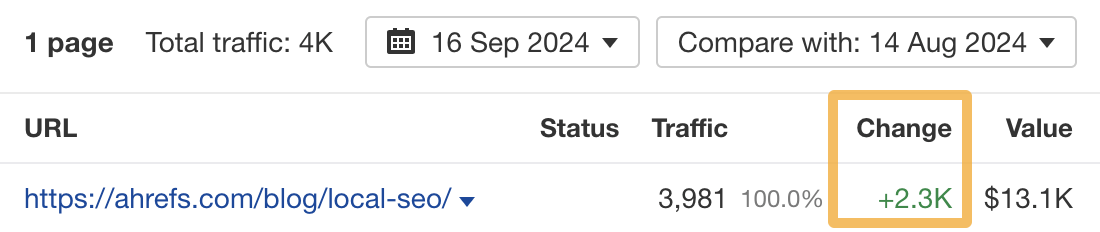
A few weeks ago, I optimized one of my blog posts for related keywords. Today, it gets an estimated 2,300 more monthly organic visits:
In this post, I’ll show you how I found and optimized my post for these related keywords.
Related keywords are words and phrases closely linked to your main keyword. There are many ways to find them. You can even just ask ChatGPT.

But here’s the thing: These keywords aren’t useful for optimizing content.
If more traffic is your goal, you need to find keywords that represent subtopics—not just any related ones.
Think of it like this: you improve a recipe by adding the right ingredients, not everything in your fridge!

Below are two methods for finding the right related keywords (including the one I used):
Method 1. Use content optimization tools
Content optimization tools look for keywords on other top-ranking pages but not yours. They usually then recommend adding these keywords to your content a certain number of times.
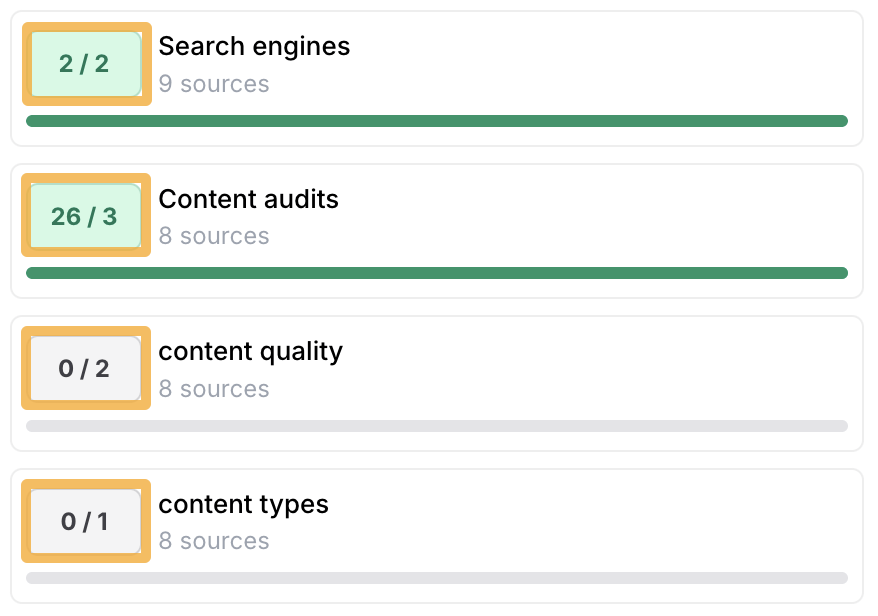

These tools can be useful if you take their recommendations with a pinch of salt, as some of them can lead you astray.
For example, this tool recommends that I add six mentions of the phrase “favorite features” to our keyword research guide.
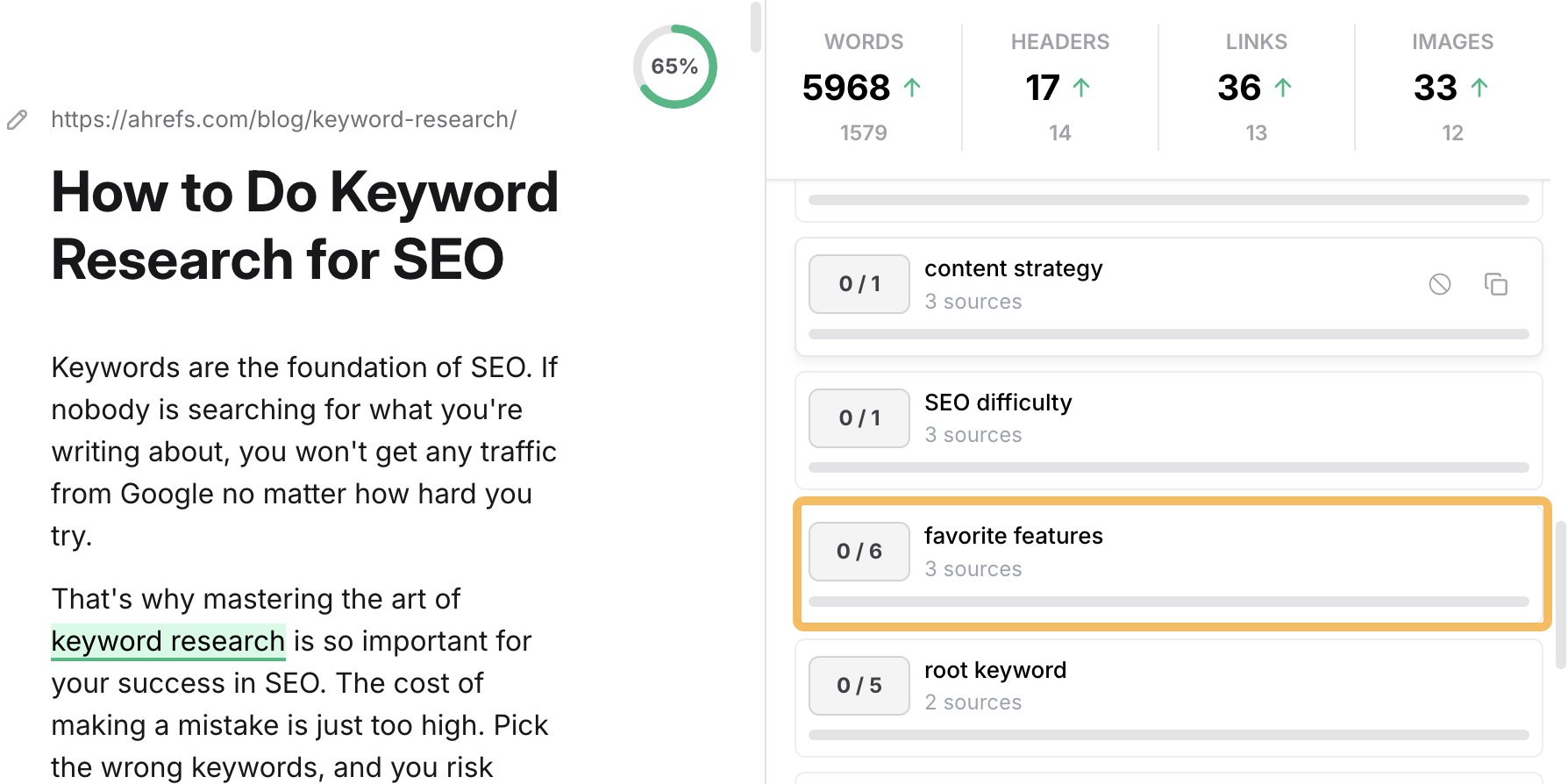

Does that seem like an important related keyword to you? It certainly doesn’t to me!
They also usually have a content score that increases as you add the recommended related keywords. This can trick you into believing that something is important when it probably isn’t—especially as content scores have a weak correlation with rankings.
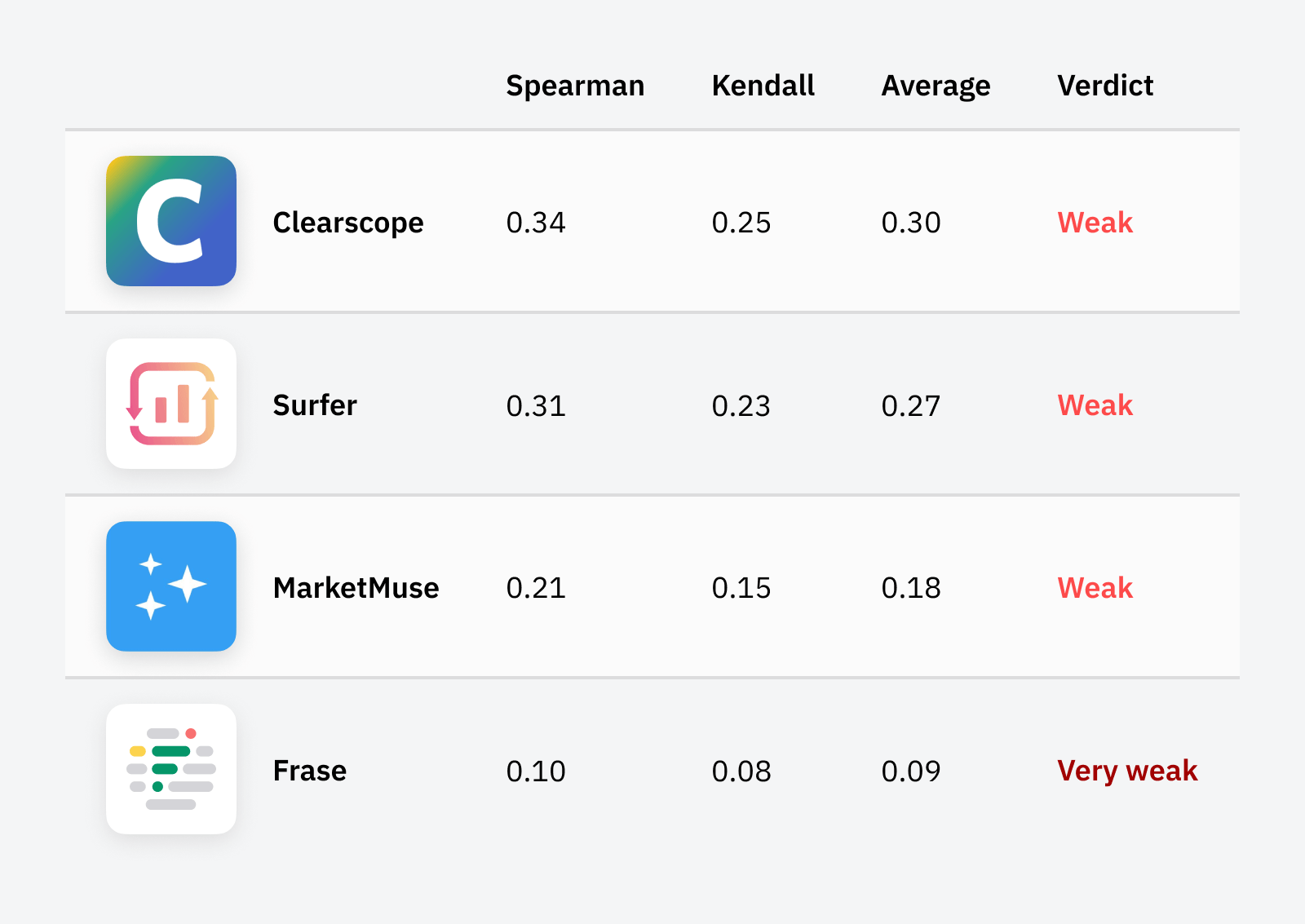

My advice? If you’re going to use these tools, apply common sense and look for recommendations that seem to represent important subtopics.
For example, when I analyze our content audit guide, it suggests adding quite a few keywords related to content quality.
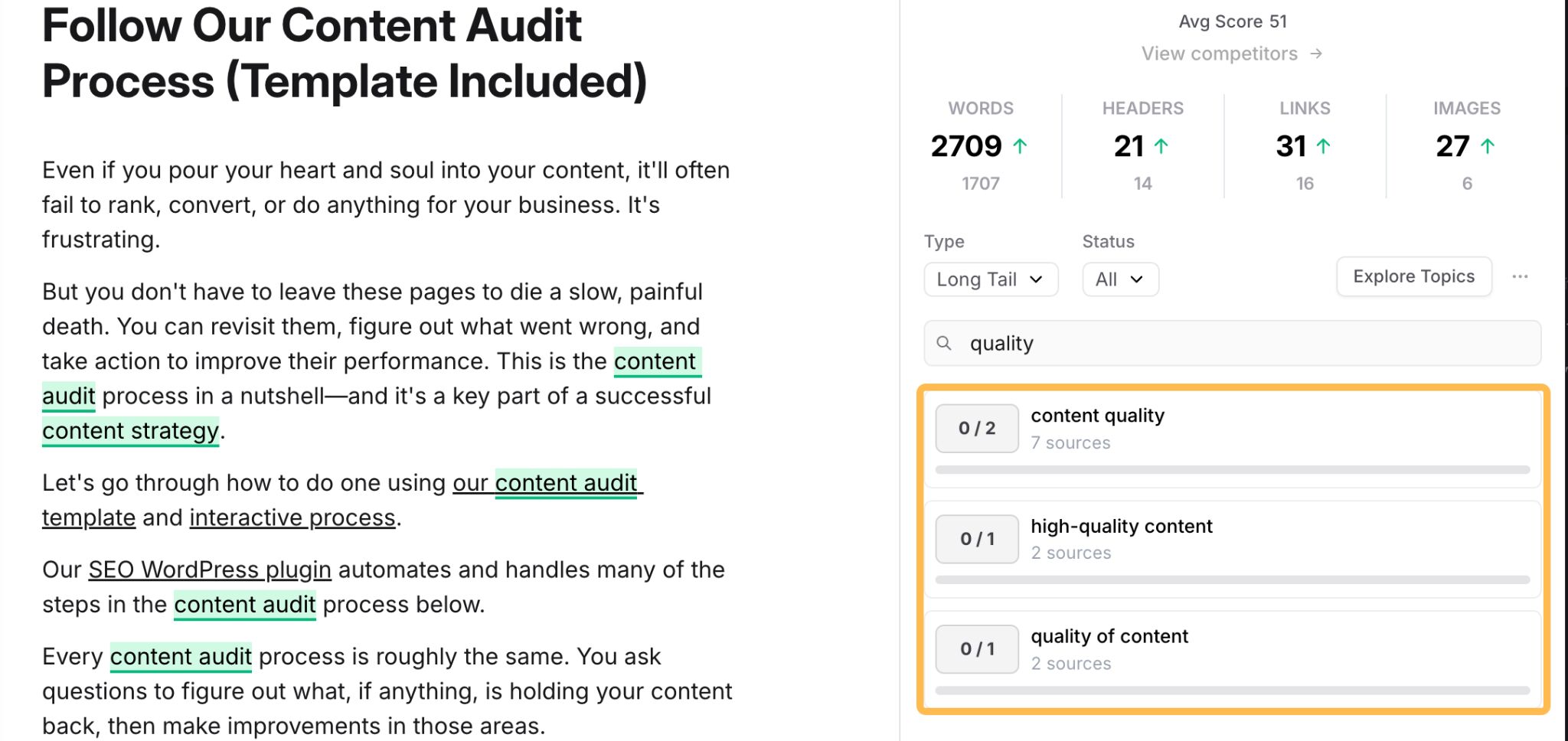

It doesn’t take a genius to work out that this is an extremely important consideration for a content audit—yet our guide mentions nothing about it.


This is a huge oversight and definitely a batch of related keywords worth optimizing for.
Try the beta version of our new AI Content Helper!
Instead of counting terms that you need to include in your content, Content Helper uses AI to identify the core topics for your target keywords and scores your content (as well as your competitors) against those topics as you write it. In effect, it groups related keywords by subtopic, making it easier to optimize for the broader picture.
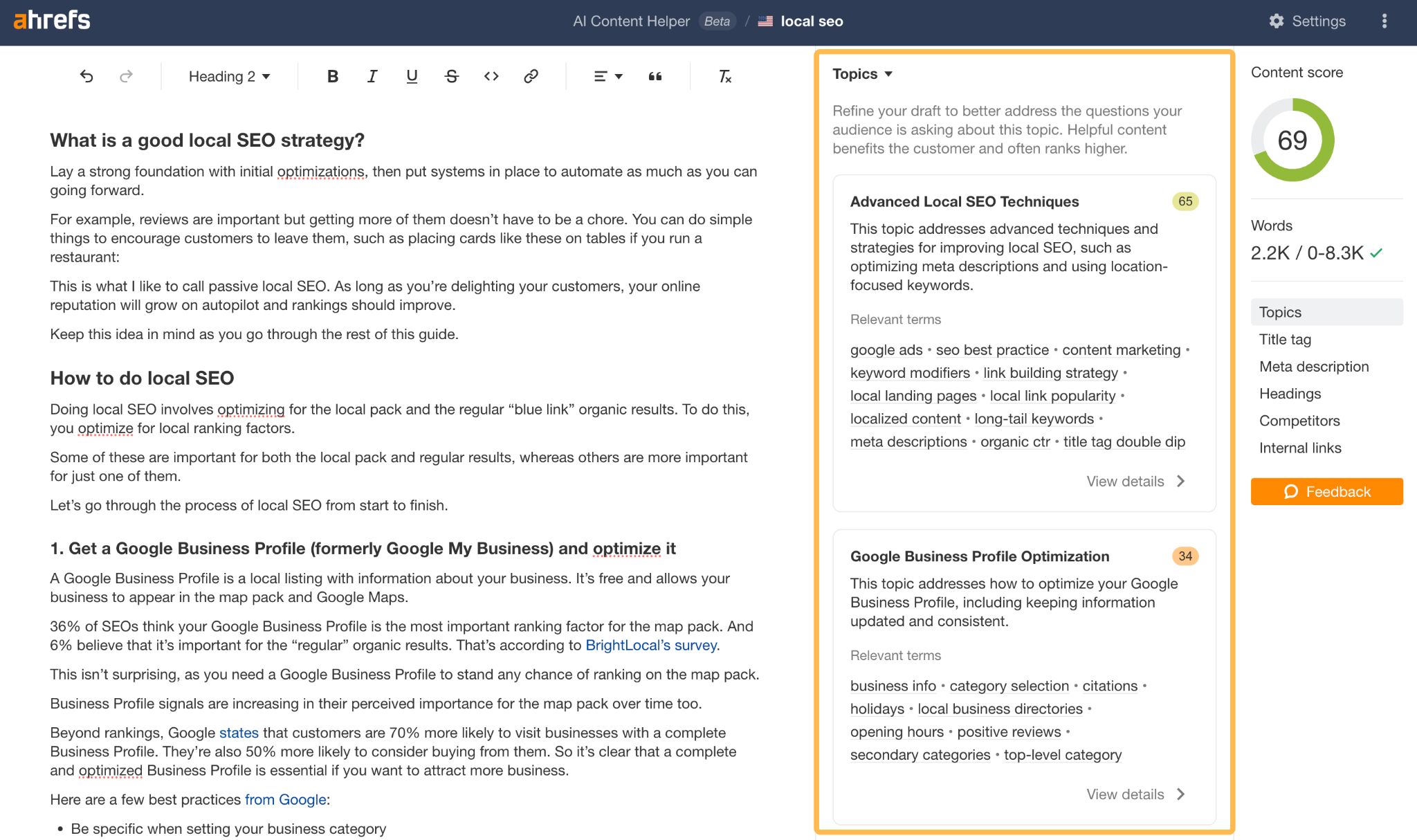

For example, it looks like my post doesn’t cover Google Business Profile optimization too well. This is something it might be worth going into more detail about.


Method 2. Do a keyword gap analysis (this is the method I used!)
Keyword gaps are when competitors rank for keywords you don’t. If you do this analysis at the page level, it’ll uncover related keywords—some of which will usually represent subtopics.
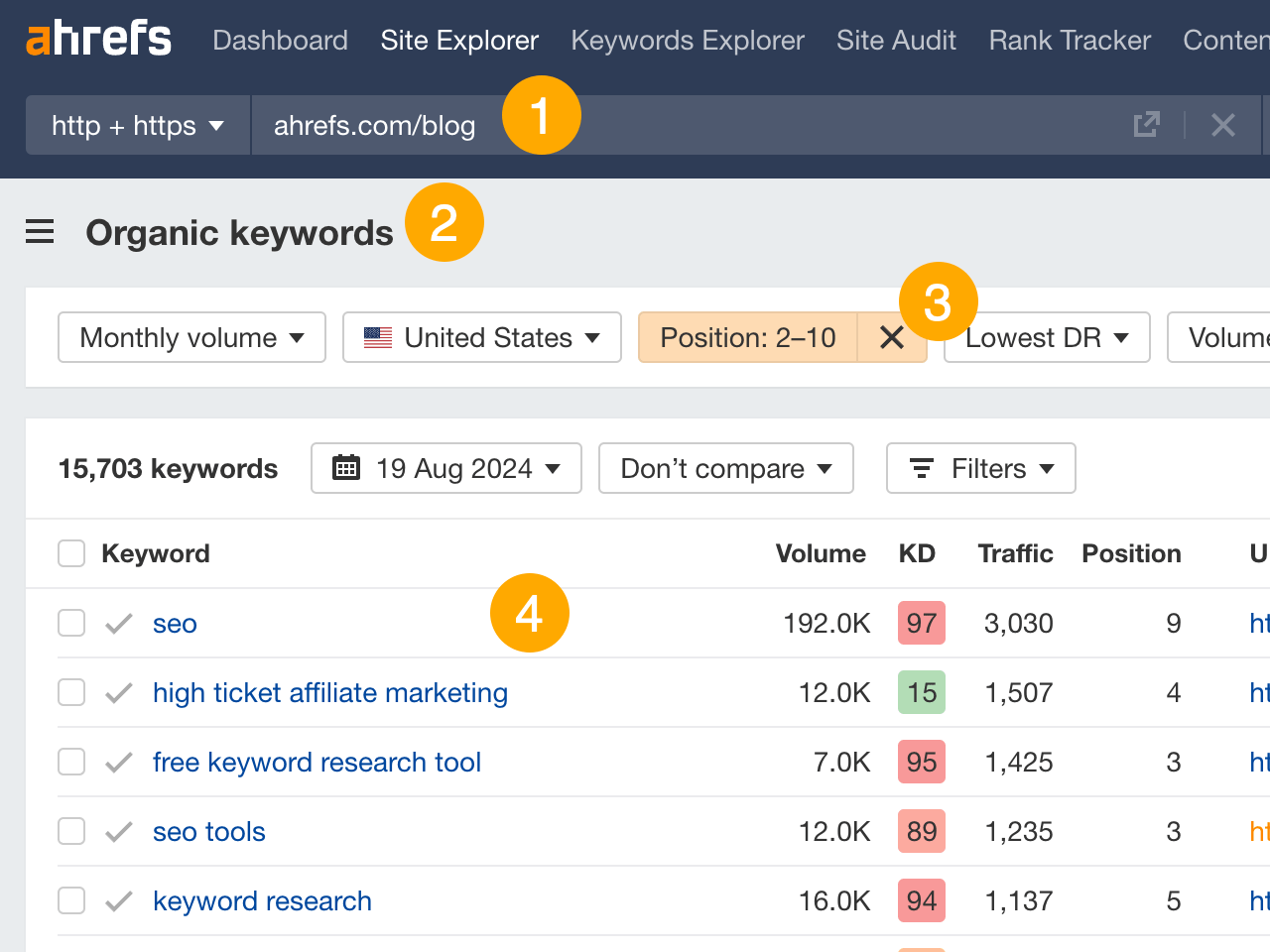
If possible, I recommend doing this for pages that already rank on the first page for their main target keyword. These pages are doing well already and likely just need a bit of a push to rank high and for more related keywords. You can find these in Site Explorer:
- Enter your domain
- Go to the Organic Keywords report
- Filter for positions 2-10
- Look for the main keywords you’re targeting

Once you have a few contenders, here’s how to do a keyword gap analysis:
a) Find competitors who are beating you
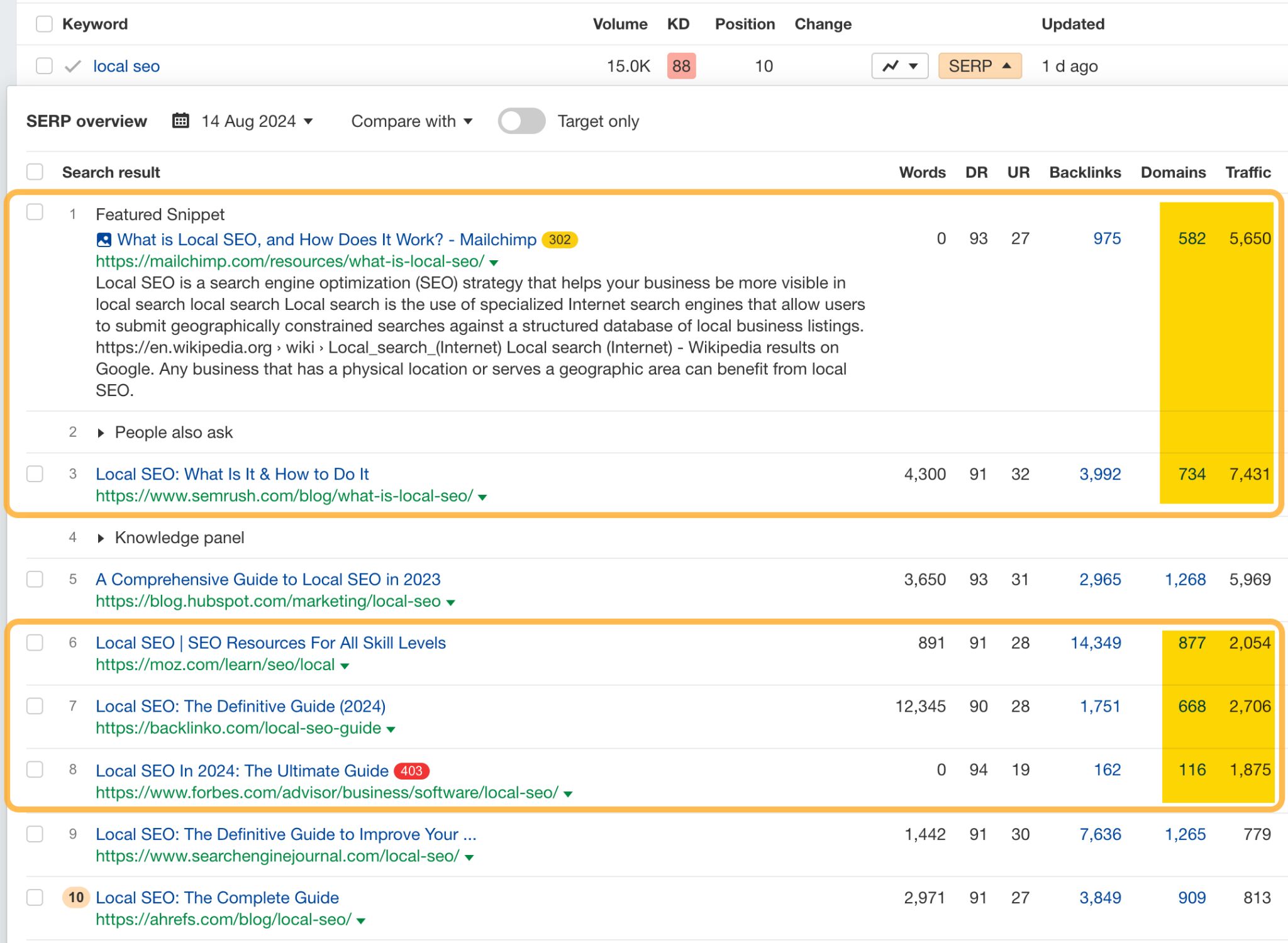
In the Organic Keywords report, hit the SERP dropdown next to the keyword to see the current top-ranking pages. Look for similar pages that are getting more traffic than yours and have fewer referring domains.
For example, our page ranks #10 for “local SEO,” has 909 referring domains, and gets an estimated 813 monthly visits:
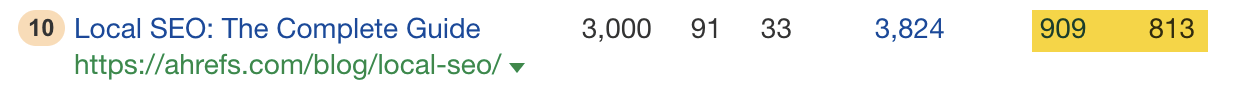
All of these competing pages get more traffic with fewer backlinks:

Sidenote.
I’m going to exclude the page from Moz going forward as it’s a blog category page. That’s very different to ours so it’s probably not worth including in our analysis.
b) Send them to the content gap tool
Hit the check boxes next to your competitors, then click “Open In” and choose Content gap.
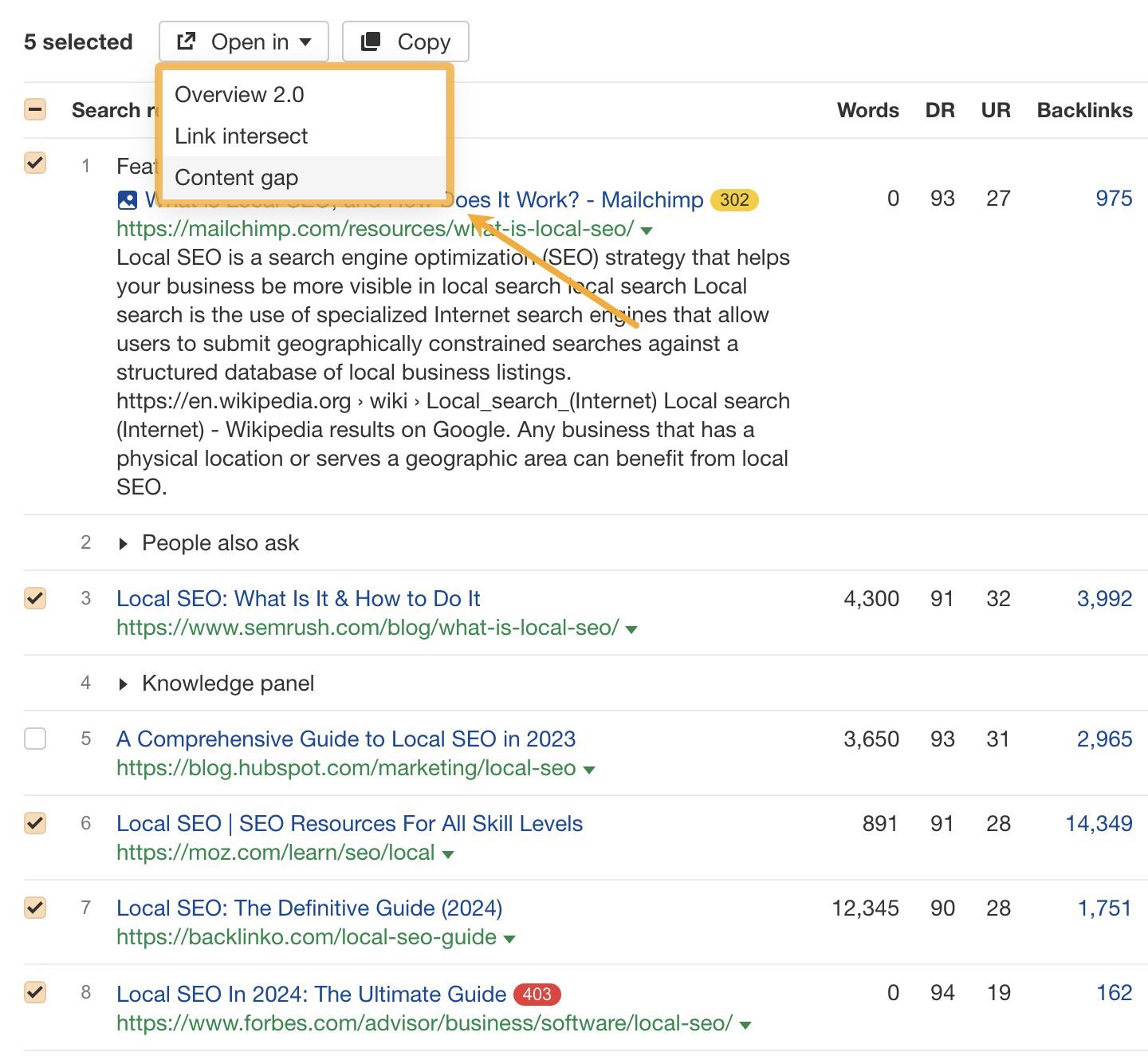

By default, this will show you keywords where one or more competitors rank in the top 10, but you don’t rank anywhere in the top 100.
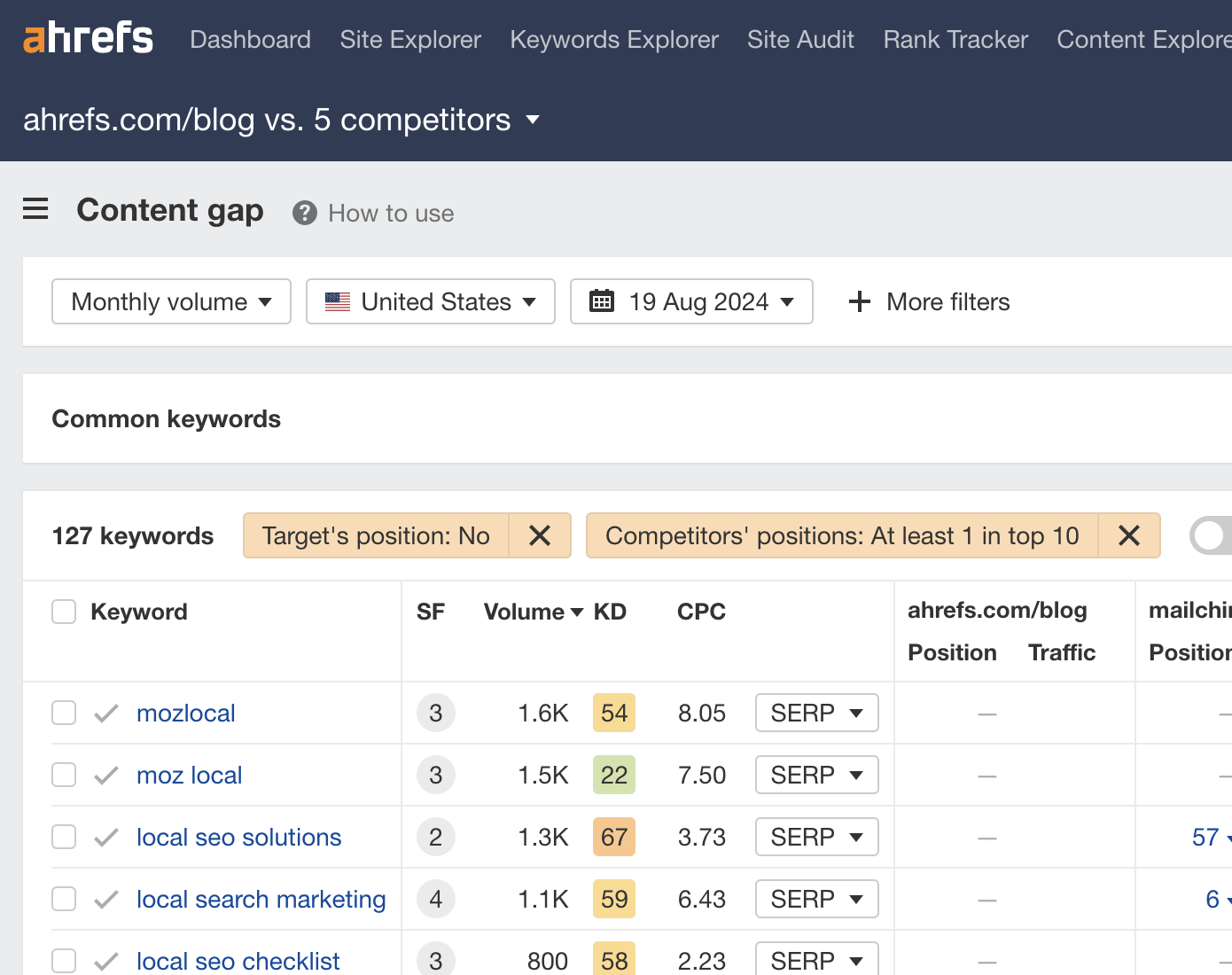

I recommend changing this so it shows all keywords competitors rank for, even if you also rank for them. This is because you may still be able to better optimize for related keywords you already rank for.
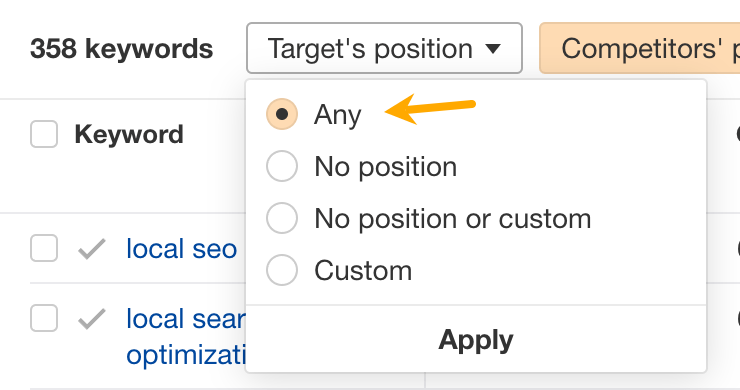

I also recommend turning the “Main results only” filter on to exclude rankings in sitelinks and other SERP features:
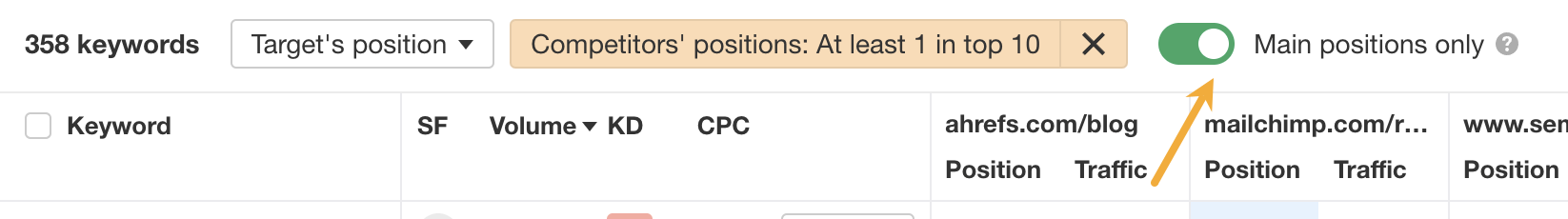

c) Look for related keywords worth optimizing for
This is where common sense comes into play. Your task is to scan the list for related keywords that could represent important subtopics.
For example, keywords like these aren’t particularly useful because they’re just different ways of searching for the main topic of local SEO:
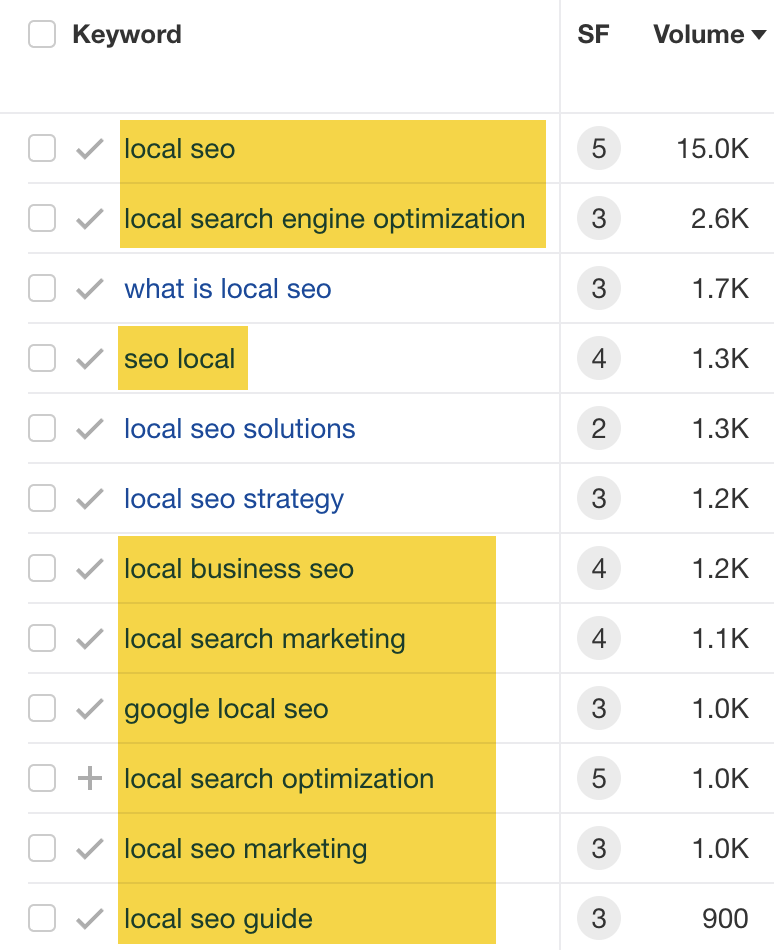

But a related keyword like “what is local SEO” is useful because it represents a subtopic searchers are looking for:
If this process feels too much like trying to find a needle in a haystack, try exporting the full list of keywords, pasting them into Keywords Explorer, and going to the “Cluster by terms” report. As the name suggests, this groups keywords into clusters by common terms:
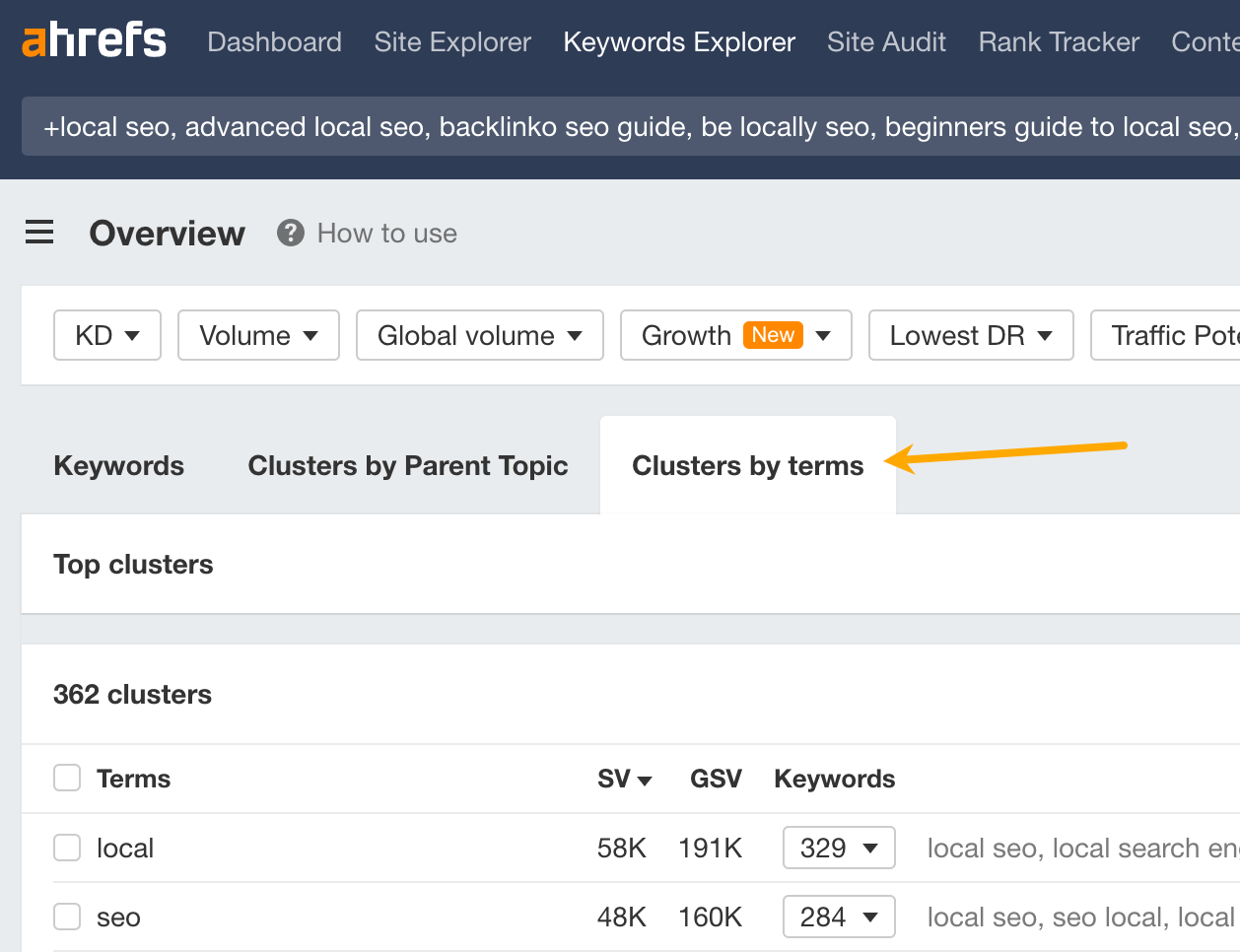

This is useful because it can highlight common themes among related keywords and helps you to spot broader gaps.
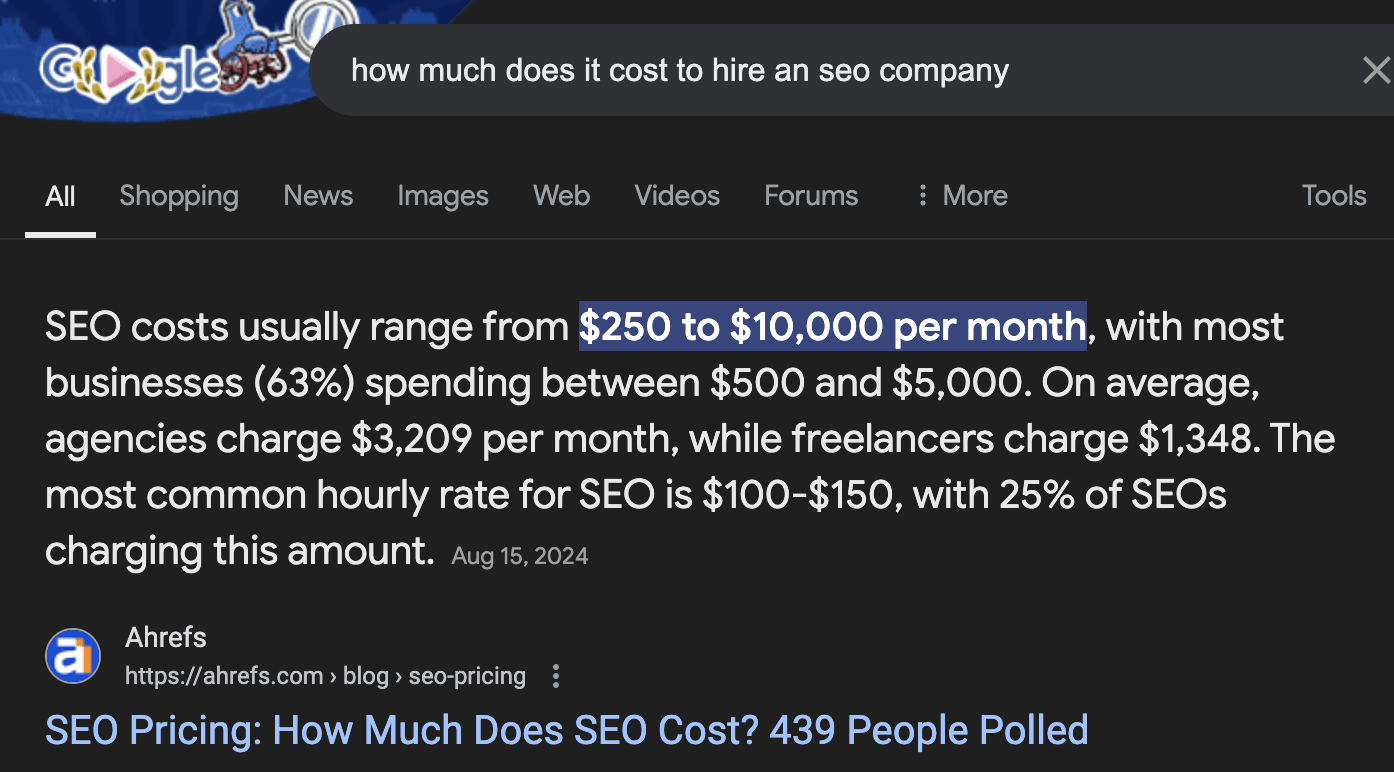
For example, when I was looking for related keywords for our SEO pricing guide (more on this later!), I saw 17 related keywords containing the term “month”:
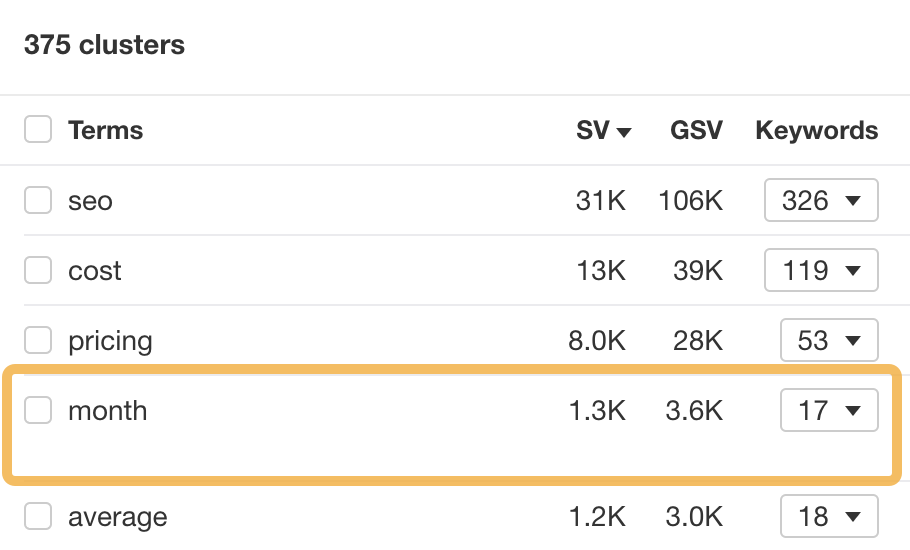

Upon checking the keywords, I noticed that they’re all ways of searching for how much SEO costs per month:
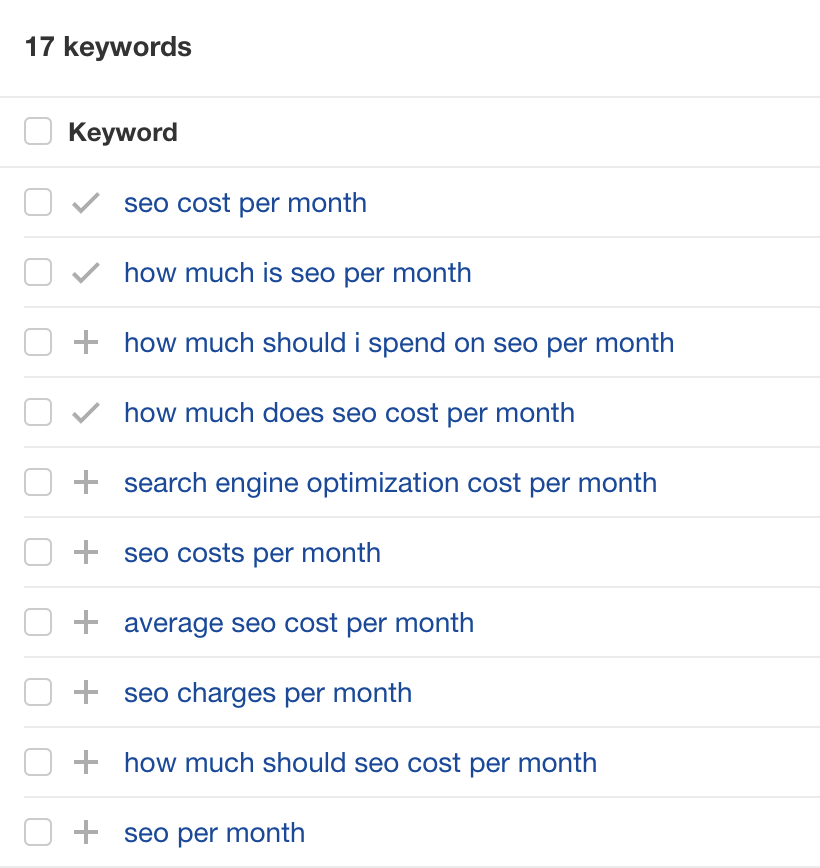

This is an easy batch of related keywords to optimize for. All I need to do is answer that question in the post.
If you’re still struggling to spot good related keywords, look for ones sending competing pages way more traffic than you. This usually happens because competitors’ pages are better optimized for those terms.
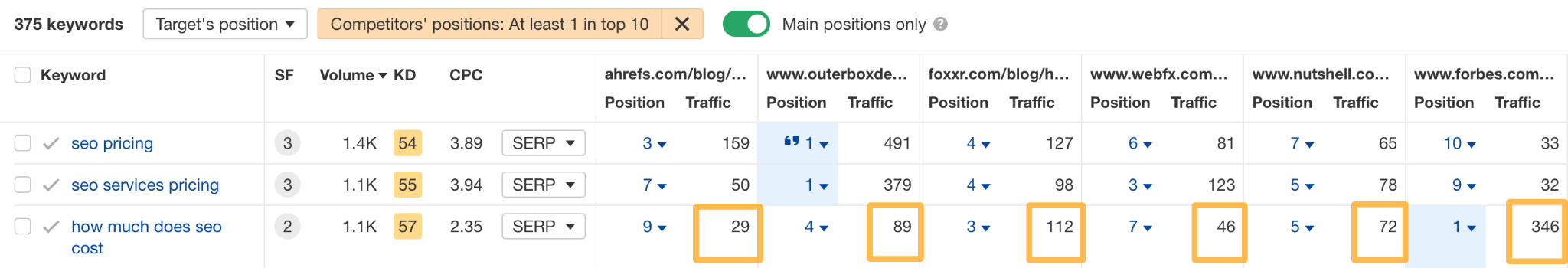
You can spot these in the content gap report by comparing the traffic columns.
For example, every competing page is getting more traffic than us for the keyword “how much does SEO cost”—and Forbes is getting over 300 more visits!

Now you have a bunch of related keywords, what should you do with them?
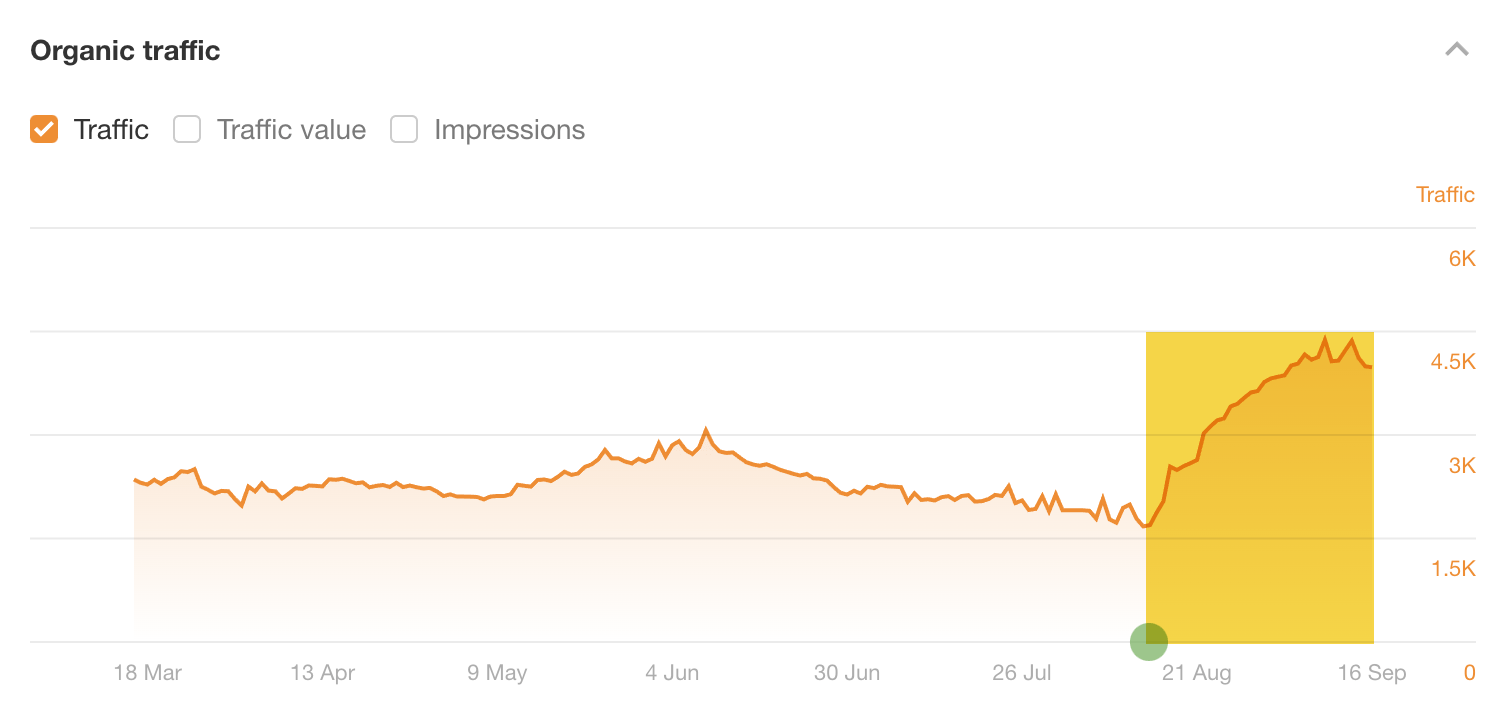
This is a nuanced process, so I’m going to show you exactly how I did it for our local SEO guide. Its estimated organic traffic grew by 135% after my optimizations for related keywords:

Sidenote.
Google kindly rolled out a Core update the day after I did these optimizations, so there’s always a chance the traffic increase is unrelated. That said, traffic to our blog as a whole stayed pretty consistent after the update, while this post’s traffic grew massively. I’m pretty sure the related keyword optimization is what caused this.
Here are the related keywords I optimized it for and how:
Related keyword 1: “What is local SEO”
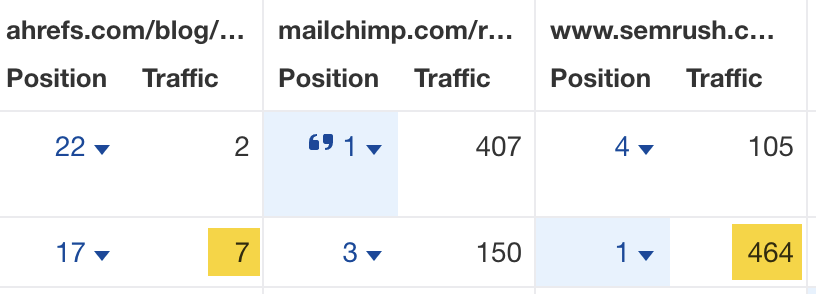
Every competing page was getting significantly more traffic than us for this keyword (and ranking significantly higher). One page was even getting an estimated 457 more visits than ours per month:

People were also searching for this in a bunch of different ways:
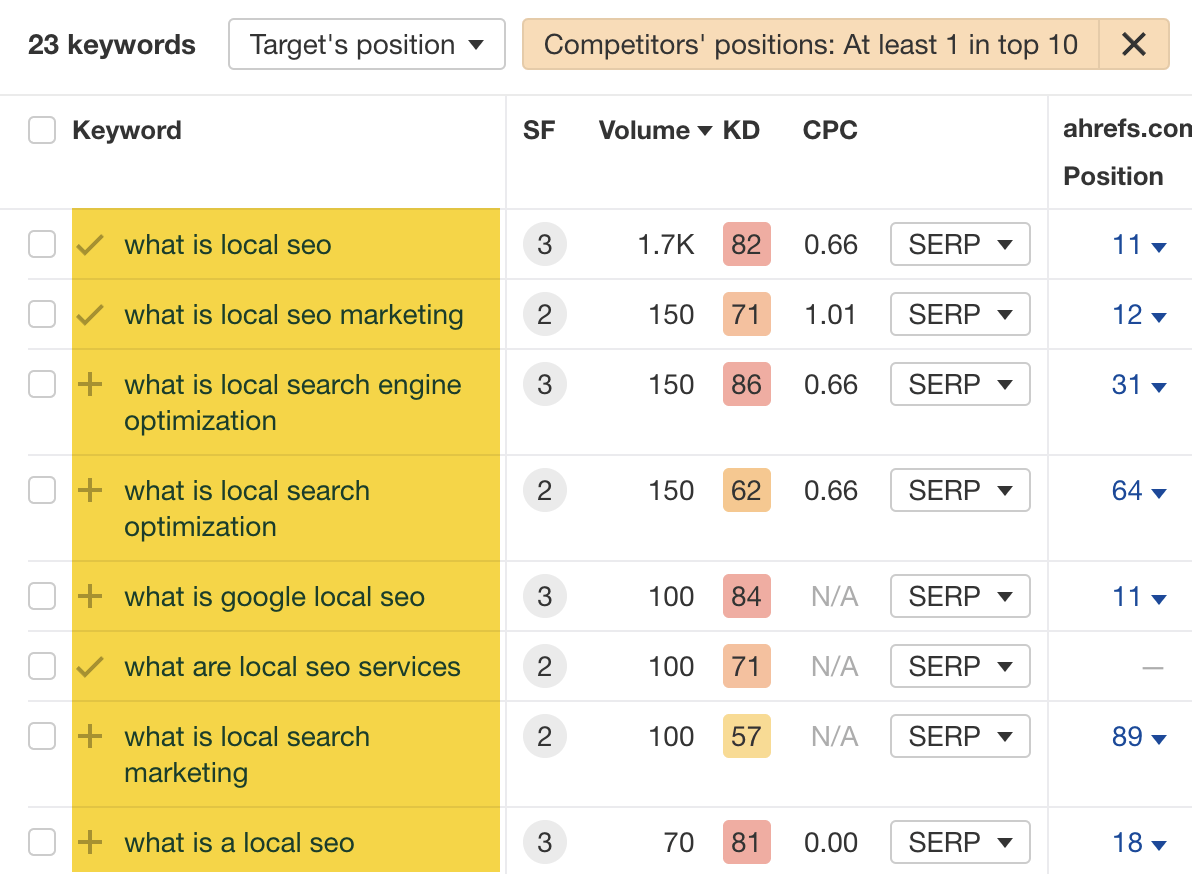

My theory on why we weren’t performing well for this? Although we did have a definition on the page, it wasn’t great. It was also buried under a H3 with a lot of fluff to read before you get to it.
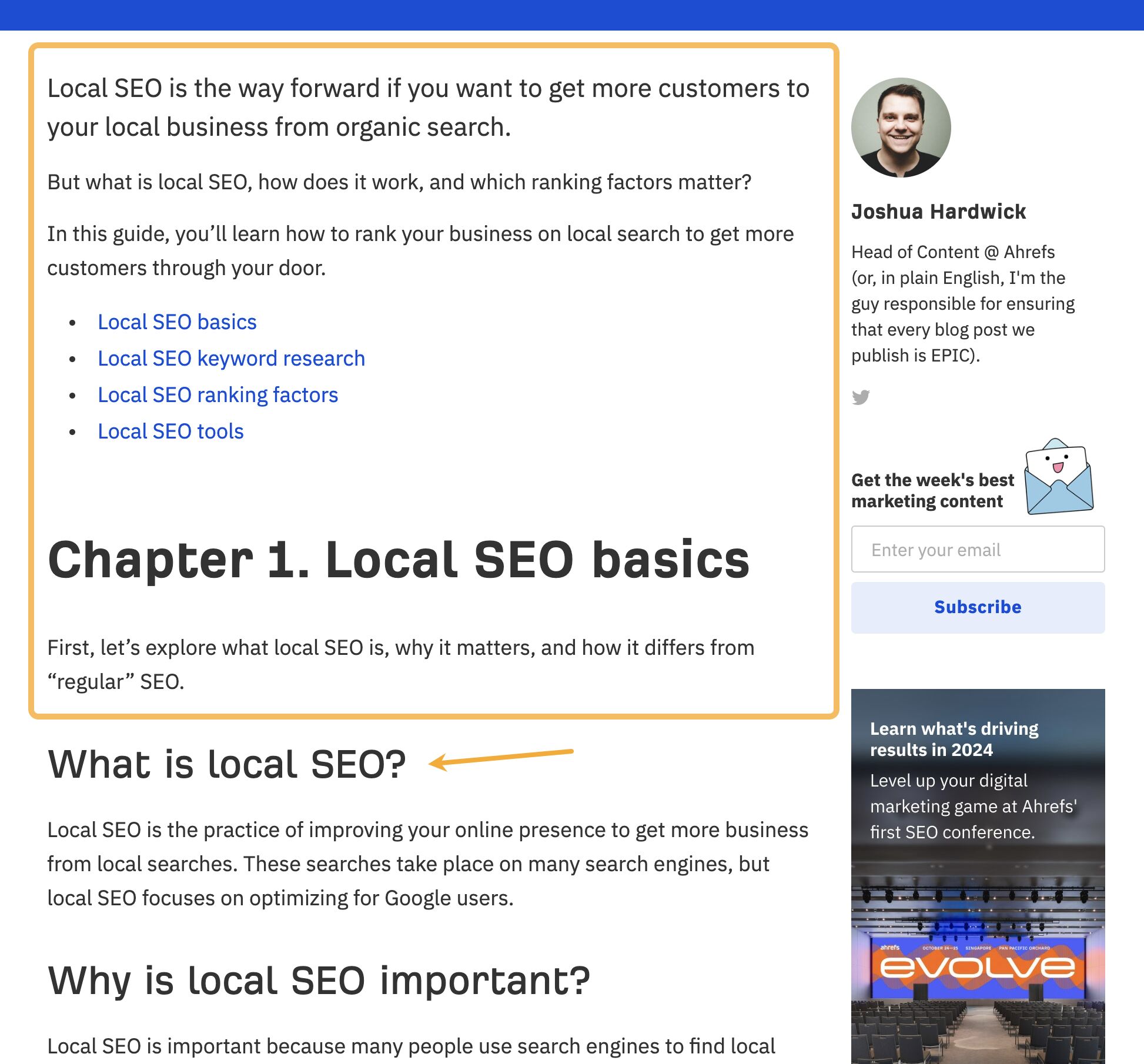

I tried to solve this by getting rid of the fluff, improving the definition (with a little help from ChatGPT), and moving it under a H2.


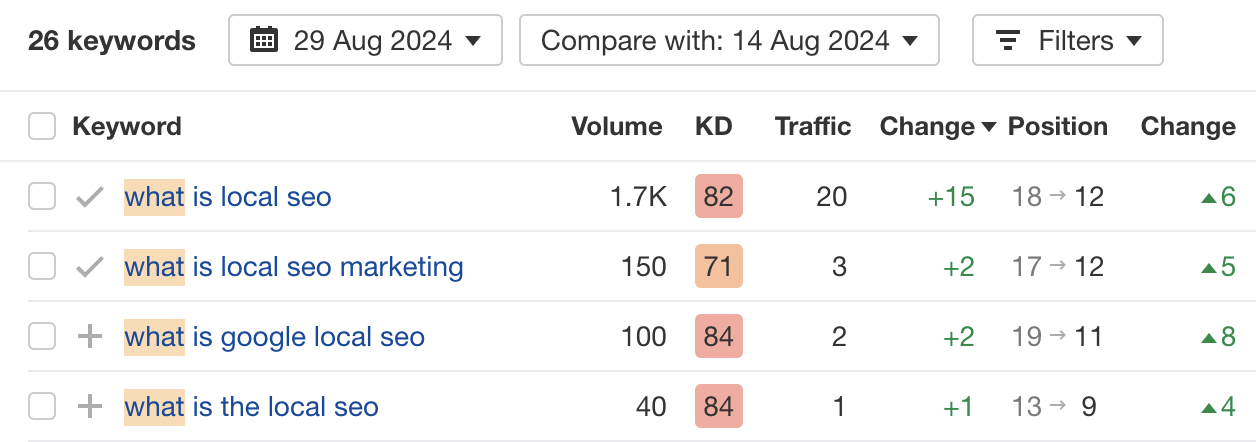
Result? The page jumped multiple positions for the keyword “what is local SEO” and a few other similar related keywords:

Related keyword 2: Local SEO strategy
Once again, all competing pages were getting more traffic than ours from this keyword.
I feel like the issue here may be that there’s no mention of “strategy” in our post, whereas competitors mention it multiple times.


To solve this, I added a short section about local SEO strategy.


I also asked ChatGPT to add “strategy” to the definition of local SEO. (I’m probably clutching at straws with this one, but it reads nicely with the addition, so… why not?)
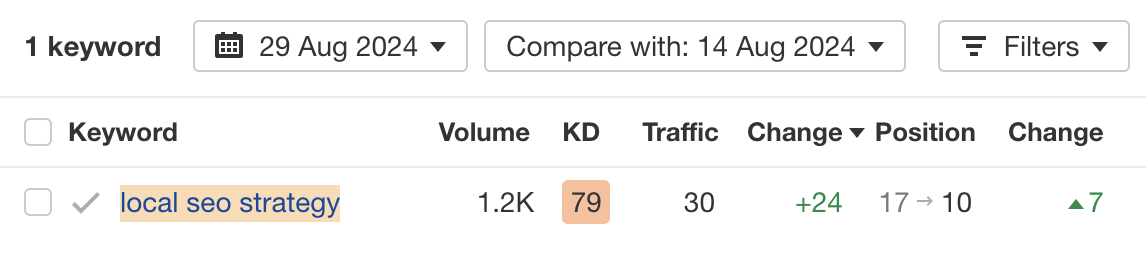
Result? The page jumped seven positions from the bottom of page two to page one for the related keyword:

Related keyword 3: “How to do local SEO”
Most of the competing pages were getting more traffic than us for this keyword—albeit not a lot.
However, I also noticed Google shows this keyword in the “things to know” section when you search for local SEO—so it seems pretty important.
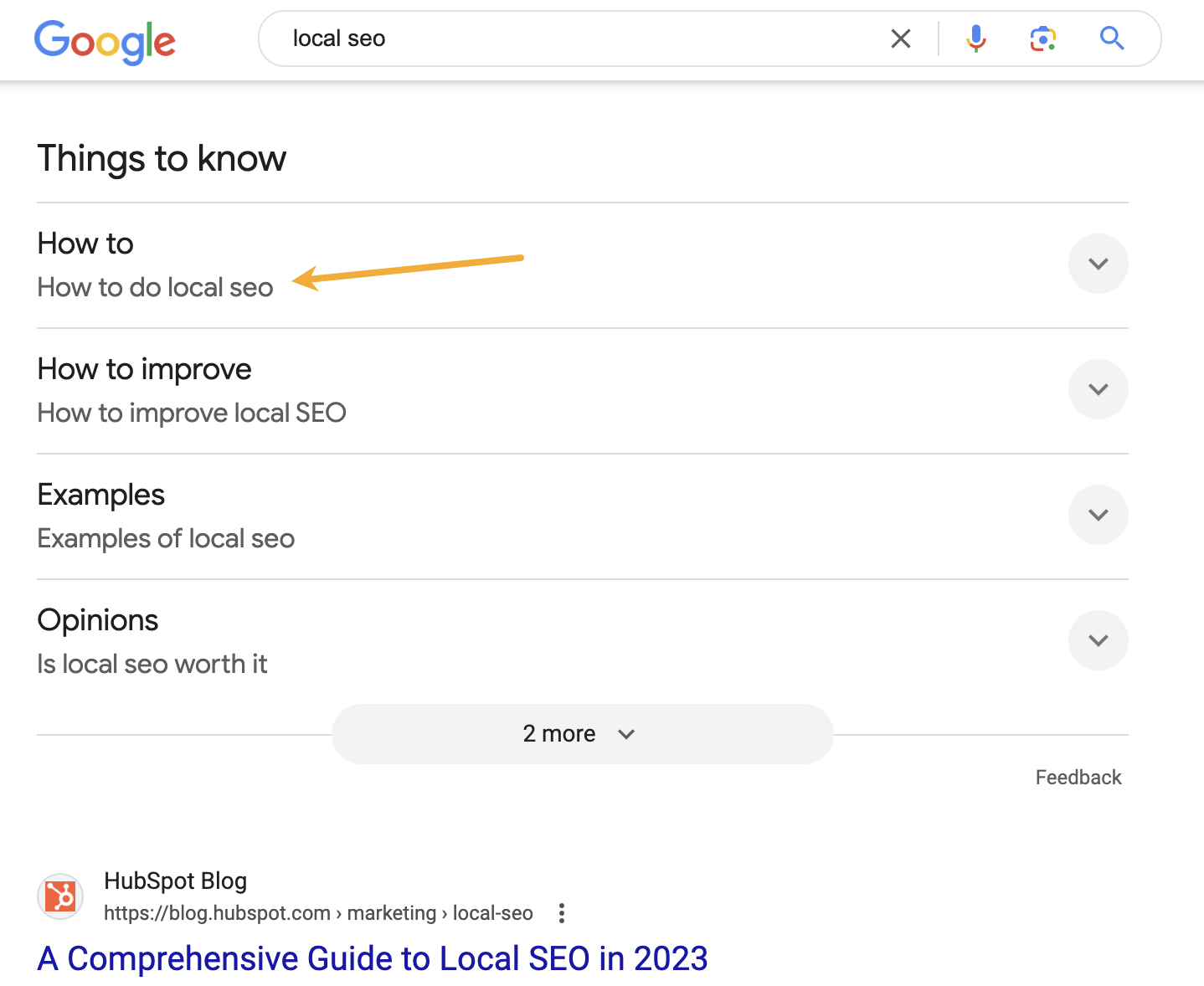

I’d also imagine that anyone searching for local SEO wants to know how to do it.
Unfortunately, although our guide does show you how to do local SEO, it’s kind of buried in a bunch of uninspiring chapters. There’s no obvious “how to do it” subheading for readers (or Google) to skim, so you have to read between the lines to figure out the “how.”


In an attempt to solve this, I restructured the content into steps and put it under a new H2 titled “How to do local SEO”:
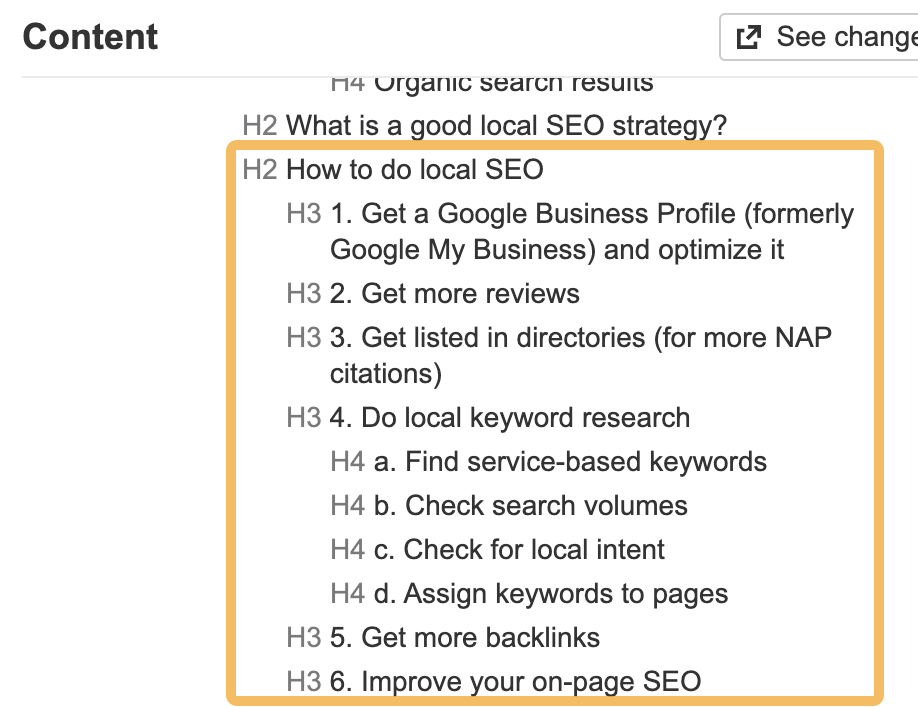

Result? Position #7 → #4
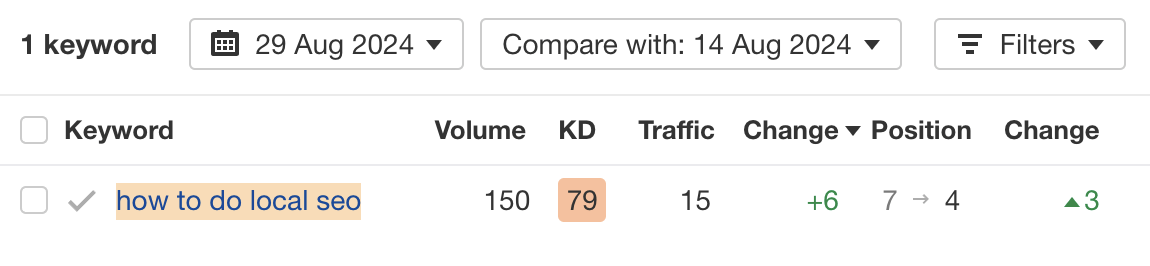

No. Nothing in SEO is guaranteed, and this is no different.
In fact, I optimized our SEO pricing guide for related keywords on the same day, and—although traffic did improve—it only improved by around 23%:
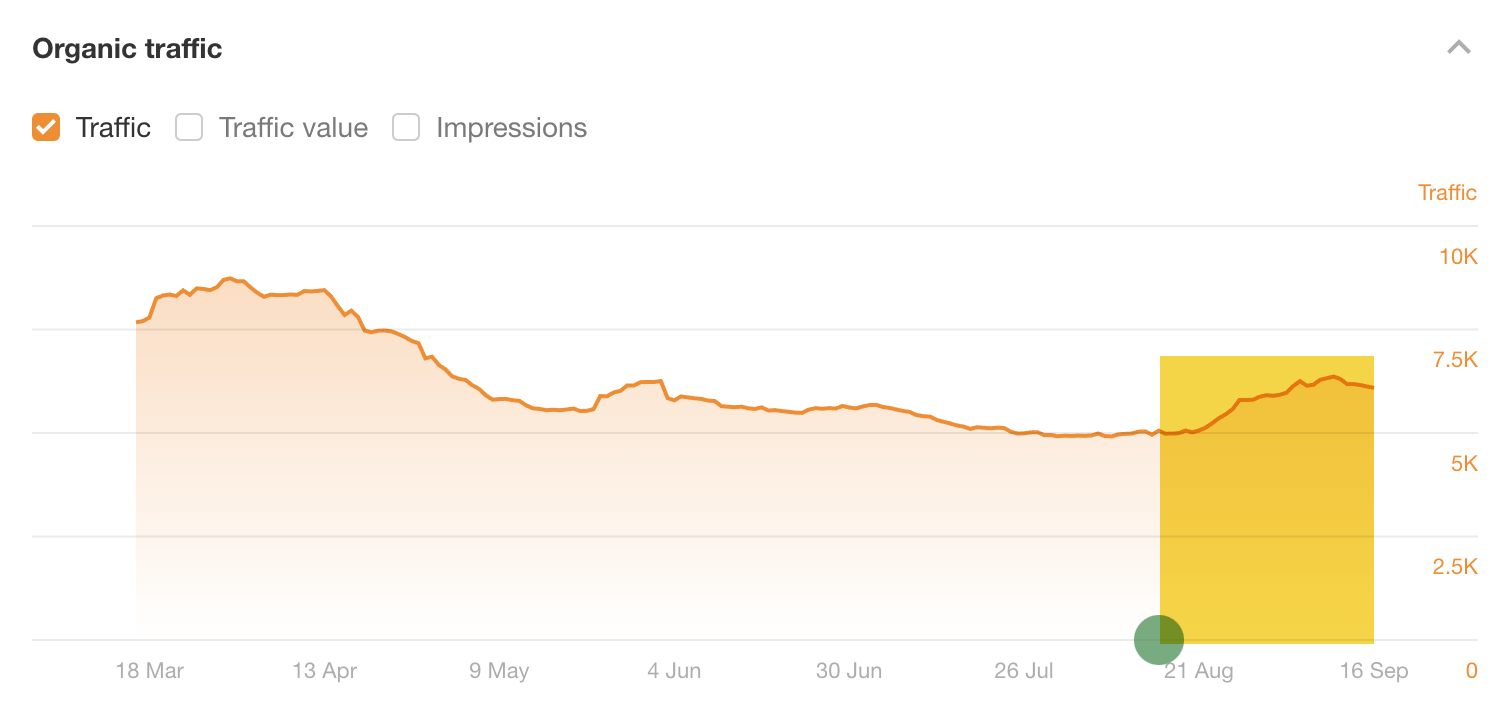

Sidenote.
You might have noticed the results were a bit delayed here. I think this is because the keywords the post ranks for aren’t so popular, so they’re not updated as often in Ahrefs.
For full transparency, here’s every related keyword I optimized the post for and the results:
Related keyword 1: “How much does SEO cost”
Each competing page got more traffic than ours from this keyword, with one getting an estimated 317 more monthly visits:
When I clustered the keywords by terms in Keywords Explorer, I also saw ~70 keywords containing the word “much” (this was around 19% of all keywords in the Content Gap report!):


These were all different ways of searching for how much SEO costs:


The issue here appears to be that although we do answer the question on the page, it’s quite buried. There’s no obvious subheading with the answer below it, making it hard for searchers (and possibly Google) to skim and find what they’re looking for:
To solve this, I added a H2 titled “How much does SEO cost?” and added a direct answer below.


Result? No change in rankings for the related keyword itself, but the page did win a few snippets for longer-tail variations thanks to the copy I added:

Related keyword 2: “SEO cost per month”
Nearly all competing pages were getting more traffic than us for this keyword, with one getting an estimated 72 monthly visits more than more us.
The term clustering report in Keywords Explorer also showed that people are searching for the monthly cost of SEO in different ways:


This is not the case for hourly or retainer pricing; there are virtually no searches for this.
I think we’re not ranking for this because we haven’t prioritized this information on the page. The first subheading is all about hourly pricing, which nobody cares about. Monthly pricing data is buried below that.


To fix this, I moved the data on monthly pricing further up the page and wrote a more descriptive subheading (“Monthly retainer pricing” →“Monthly retainer pricing: How much does SEO cost per month?”).
I also changed the key takeaways in the intro to focus more on monthly pricing, as this is clearly what people care about. Plus, I simplified it and made it more prominent so searchers can find the information they’re actually looking for faster.


Result? The page won the featured snippet for this related keyword and a few other variations:

Related keyword 3: “Local SEO pricing”
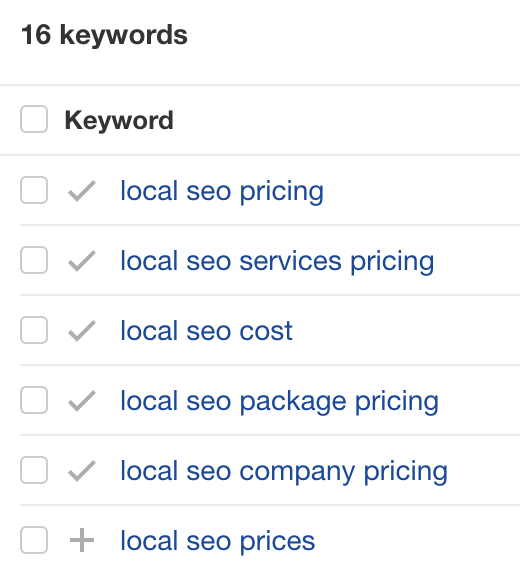
I found this one in the term clustering report in Keywords Explorer, as 16 keywords contained the term “local.”


Upon further inspection, I realized these were all different ways of searching for the cost of local SEO services.

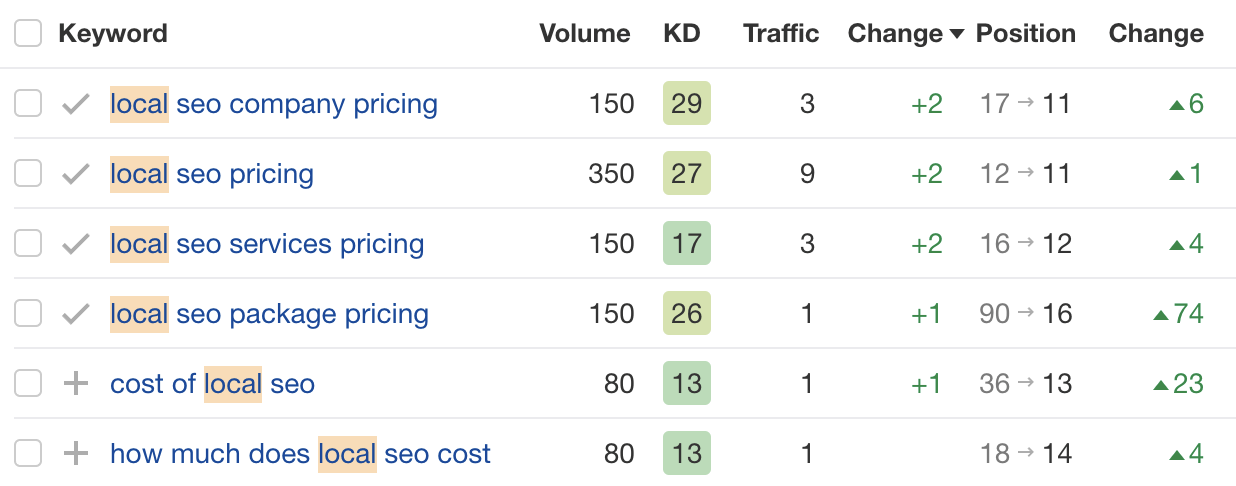
I think the problem here is although our post has some data on local SEO pricing, it doesn’t have the snappy figure searchers are likely looking for. Plus, even the information we did have was buried deep on the page.
So… I actually pulled new statistics from the data we collected for the post, then put them under a new H3 titled “How much does local SEO cost?”


Result? Small but notable improvements for this keyword and a few other variations:

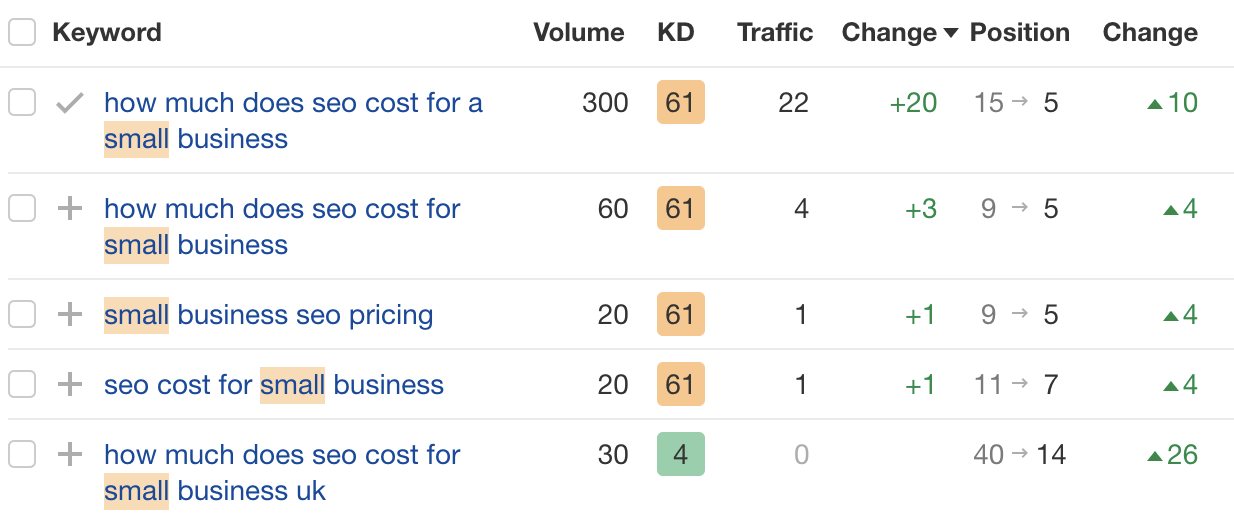
Related keyword 4: “How much does SEO cost for a small business”
I saw that one competing page was getting an estimated 105 more monthly organic visits than us from this term.
When clustering by terms in Keywords Explorer, I also saw a cluster of nine keywords containing the word “small.” These were all different ways of searching for small business SEO pricing:
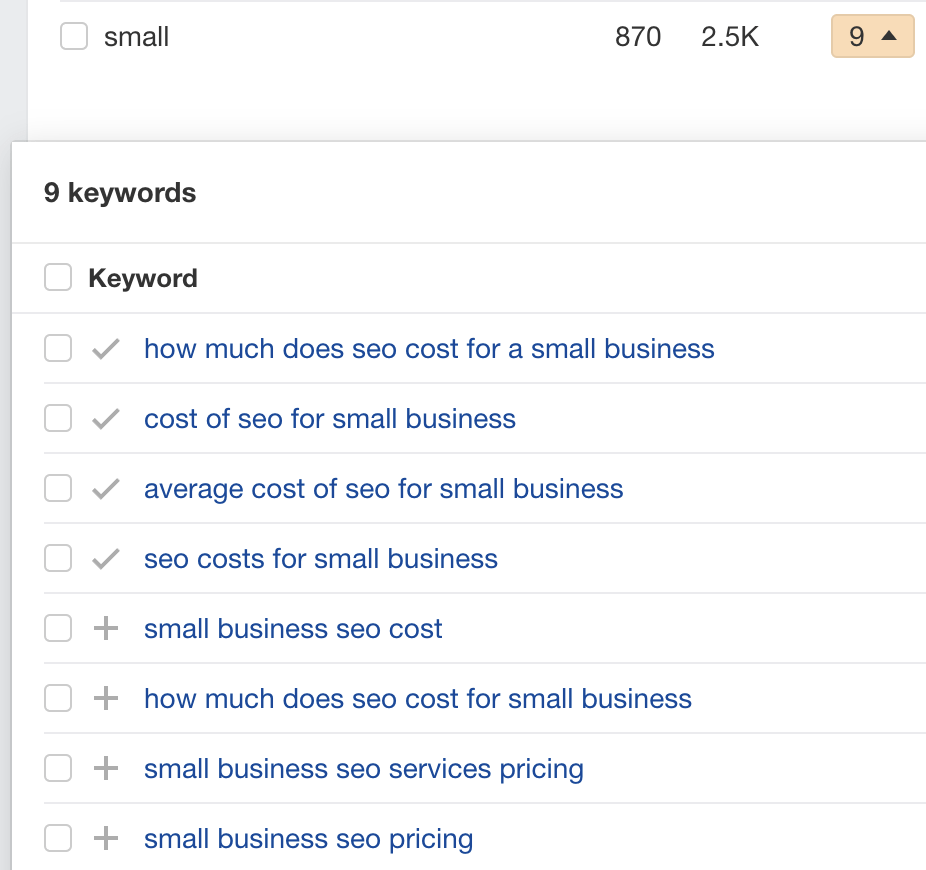

Once again, the issue here is clear: the information people are looking for isn’t on the page. There’s not even a mention of small businesses.


This is good as it means the solution is simple: add an answer to the page. I did this and put it under a new H3 titled “How much does SEO cost for small businesses?”


Result? #15 → #5 for this related keyword, and notable improvements for a few other variations:

Related keyword 5: “SEO pricing models”
This related keyword probably isn’t that important, but I spotted it looking through the Content gap report and thought it’d be pretty easy to optimize for.
All I did was create a new H2 titled “SEO pricing models: a deeper breakdown of costs.” I then briefly explained the three common pricing models under this and re-jigged and nested the rest of the content from the page under there.


Result? #5 → #1:


Final thoughts
Related keyword optimization isn’t about shoehorning a bunch of keyword variations into your content. Google is smart enough to know that things like “SEO” and “search engine optimization” mean the same thing.
Instead, look for keywords that represent subtopics and make sure you’re covering them well. This might involve adding a new section or reformatting an existing section for more clarity.
This is easy to do. It took me around 2-3 hours per page.