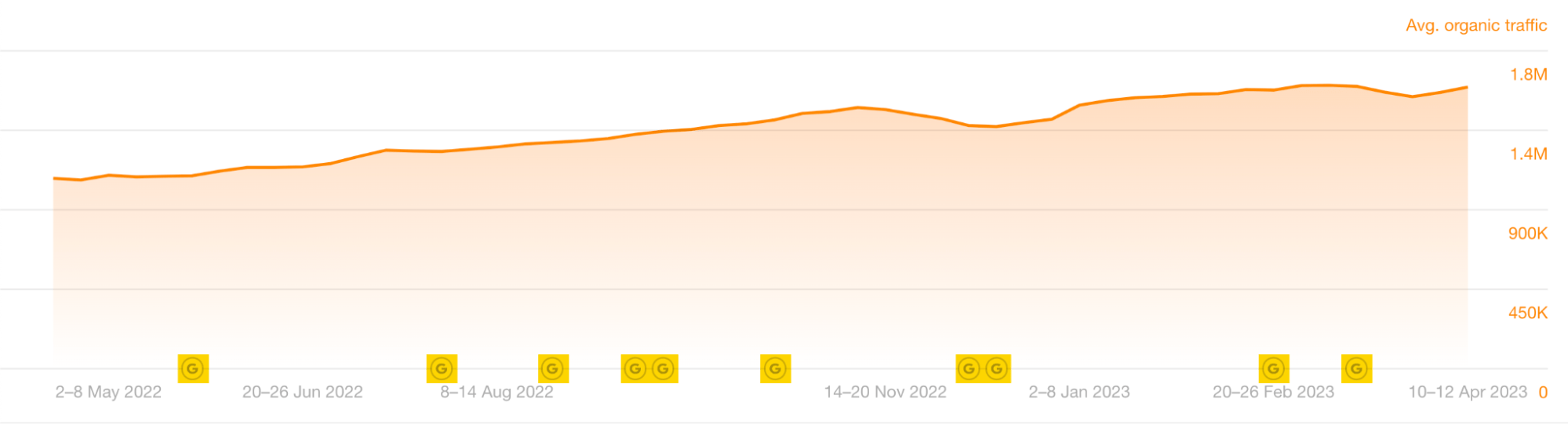
Hovering over the Ⓖ symbols will give you more detailed information about the updates.
Once you’ve established there’s been a Google update, you’ll need to check its date against your total organic traffic to see if there’s been a drop at the same time.
To check your organic traffic in Site Explorer, you can:
- Plug in your domain and scroll down to the Overview 2.0 chart.
- Uncheck everything apart from “Avg. organic traffic.”
- Set the timeline to “All” and “Weekly.” This helps you to see the complete timeline for the organic traffic, giving you a better idea of how significant the drop is.
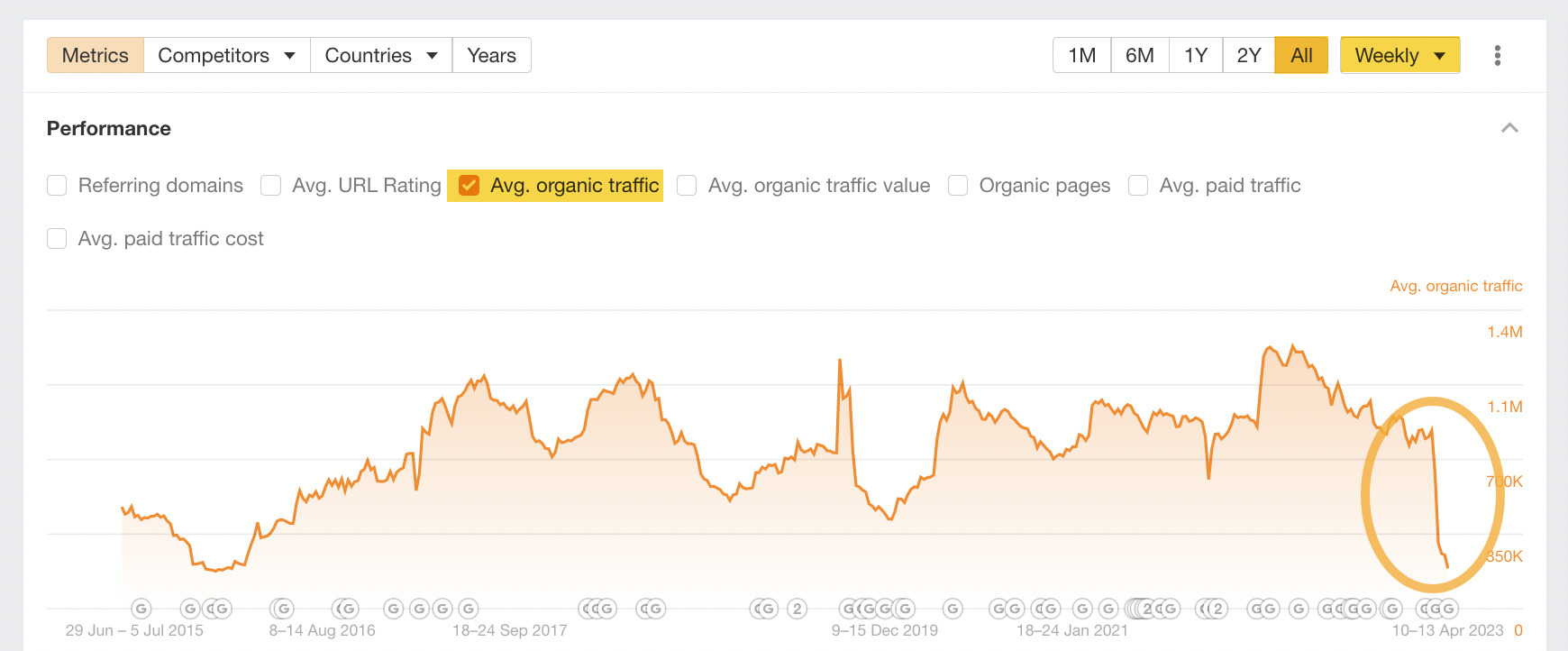
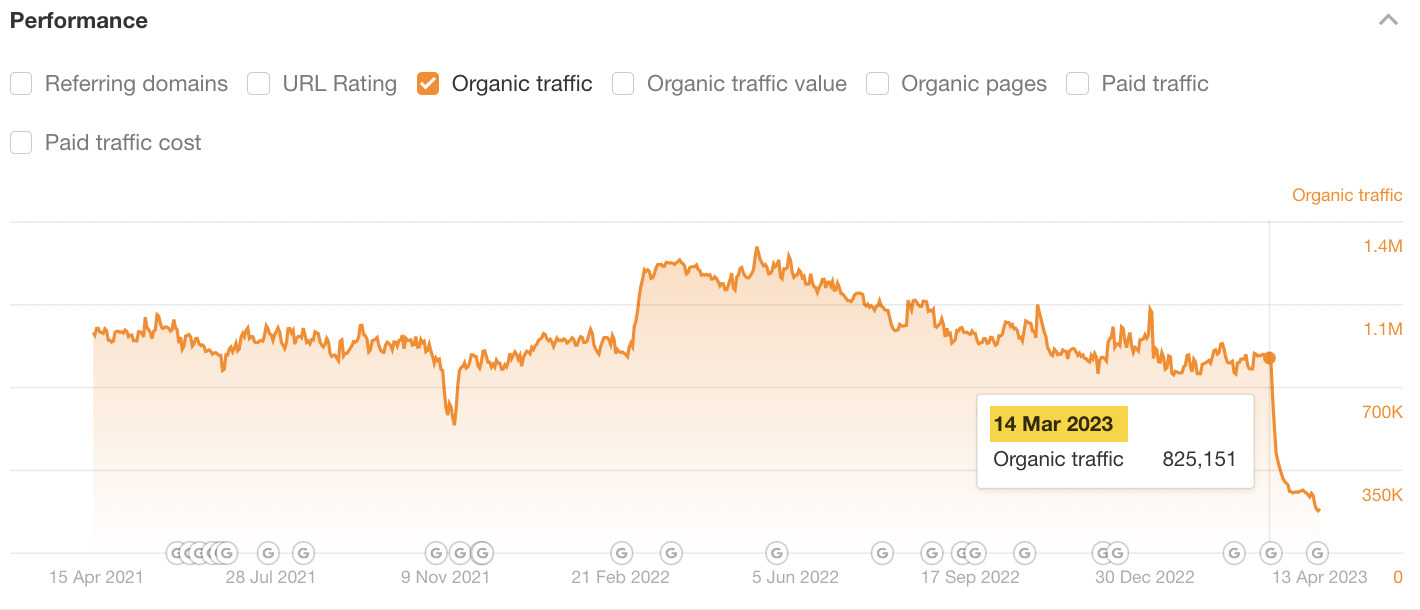
I’ve highlighted the most recent traffic drop for this website. Let’s see if we can work out why this happened. Let’s zoom in and change the timeline to “1Y,” hovering our cursor around the time of the drop.
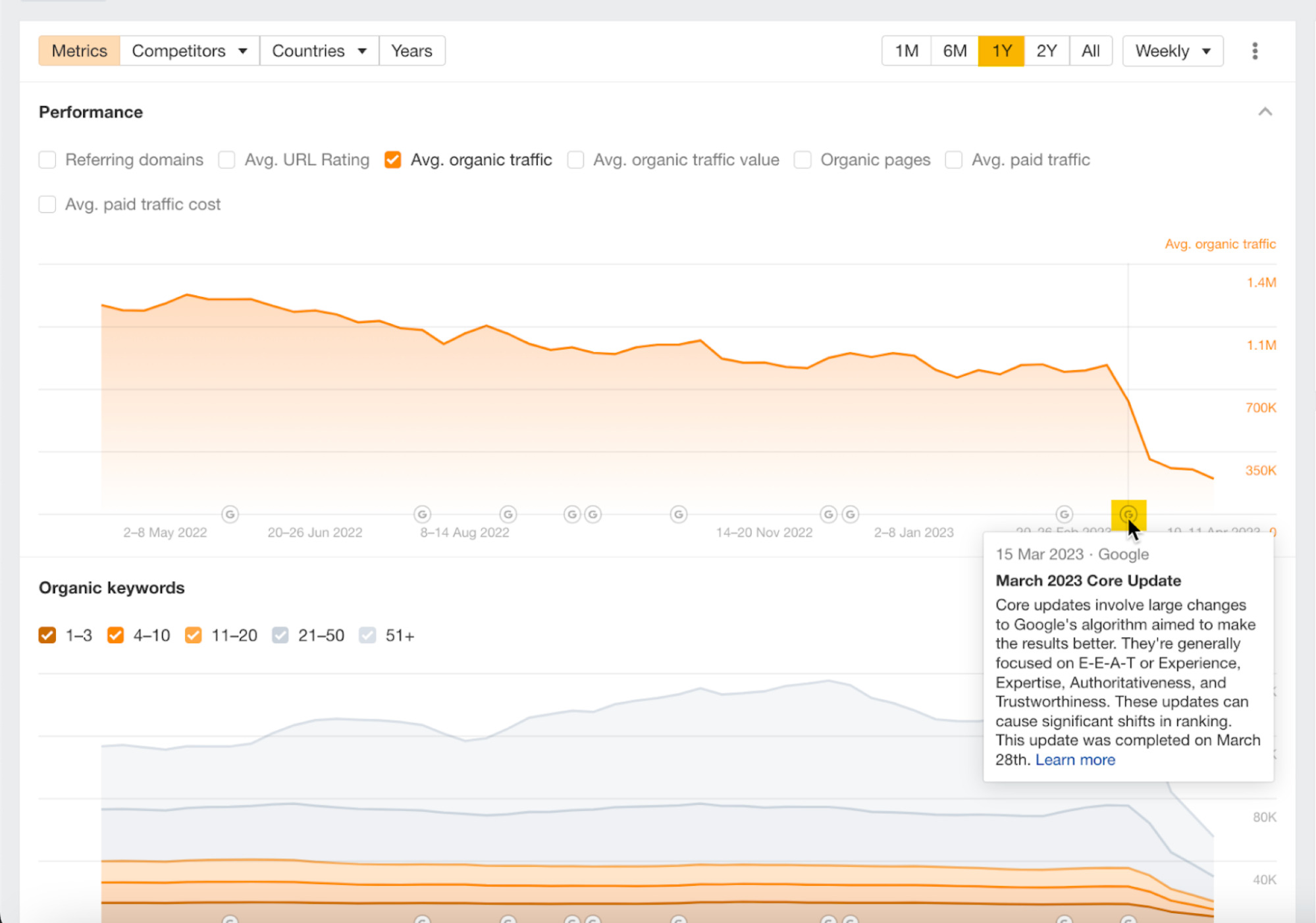
The March 2023 Core Update roughly aligns here.
It may have contributed to the loss of traffic, but we can also see that the exact date of the organic traffic drop doesn’t align with the release of this update.
So we can’t say that this algorithm update caused the drop. In this situation, it’s usually best to keep investigating.
If your website’s organic traffic drop does align exactly with an update, then a Google update has likely impacted you.
Once you’ve established a significant drop in organic traffic, you’ll want to know which of your website’s keywords have lost rankings.
To do this, head to the Organic keywords report in Site Explorer. I like to compare keywords year on year (YoY), so let’s add a YoY “Compare” filter.
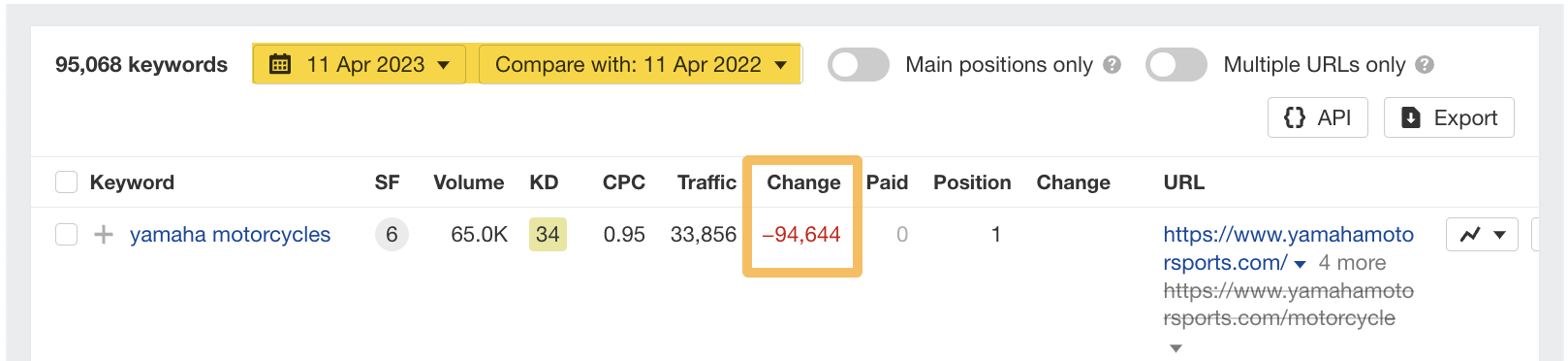
We can see that in the “Change” column, there’s been a significant drop for this website’s top keyword, “yamaha motorcycles.”
Let’s head over to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer by clicking on the keyword “yamaha motorcycles.”
Scrolling down to the SERP overview, we can see what happened if we make a year-on-year (YoY) comparison.
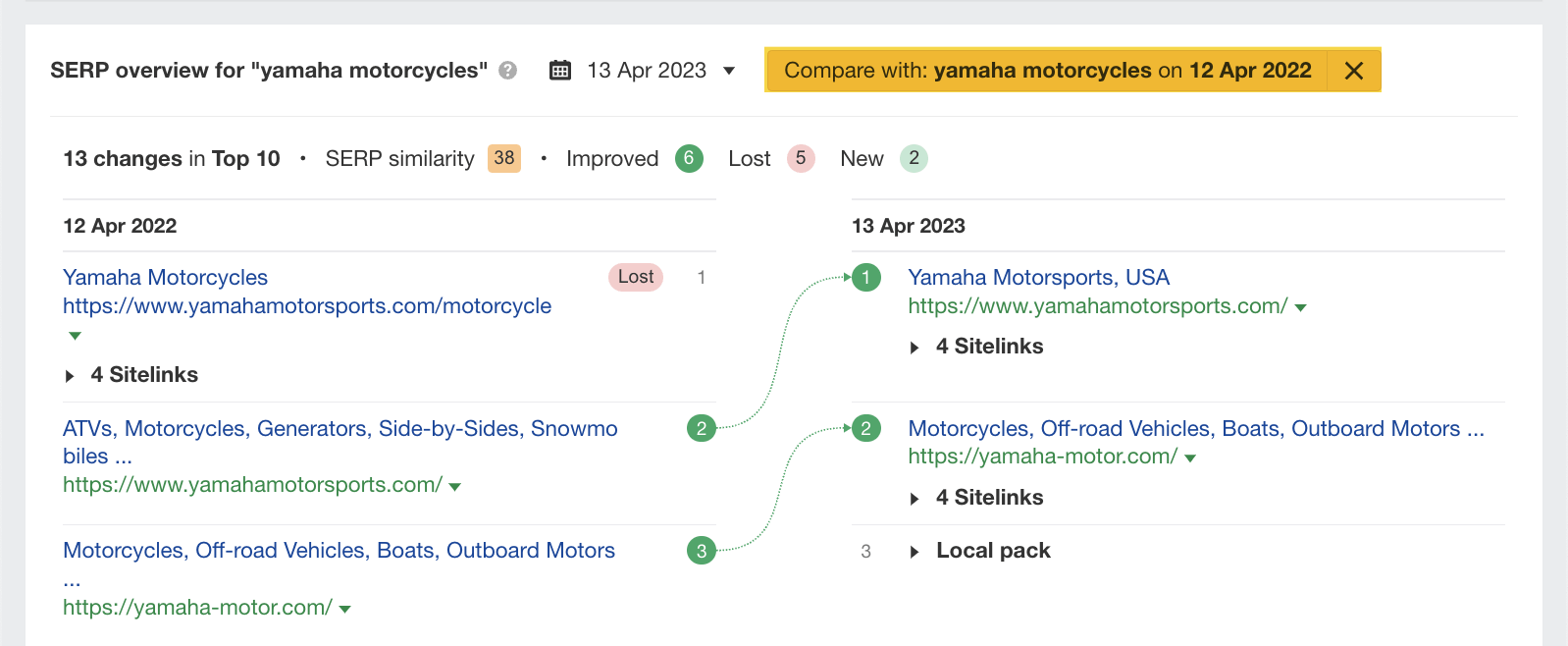
Google has switched the /motorcycle page for the homepage. So there may be an issue with the /motorcycle page.
For reference, in Site Explorer, we can see the exact date of the drop is March 14.
Let’s remove the comparison and plug this date into the SERP overview in Keywords Explorer.

Using the SERP overview, we can see that this page was a 404 page on that date. If we change the date to March 16, 2023, we can see that this page disappears from the SERPs.

As this date matches up, it’s likely to be the reason for the significant drop in traffic for this website.
Using Site Explorer and Keywords Explorer in conjunction is a great way to diagnose the reasons for ranking drops.
Technical issues can impact your Google rankings. You’ll need to run a website crawl to determine these issues.
In my opinion, the easiest way to identify technical issues with your site is to run a crawl using Ahrefs’ Site Audit.
To set one up, head to Site Audit, click “+ New project,” and follow the prompts.
Once you’ve completed the crawl, you’ll see an “Overview” screen similar to the screenshot below.
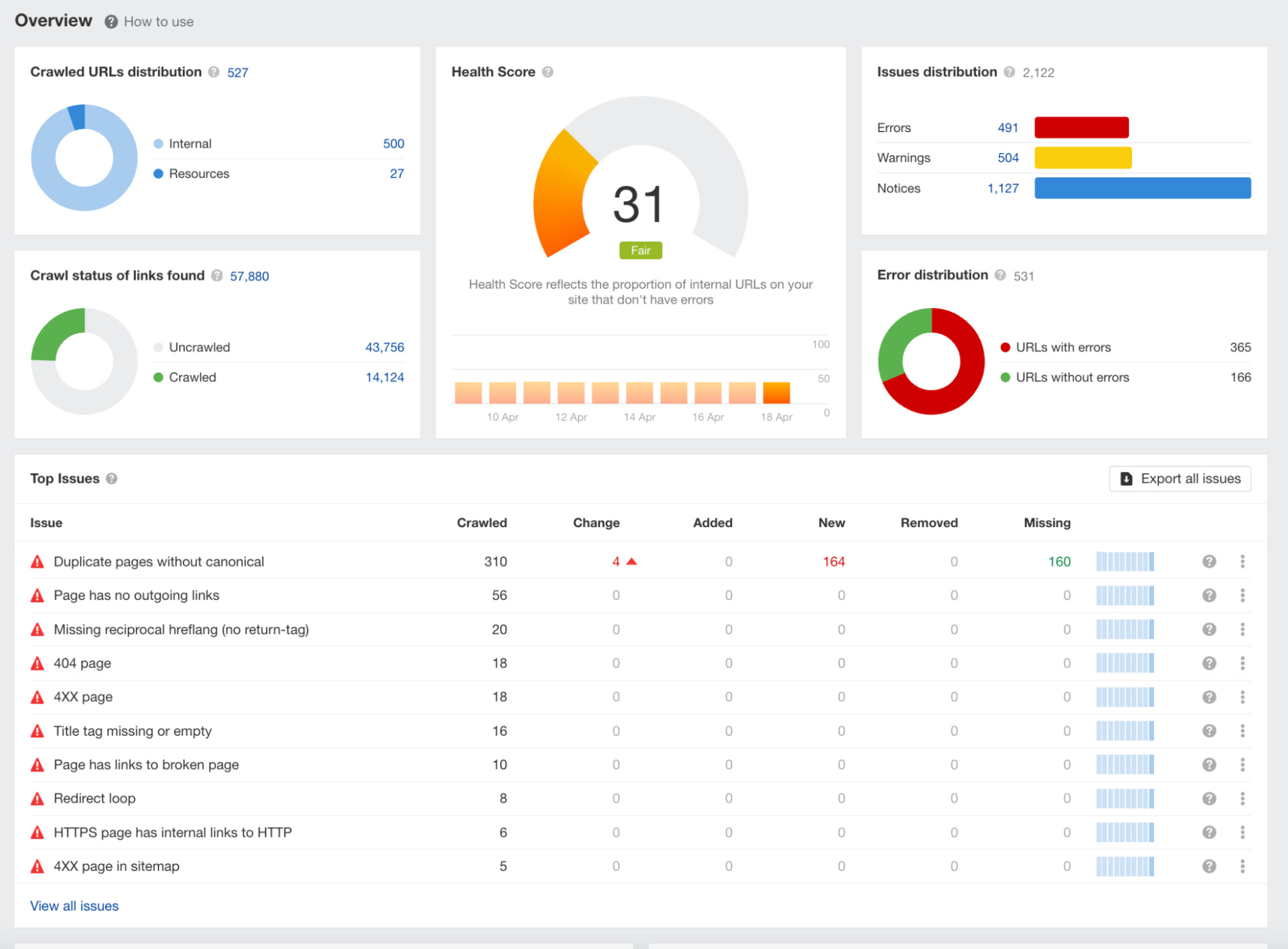
This page gives a bird’s-eye view of technical issues and monitors your website’s health score.
Once you’ve clicked on a specific issue, click “Why and how to fix.” A sidebar will then appear, explaining the problem and how to fix it—this information is critical to helping you solve your technical issues.
If your website crawl reveals that you’ve got many technical issues, it’s worth spending time fixing each problem until your overall health score improves.
Once you’ve done this, you’ll be able to eliminate the possibility of any technical issues impacting your site’s Google rankings.
Tip
Now we know how to set up and analyze a Site Audit, let’s look at some specific technical issues that often result in lost rankings and organic traffic.
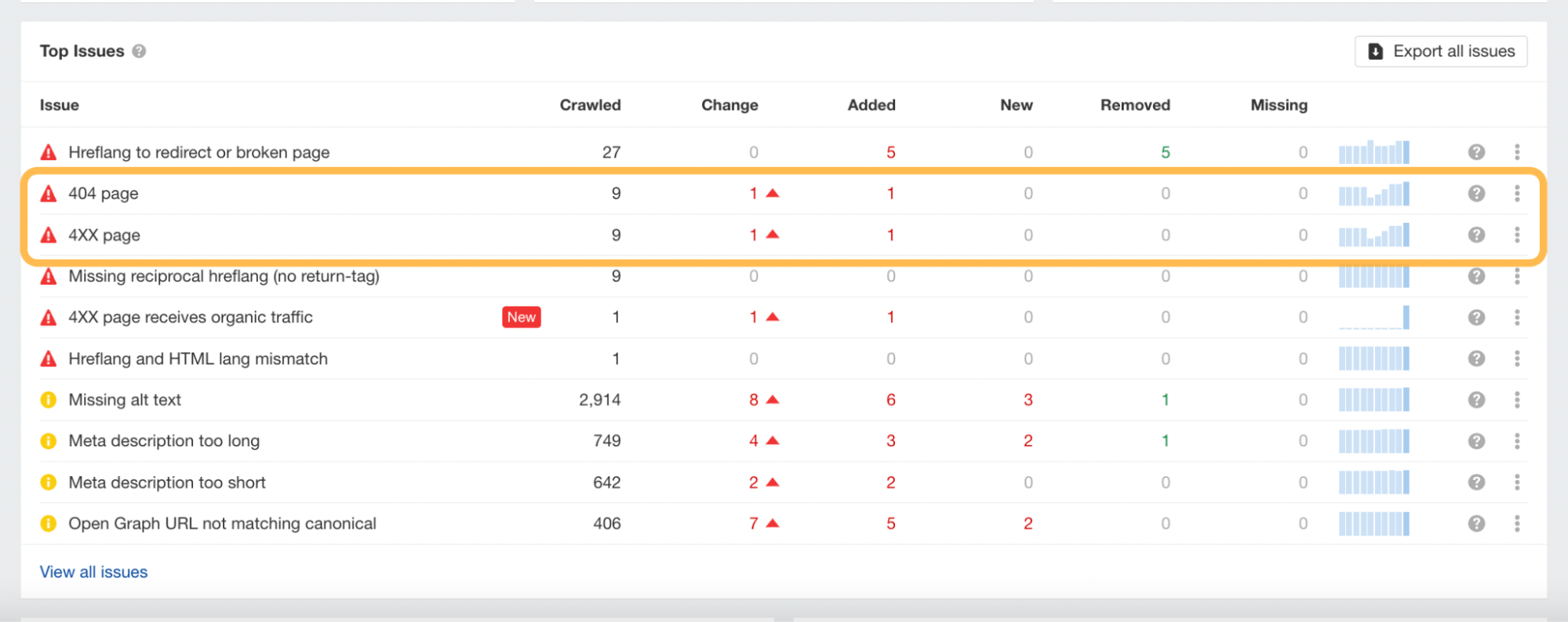
4XX Pages

4XX pages are error pages. You’ll probably be most familiar with the classic “404 page not found.” When these types of pages occur, it can result in lost traffic.
If we return to our earlier website (/motorcycle page) example in Keywords Explorer and scroll down to the SERP overview, we can see it’s a 404 page.

But are there any more 404 pages on this site? Let’s return to the Organic keywords report and click through other top keywords, such as “r7” and “yamaha r1.”
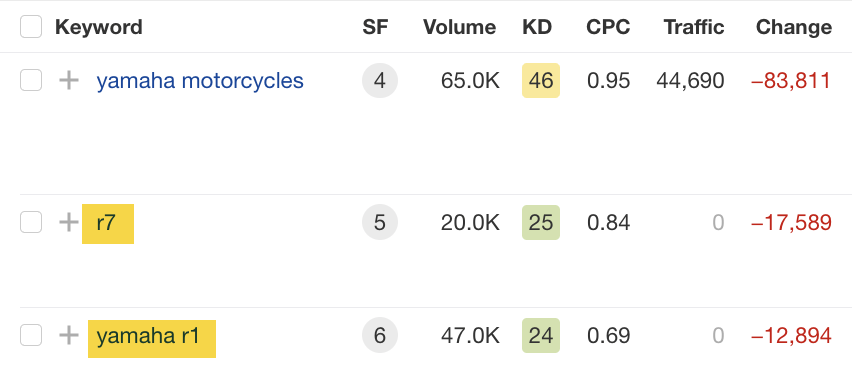
If we click through on the keyword “r7” to Keywords Explorer, scroll to the SERP overview, and set the date to March 14, 2023, we can see that this keyword also has a 404 status code.

Repeating the process with the “yamaha r1” keyword, we can see this page is also a 404 page on March 14, 2023.

It seems fair to conclude that this website’s top traffic-driving pages were dead pages.
Although we have quickly used Keywords Explorer and Site Explorer to find this information, the same information can be found using Site Audit.
This is what it will look like once your crawl has been completed and where you can identify the 404 or 4XX pages in the report.
Canonicals
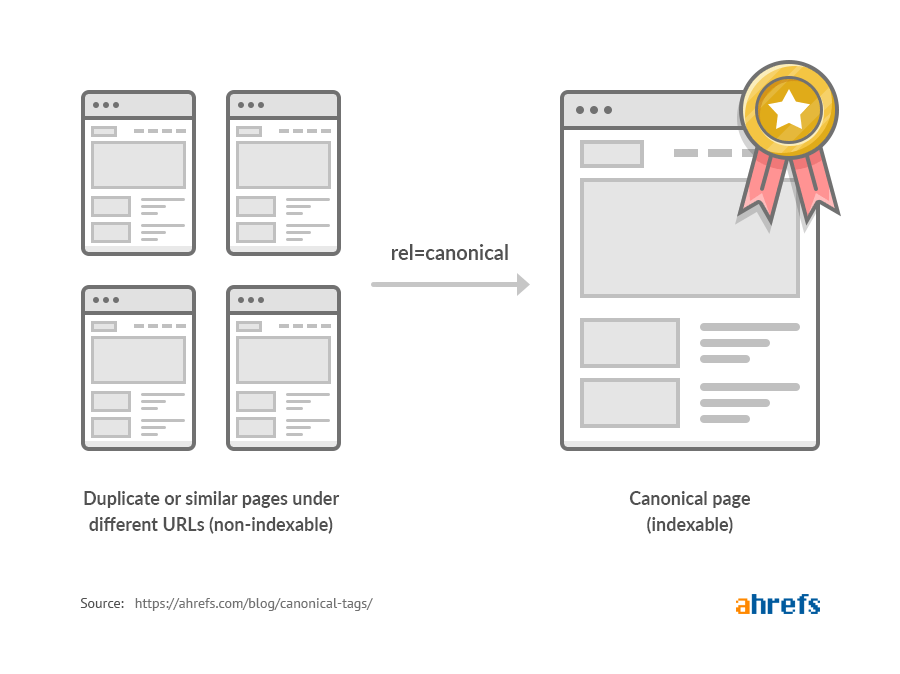
Lack of or poorly implemented canonical tags is another technical issue that can cause problems for your site.
When it comes to identifying them, you can spot-check them on a page-by-page basis using Ahrefs’ SEO Toolbar, or you can run a Site Audit crawl to get a full view.
I’ve highlighted below the types of issues that can be flagged by the Overview report.
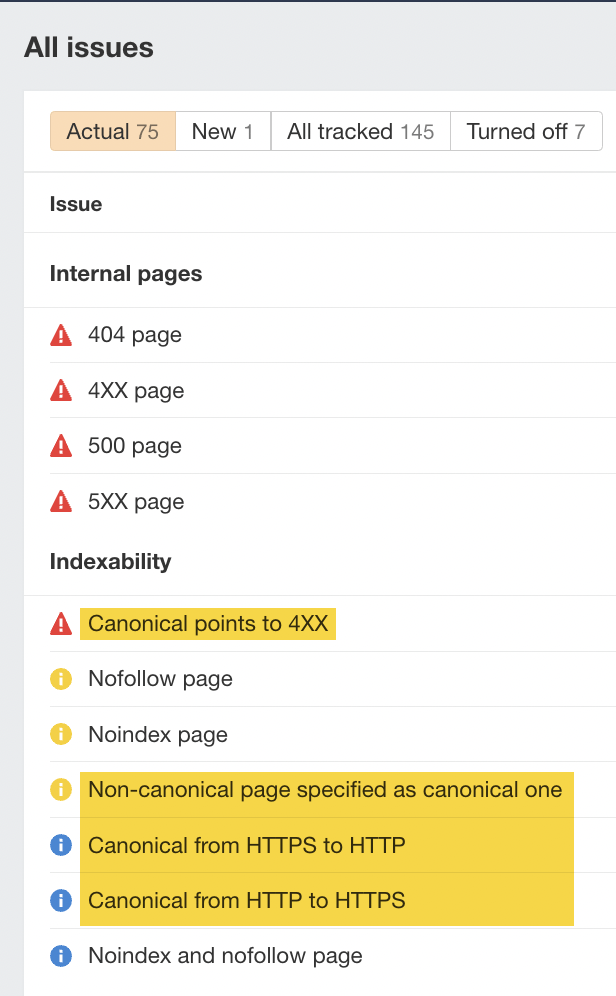
For more tips, check our “canonical tags” beginner’s guide to learn more.
Redirects
Forgetting to add or poorly implementing redirects is one of the most common reasons for a drop in rankings and organic traffic.
There are a couple of simple points to remember with redirects:
Detecting these redirect issues is best done using Ahrefs’ Site Audit. Simply run a crawl of your website and then check the Redirects report to get a view of the issues.
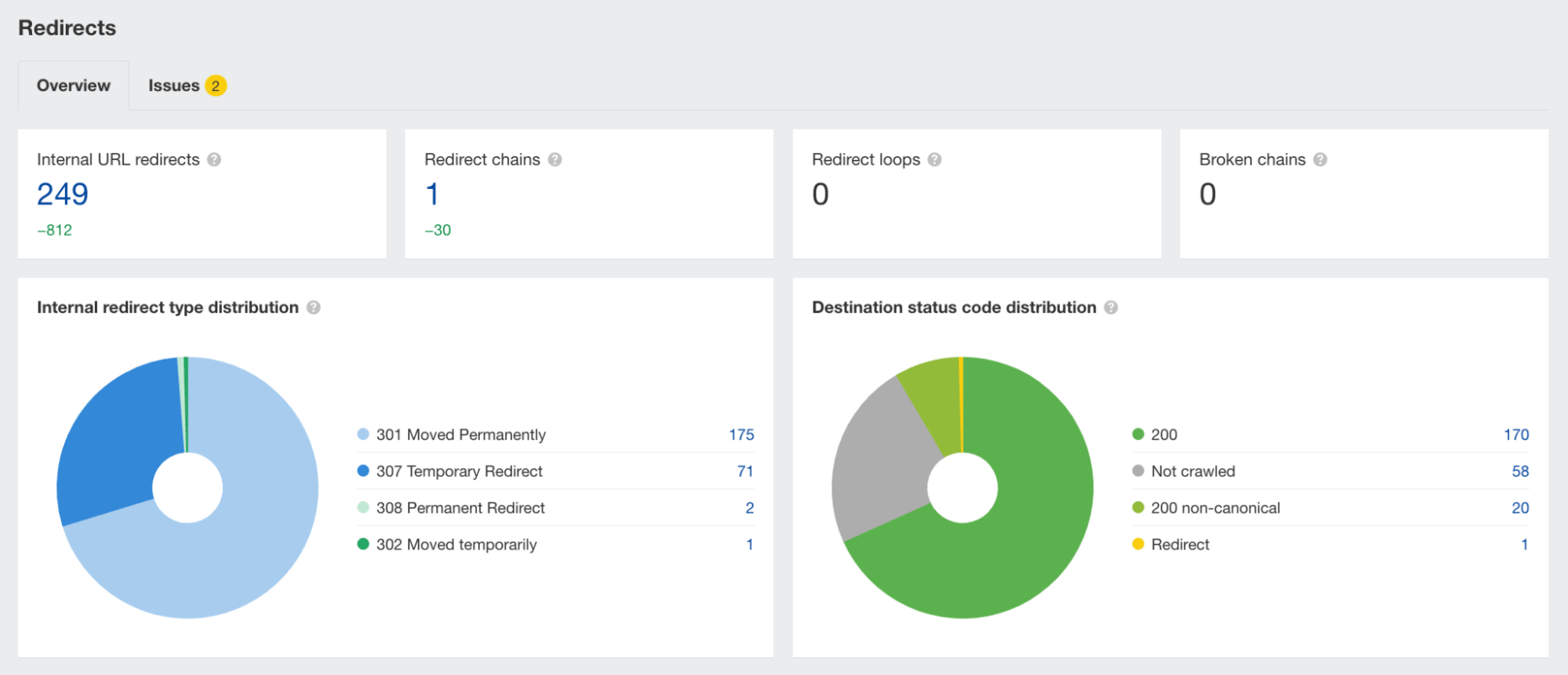
Check out our redirects for SEO guide to learn more.
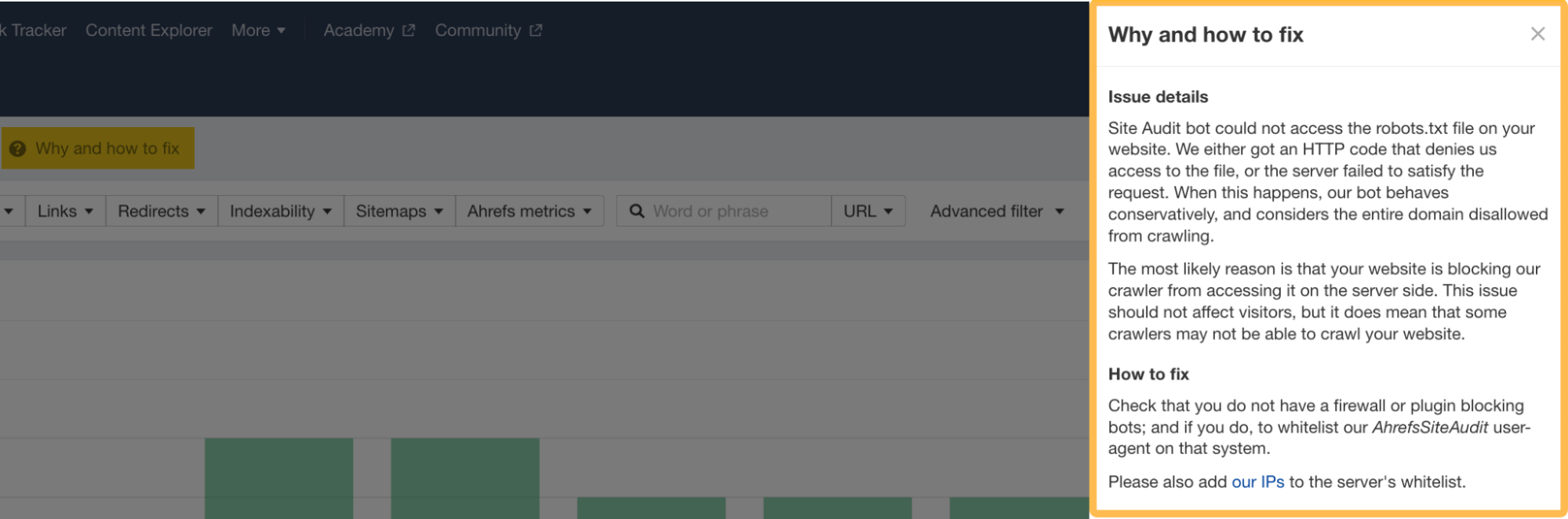
Robots.txt
Changes to a website’s robots.txt file can also impact how Google crawls your website. Sometimes you, or another stakeholder, can accidentally block some essential pages.
You can keep track of your robots.txt file changes if you run a regular crawl of your site using Ahrefs’ Site Audit.
For each crawl, Page Explorer stores the details of your robots.txt file, making it easy to understand if any changes have been made to the file that could negatively affect the website.
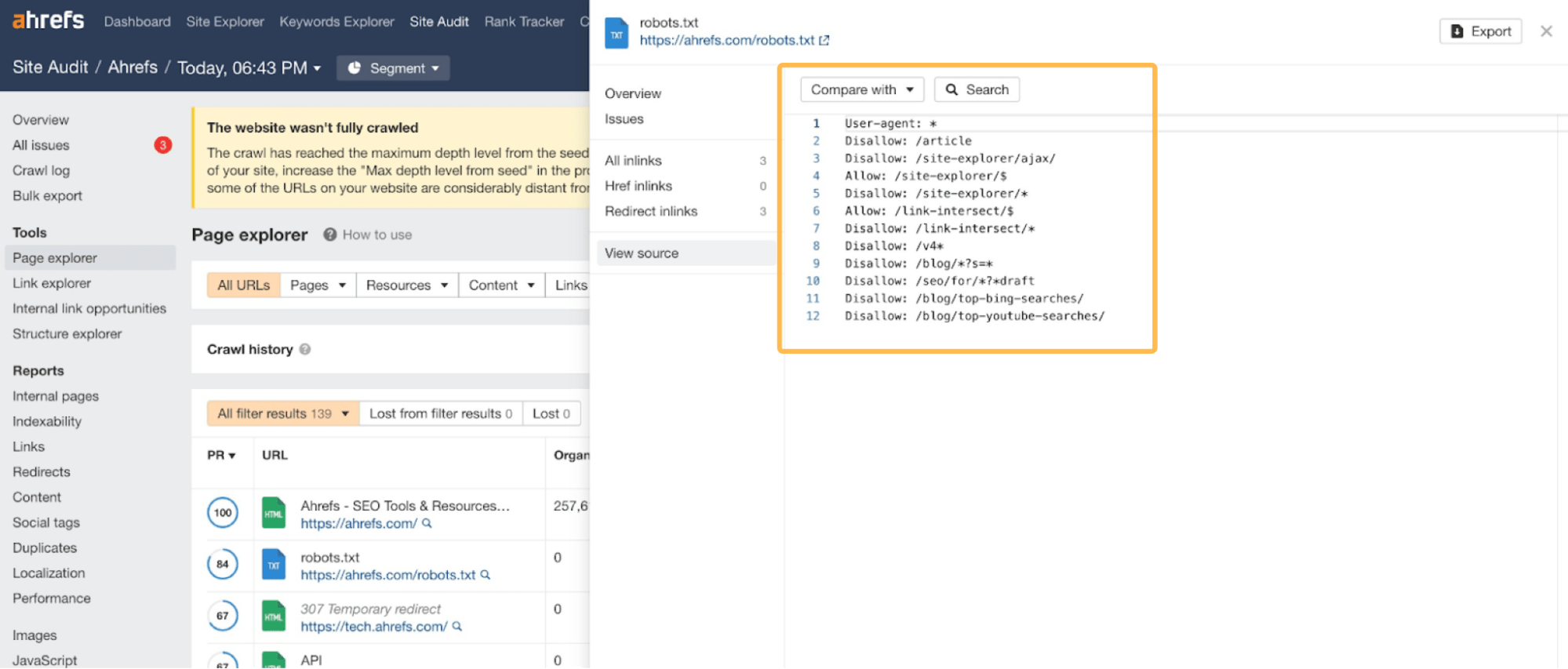
If you’ve seen a ranking drop while migrating your site, it’s worth heading to your robots.txt file to see if you are blocking the crawling of any search engine bots or essential pages of your website.
Check our robots.txt beginner’s guide to learn more.
If you’re confident your website’s technical SEO is in order, it’s worth checking to see if your competitors have outranked your website on some of its keywords.
It may sound obvious, but this is another common reason a website loses rankings. Unfortunately, sometimes your competitors are better at SEO than you are.
The quickest way to monitor a competitor’s rankings is by plugging its domain in Site Explorer and heading to the Organic keywords report.
In this example, I’ve entered Backlinko’s domain.
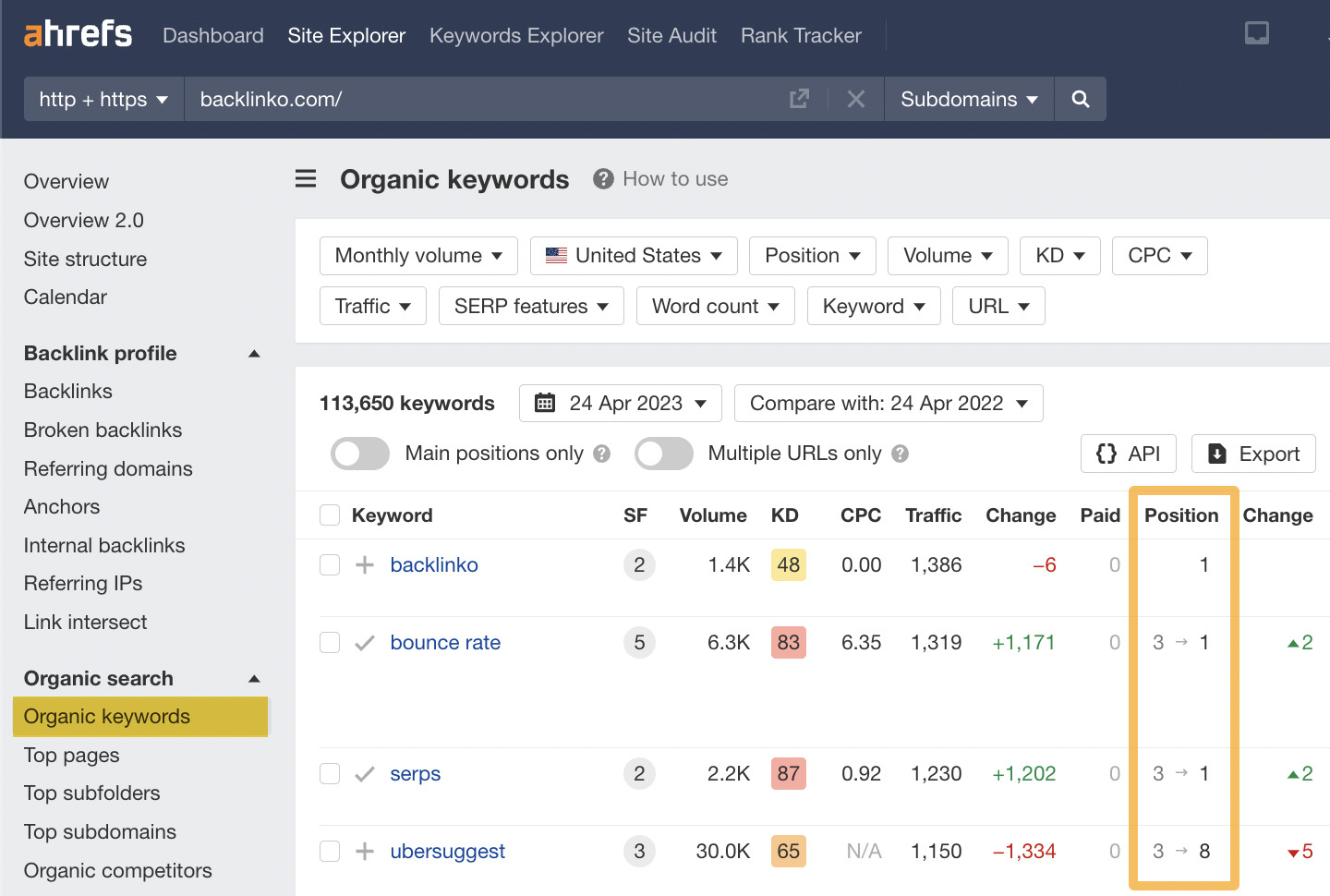
Here, you can see the rankings of your competitor’s website and performance week on week, month on month, or any other custom date comparisons.
Check your tracked keywords against theirs
Another way to check your competitors’ recent activities is with Ahrefs’ Rank Tracker.
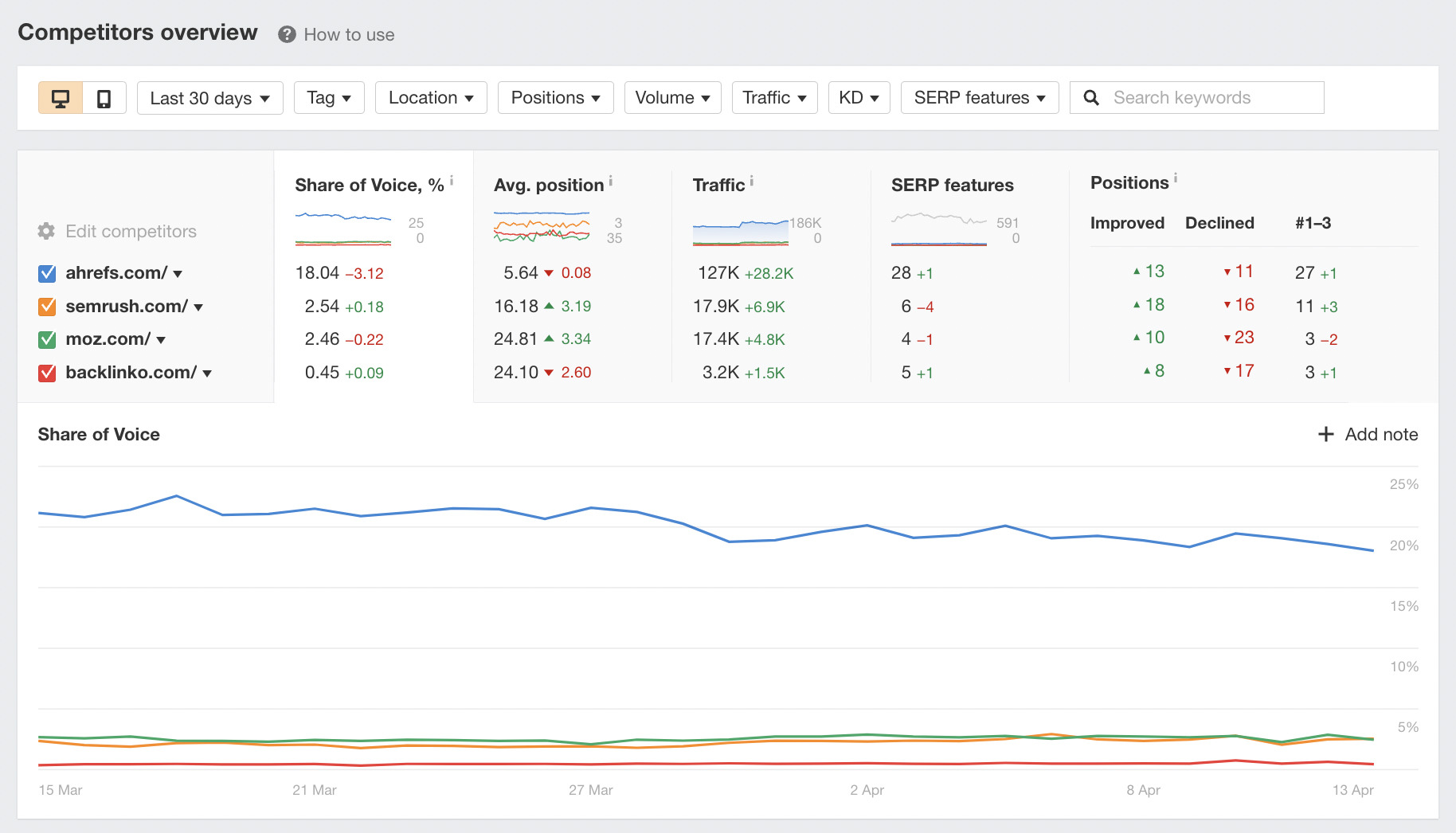
The great thing about this tool is that you can compare the rankings of your competitors and your website side by side.
Here’s an example of me looking at three different competitors’ rankings.
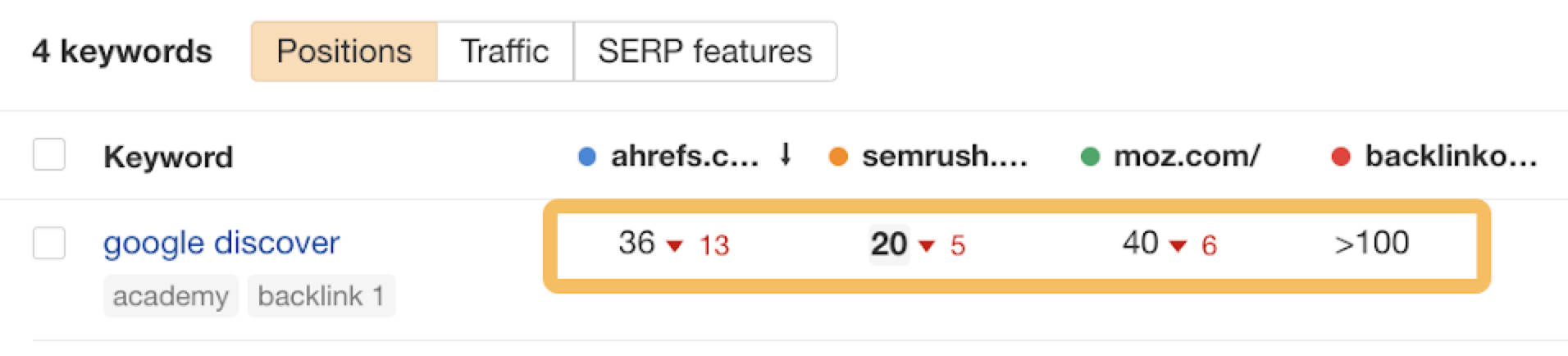
Once you’ve established that a competitor performs better than you on specific keywords, you might want to learn more about their total strategy. It’s worth checking out our guide to keyword competitor analysis to learn more about this topic.
As links are a confirmed Google ranking factor (yes, they still matter), here’s what you should check:
Check for broken links
Keeping track of all broken links to your website can be a time-consuming task. Many websites rarely check broken links that point to them.
Using Site Explorer, we can look at any website’s broken links by plugging in a domain and heading to the Broken backlinks report.
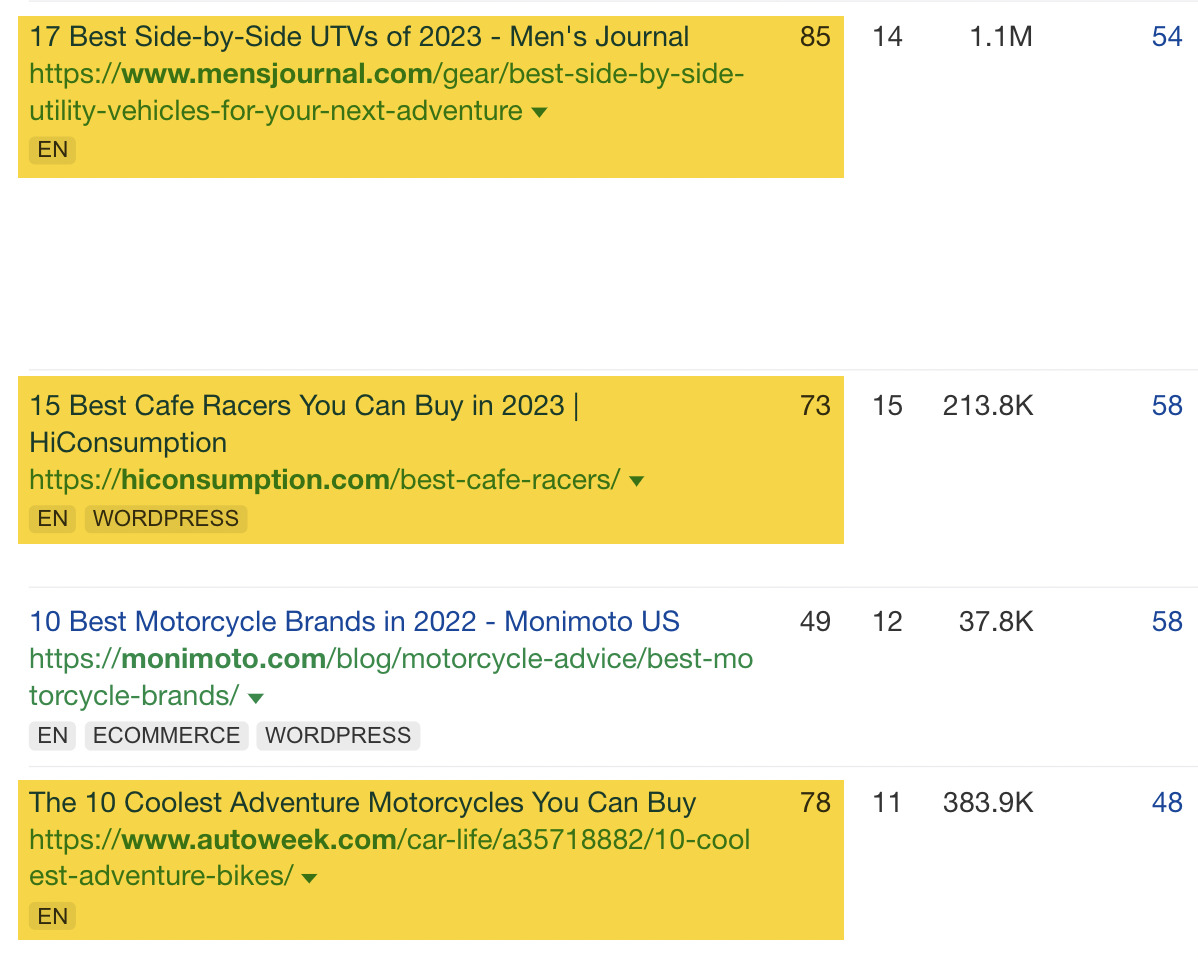
Here’s an example of the broken backlinks for the website we looked at earlier.
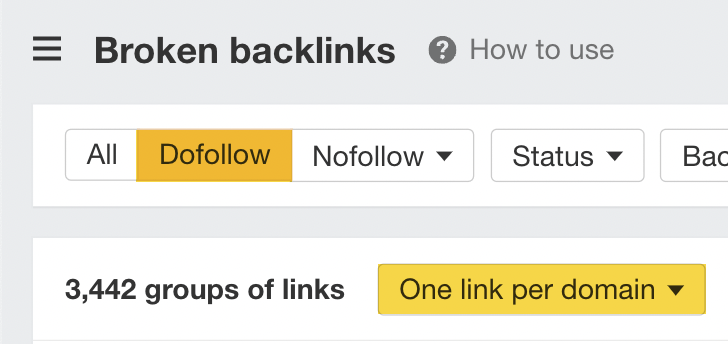
There are 3,442 groups of follow links that we can fix here.
If you can’t see anything else wrong with your site, looking at this report is an excellent place to start.
The report shows this website has lost three high Domain Rating (DR) links from high-profile sites.
Do a backlink audit (and if you need to, disavow)
Once you’ve checked your broken links, it’s a good idea to run a backlink audit on your site if you believe there is an issue with the overall quality of your website’s links.
In some instances, you may see unnatural links pointing to your site that may impact your rankings. Here are some examples of what Google may classify as “bad links”:
If you believe you have some links that negatively impact your site, you may want to consider using Google Search Console’s disavow tool.
But remember to use the disavow tool with caution:
We said multiple times that the disavow tool is a very heavy gun. And if you don’t know what you are doing, you can shoot yourself in the foot with it.
If your site has a lot of low-quality content and you lost rankings during a content-focused Google update, you’ll need to improve it.
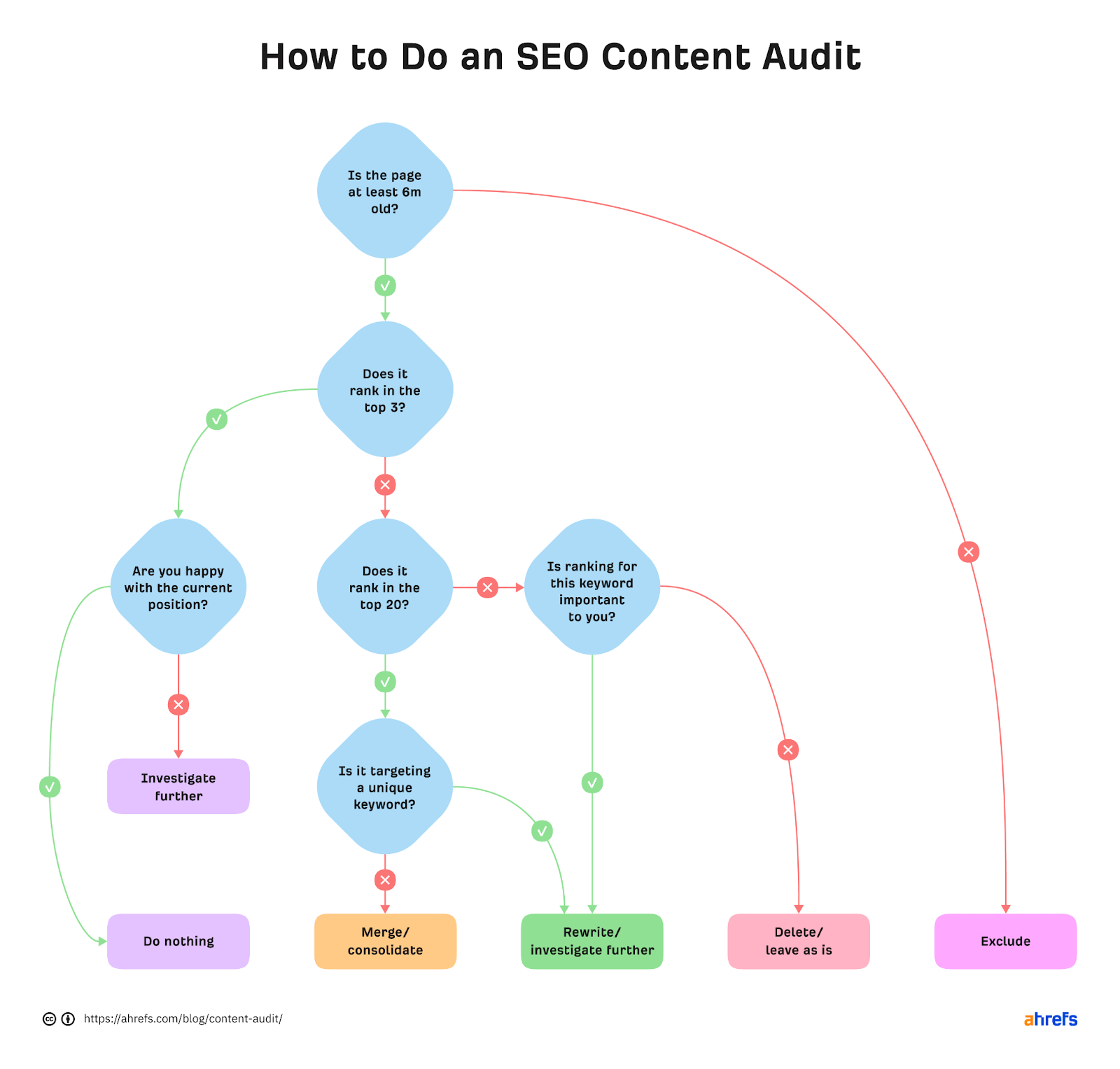
But how exactly can you improve your content? The first step is to do a content audit of your website. Here’s a visual representation of the process we use to audit content at Ahrefs.
Google also offers some self-assessment questions that you can use to further audit and improve your content:
- Does the content provide original information, reporting, research, or analysis?
- Does the content provide a substantial, complete, or comprehensive description of the topic?
- Does the content provide insightful analysis or interesting information beyond the obvious?
- If the content draws on other sources, does it avoid simply copying or rewriting those sources and instead provide substantial additional value and originality?
- Does the main heading or page title provide a descriptive, helpful summary of the content?
- Does the main heading or page title avoid exaggerating or being shocking in nature?
- Is this the sort of page you’d want to bookmark, share with a friend, or recommend?
- Would you expect to see this content in or referenced by a printed magazine, encyclopedia, or book?
- Does the content provide substantial value when compared to other pages in search results?
Although there is no guarantee that improving content will immediately impact your rankings, ensuring your content is the best for your visitors is a good idea.
Google SERPs are constantly changing. And yes, it’s another factor that can impact rankings and organic traffic to your site—one that you have little control over.
To explain this concept, let’s look at a historical example of a dramatic SERP intent shift by plugging the keyword “corona” into Keywords Explorer.
We’ll set the date to March 31, 2020, and compare it to the SERP pre-pandemic on January 3, 2020.
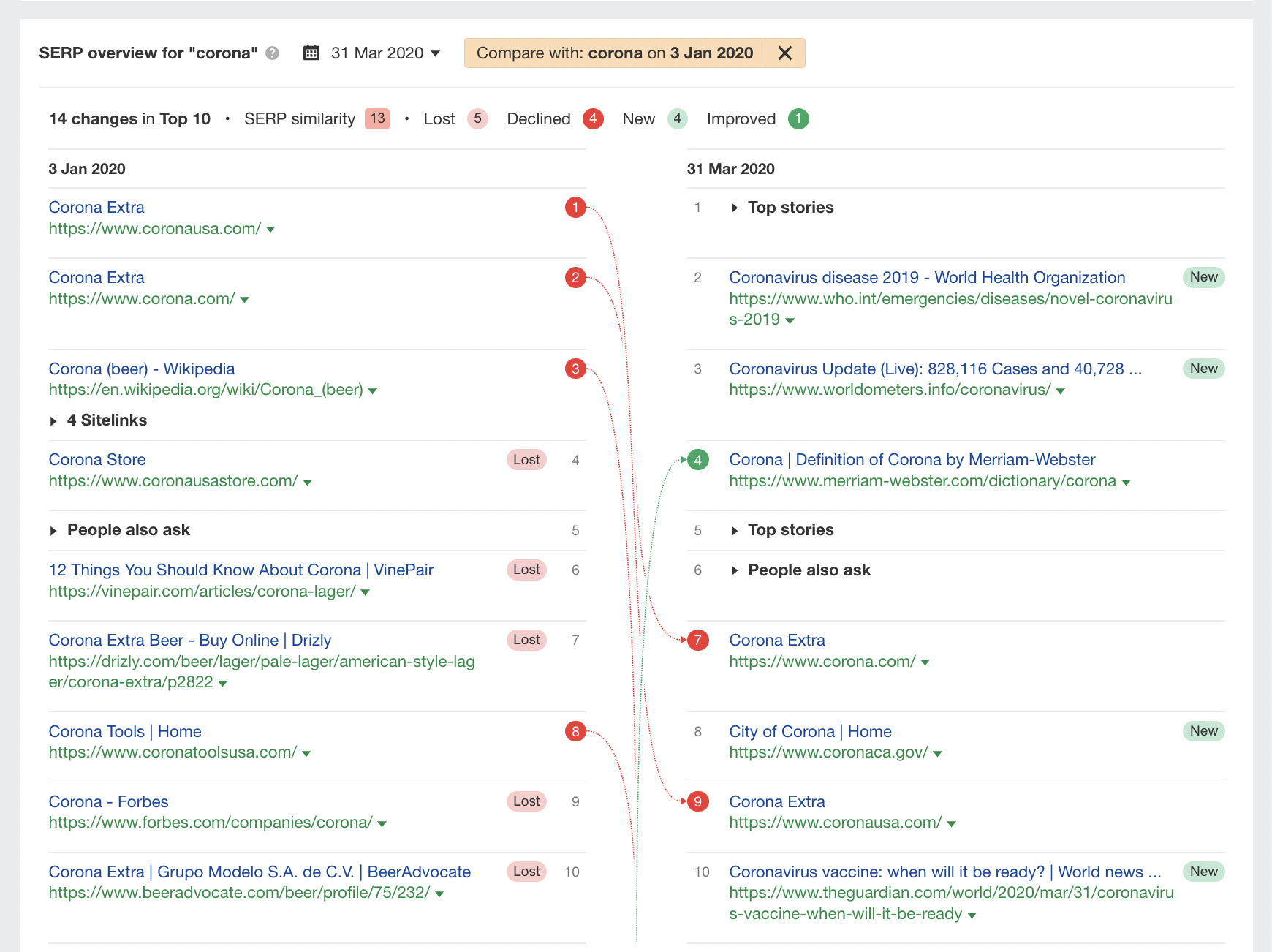
In this example, we can see Corona beer–related websites on the left-hand side were displaced by websites covering COVID-19 and “Top stories” in the space of a few months.
If we set the date to something more recent, we can see that Corona, the beer, has regained its number #1 position. Why? Well, the search intent has reverted.
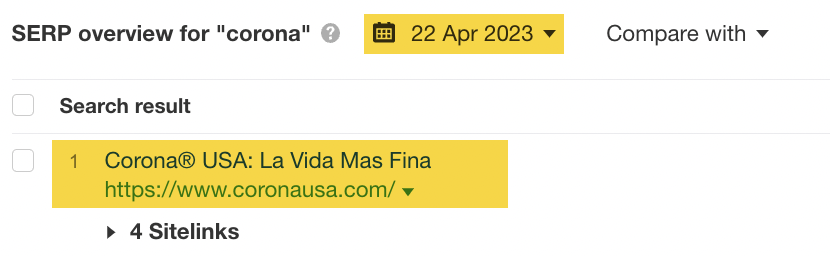
If you think a SERP intent shift may have impacted your website, then it’s worth using the “SERP overview” tool in Keywords Explorer to see how the historical SERP has changed.
If your website has lost all organic search traffic, you should check Google Search Console’s “Manual actions” report.
To do this, click on the tab on the left-hand side:

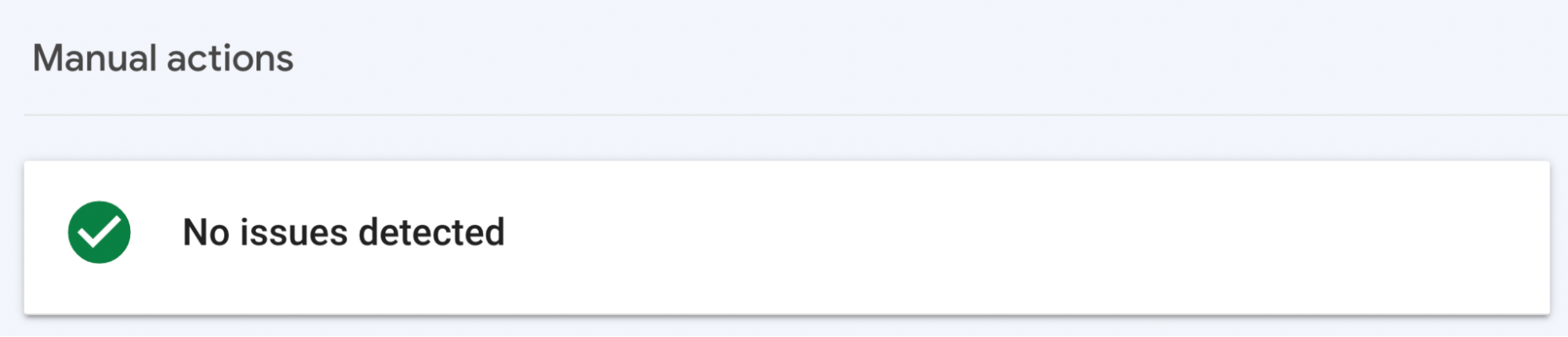
If there’s no issue, you’ll see a “No issues detected” notice in Google Search Console that looks like this:
If there is a problem, it will look similar to this. This is a “Pure spam” manual action.
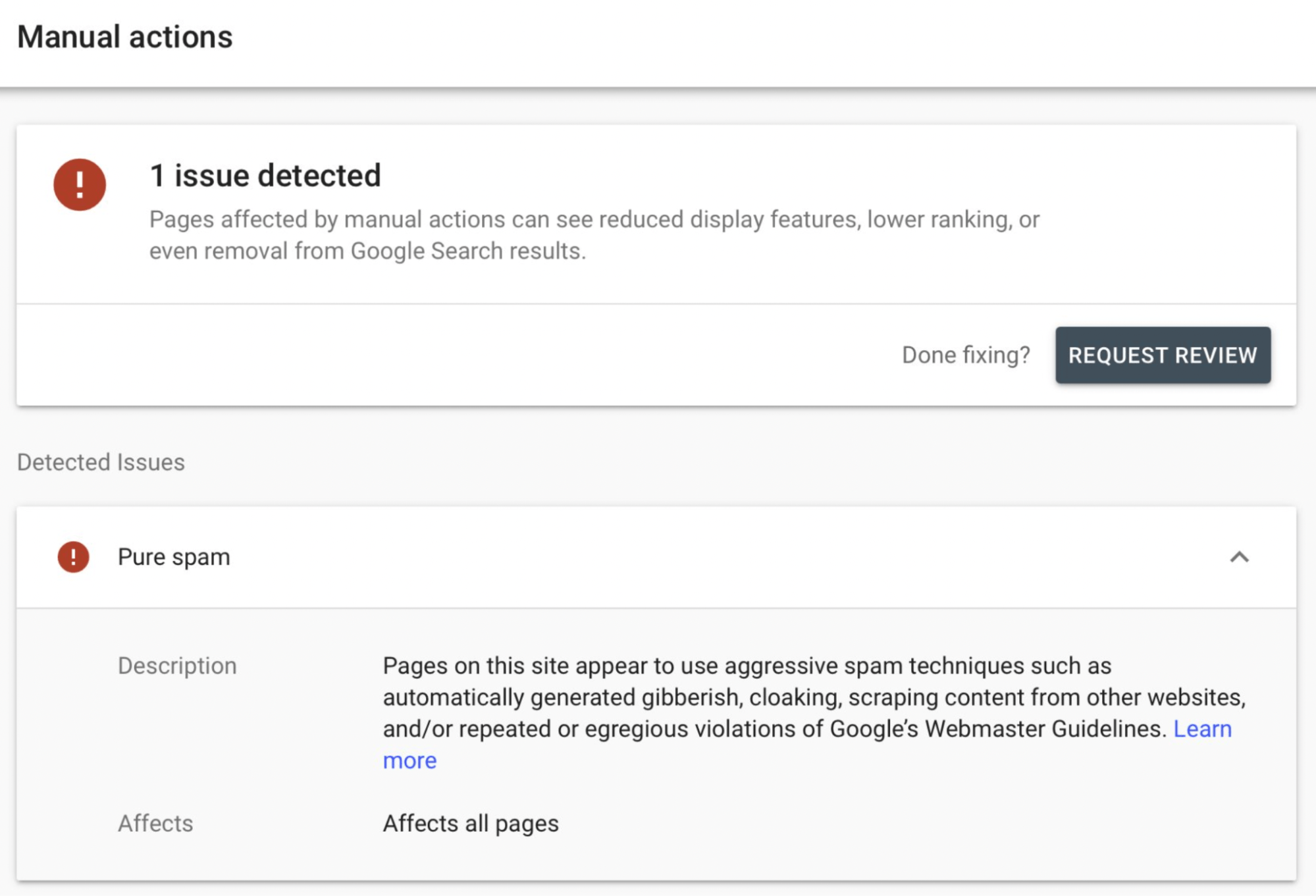
If your site gets a manual action, a human reviewer at Google believes you have violated the search quality guidelines severely. Google will then generally remove your website and its pages from the search index.
Here’s a list of the different types of manual actions you can receive:
- Site abused with third-party spam
- User-generated spam
- Spammy free host
- Structured data issue
- Unnatural links to your site
- Unnatural links from your site
- Thin content with little or no added value
- Cloaking and/or sneaky redirects
- Pure spam
- Cloaked images
- Hidden text and/or keyword stuffing
- AMP content mismatch
- Sneaky mobile redirects
- News and Discover policy violations
Guidance from Google on how to fix these types of issues can be found here.
It’s usually rare to receive a manual action, but it’s not unheard of. To stay on the right side of Google, remember to take our SEO training course and follow the Google Search Essentials.
Final thoughts
It’s never easy working out why your website’s rankings have dropped dramatically. It involves investigating, analyzing, and finding data you can rely on to make decisions.
Tools like Ahrefs can help, as they enable you to look behind the curtain to see what’s going on.
Got more questions? Ping me on Twitter. 🙂

