Search traffic isn’t just a metric — it’s a business model. Companies like HubSpot, Nerdwallet, and Zapier have built multimillion dollar empires on it.
I’ve personally witnessed a gaming brand use search share of voice data to justify a $60M acquisition and market expansion.
The bottom line is: search rankings and revenue are intrinsically linked. That’s why SERP volatility, even down to the keyword level, can make a huge dent in business value.
Think about it: a law firm ranking for a high-value keyword ($75 CPC) would have to shell out $186K a month on ads if their organic visibility halved, just to keep revenue steady.
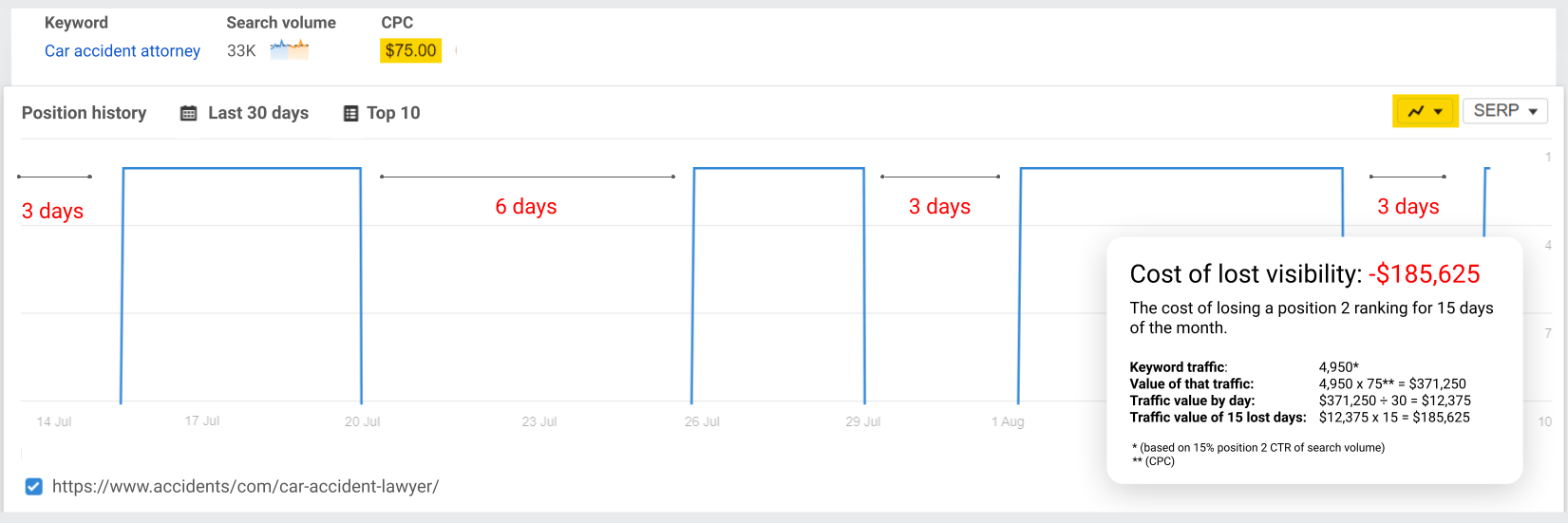
Sidenote.
Ahrefs calculates a unique CTR for every single keyword, to give the most accurate page-level traffic figures. For the purpose of this example, however, we’ve used a generic position 2 CTR to work out traffic and value on the keyword level.
Now imagine that multiplied across tens, if not hundreds of equally valuable keywords.
That’s the cost of SERP volatility.
SERP volatility refers to the degree of fluctuation in Google’s search results. In volatile SERPs, different pages shift in and out of the top 10, while stable SERPs stay relatively steady over time.
SERP flux is an inevitability. You’ll experience it across all pages on your site to various extents, and, yes, even “stable” SERPs experience a level of volatility.
In the words of Google’s Senior Search Analyst, John Mueller
…there is no one-shot secret to long-lasting online success. Even if you find something that works now, the web, user desires, and how they engage with websites changes. It’s really hard to make good, popular, persistent things.
The reality is, Google is always testing and indexing to better meet searcher needs.
When the SERPs are volatile, it’s a sign Google is looking for opportunities to serve more relevant content.
What a “stable” SERP looks like
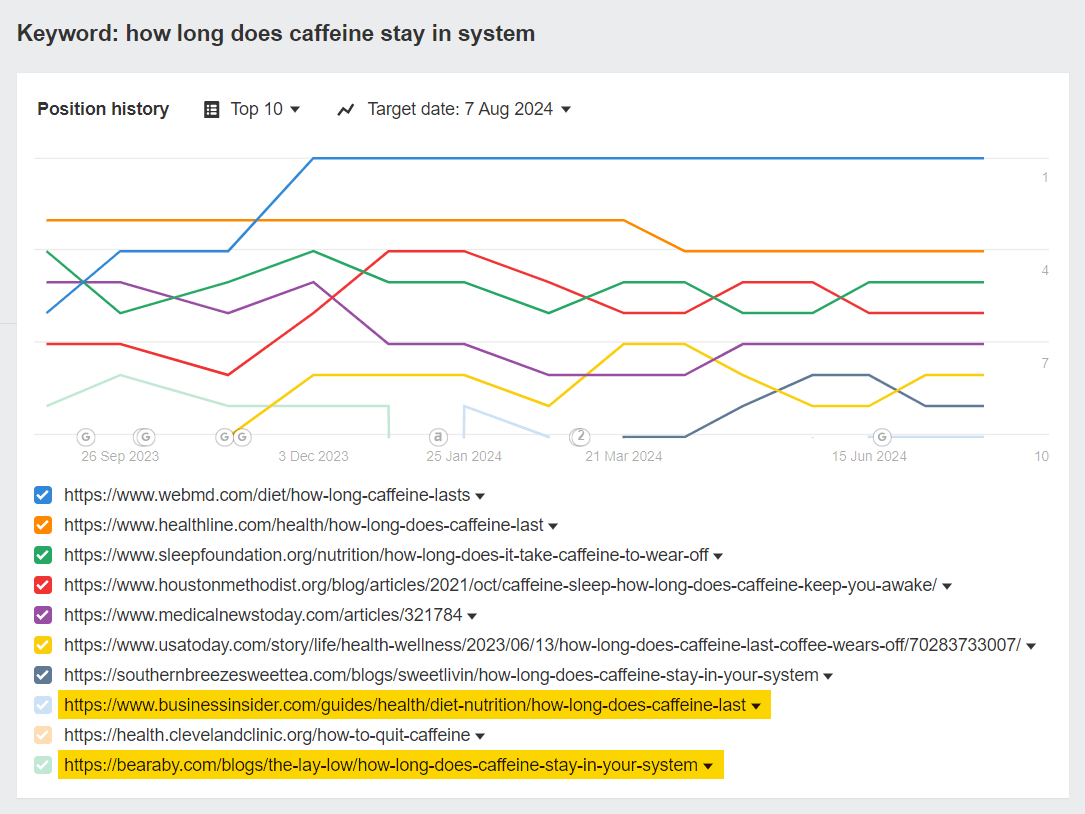

This chart may still look a little shaky, but it was just about the most stable SERP I could find after checking through what felt like hundreds of queries.
Only two sites (highlighted in yellow) dropped out of the top 10 over the course of the year, and the remaining eight pages saw relatively minor flux or position flipping.
In most other SERPs, sites flitted in and out on a near-constant basis.
It’s clear from this example that individual SERPs are intrinsically volatile. Tackling volatility at the keyword-group level is likely a more efficient way to improve your traffic and rankings.
What a “volatile” SERP looks like
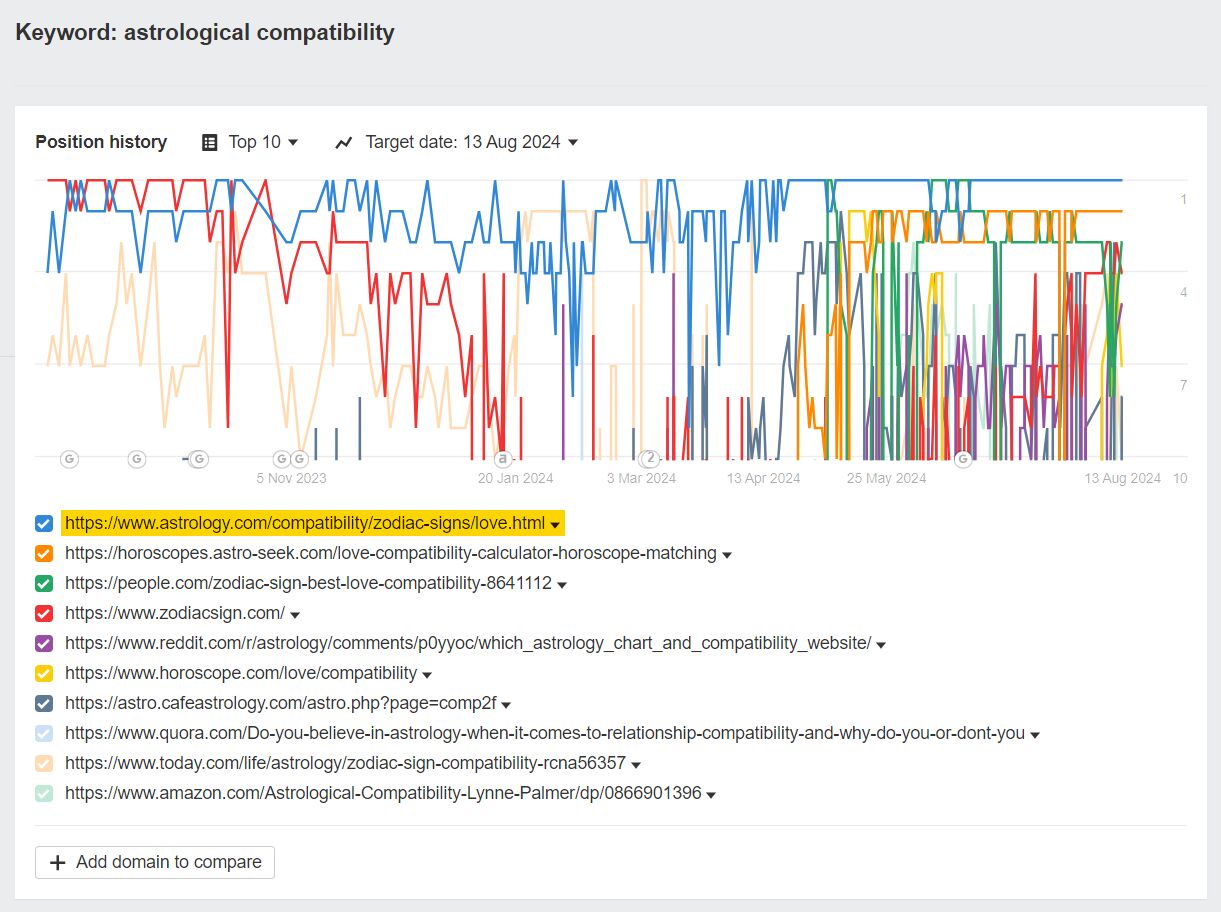

Hopefully you can see the difference here.
In a volatile SERP, pages move in and out of the top 10, experiencing flips and tremors on an almost daily basis.
I’ve highlighted astrology.com because it’s the only result that, despite considerable flux, manages to maintain top 10 visibility all the way throughout the year.
There are two ways to think about SERP volatility
Multi-keyword flux
Multi-keyword flux is when the traffic and rankings of multiple keywords oscillate in the SERPs.
If you’re affected by this kind of volatility, you’ll feel an impact at the page, site, or industry level.
Multi-keyword flux can be triggered by search engine algorithm updates and shifting search intent, amongst other things.
Single keyword flux
Single keyword flux is when your content is experiencing traffic or ranking volatility for one keyword only.
This type of volatility impacts just a single page, but it’s worth investigating if the associated keyword holds significant value – whether that’s monetary value (e.g. CPC) or brand value (e.g. a branded keyword).
When your rankings fluctuate, it’s not by chance. Here’s a look at the main causes of SERP volatility – also known as SEO volatility – including algorithm updates, content issues, and changing search intent.
Algorithm updates
Search engines are always updating their algorithms to a greater or lesser extent, to improve results for users.
As a Google spokesperson told the BBC
“Our recent updates aim to connect people with content that is helpful, satisfying and original, from a diverse range of sites across the web,”
These improvements can cause long-lasting Google volatility across entire industries.
Take the latest August core update, for example. Google made algorithmic adjustments to promote useful content by small and independent publishers, and issued a notice to say that it would take a full month to roll out.
Similarly, the March 2024 core update targeted hundreds of sites with manipulative content, and took 45 long days to complete.
Search engines usually announce major updates in advance, giving the SEO community a chance to address issues before they take root.
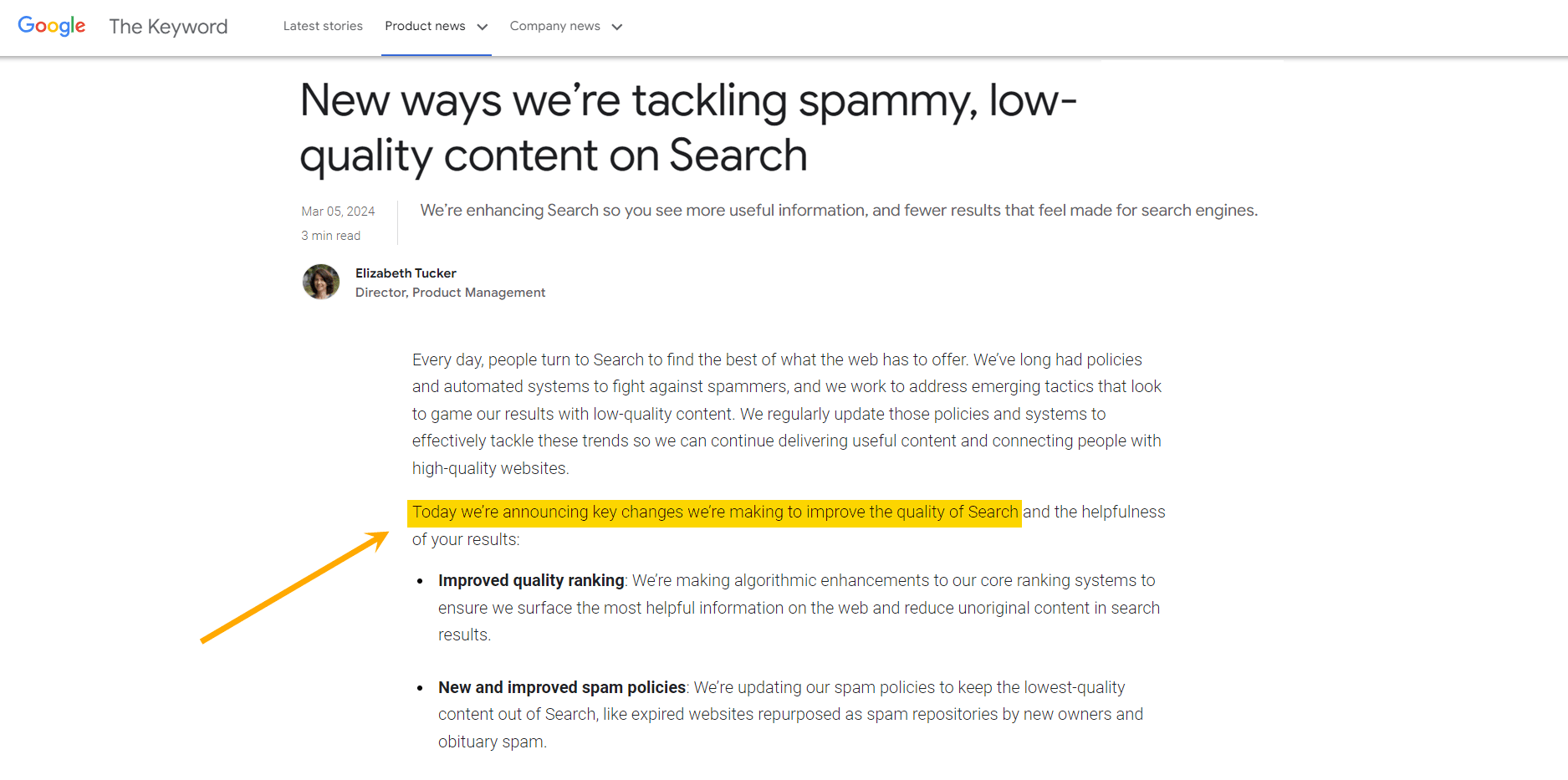

I say “usually”, because Google also has a habit of pushing smaller updates live without warning – like this one, where it deindexed a large number of URLs due to a “shift in perception” (in the words of Google Analyst, Gary Illyes).
Just like official updates, unconfirmed updates can lead to wide scale fluctuation.
Content needs refreshing
Search engines want to serve the freshest information possible to keep searchers coming back.
When the SERPs evolve but your content doesn’t, you’ll tend to see some SERP volatility.
If your page is littered with broken links or redundant information, pages delivering a better experience will inevitably outrank you.
Sites ranking for freshness related keywords are more susceptible to movement because searchers are on the lookout for new information. Google refers to these keywords as “Queries that deserve freshness”.
Examples of QDF keywords with volatile SERPs:
Crawling/indexing issues
If Google doesn’t crawl and index your pages properly, your content may appear only fleetingly in search results.
Equally, when resources like JavaScript or CSS are blocked from crawling, Google can misinterpret your page, which leads to peaks and troughs in ranking.
Cannibalization
Ever since the 2019 diversity update, Google has preferred to rank one site per SERP – making exceptions only for highly relevant content.
As a result, when you have two or more pieces of content fulfilling the same search intent, your rankings will flip and traffic can be inconsistent.
You’re essentially muddying the waters by giving search engines too many options; on top of competing with your rivals, you end up competing with yourself.
Irrelevant/low-quality content
There’s a goal behind every query, and it’s reflected in user search behavior; the keywords they choose, the results they click – even the time they spend on site.
Thanks to some leaked Google search documentation shared by SparkToro’s Rand Fishkin and iPullRank’s Mike King, we can now say with quiet confidence that Google processes all of this user activity when it ranks content.
If user behavior indicates that your content is underperforming, your page is more likely to drop in and out of Google.
Low quality content looks like:
- Thin content
- Misinformation
- A lack of E-E-A-T
- Slow load times
- Intrusive ads
- Keyword stuffing
Competitor content improvements
Competitors creating, updating, and ultimately improving their content can cause a certain level of volatility for your site – especially if they have greater brand authority.
Brand authority is the trust and credibility your brand commands in its industry. It’s shaped by factors like the quality of your content, the strength of your backlinks, and how much your brand gets talked about online.
Search intent is changing
Google is ultimately trying to understand what the user is expecting to find when they search a keyword, so it tests and reshuffles results, causing rankings to flip.
Search volatility is even more pronounced when intent shifts and keywords take on a new meaning.
Here’s an example.
Before OpenAI announced ChatGPT, the dominant intent behind the keyword “LLM” was about “Understanding LLM Programs” – in other words, 79% of the top 10 search results catered to users interested in learning about “Master of Law” degrees.
Before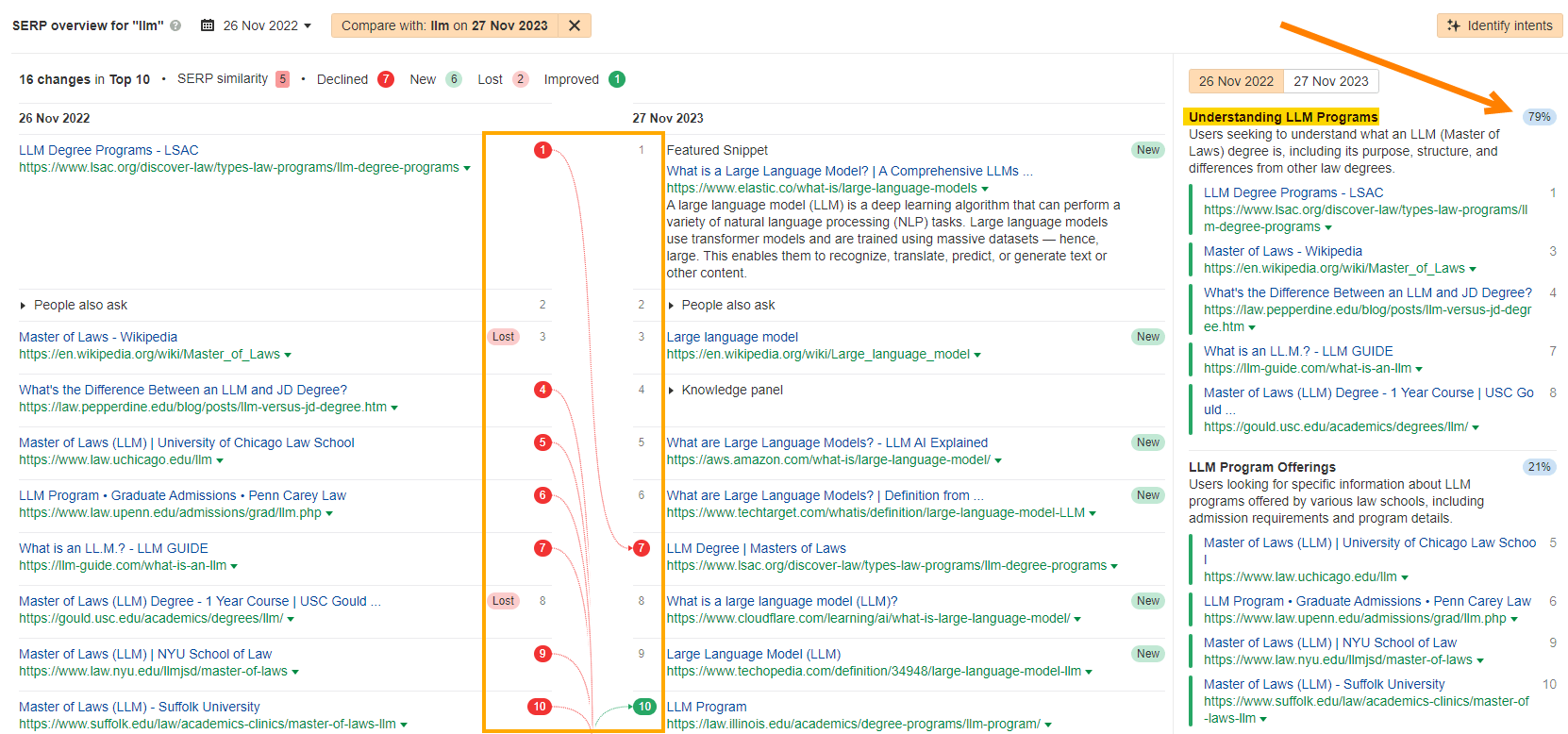

A year on, and by the time ChatGPT had become firmly embedded in our tech stack, the SERP had seen 16 changes in the top 10 and intent had shifted almost entirely to “Understanding Large Language Models” — the technology foundational to modern AI.
After
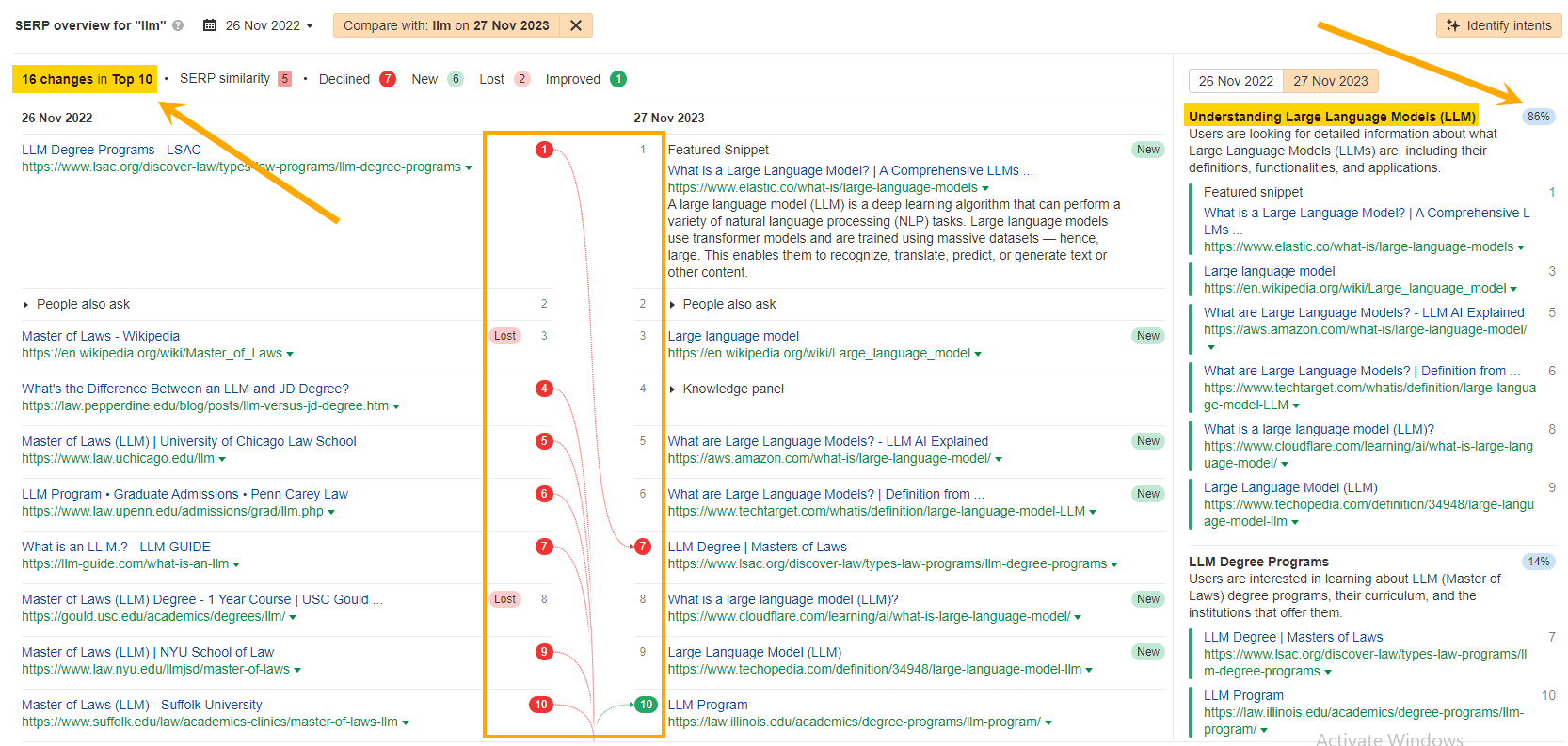

Sometimes, SERP volatility settles as the search engine better understands the intent. Other times, results stay in flux as a result of constantly changing intent (e.g. queries that deserve freshness).
But at what point does volatility turn into a full-on SERP switch? Can it be measured by the passing of time or the “SERP differential” – the degree to which the results change?
The only way to find out is to study the SERP.
Search results can change slowly
Search intent can shift gradually. Recently, while looking for content to update on the Ahrefs blog, I noticed a piece on “Website traffic” that had once driven impressive amounts of traffic.
But, when I did more digging into the SERPs (using the Identify Intents tool in Keywords Explorer), I noticed a slow shift in intent from informational guides in 2021, to free tools and tool compilation lists in 2024.
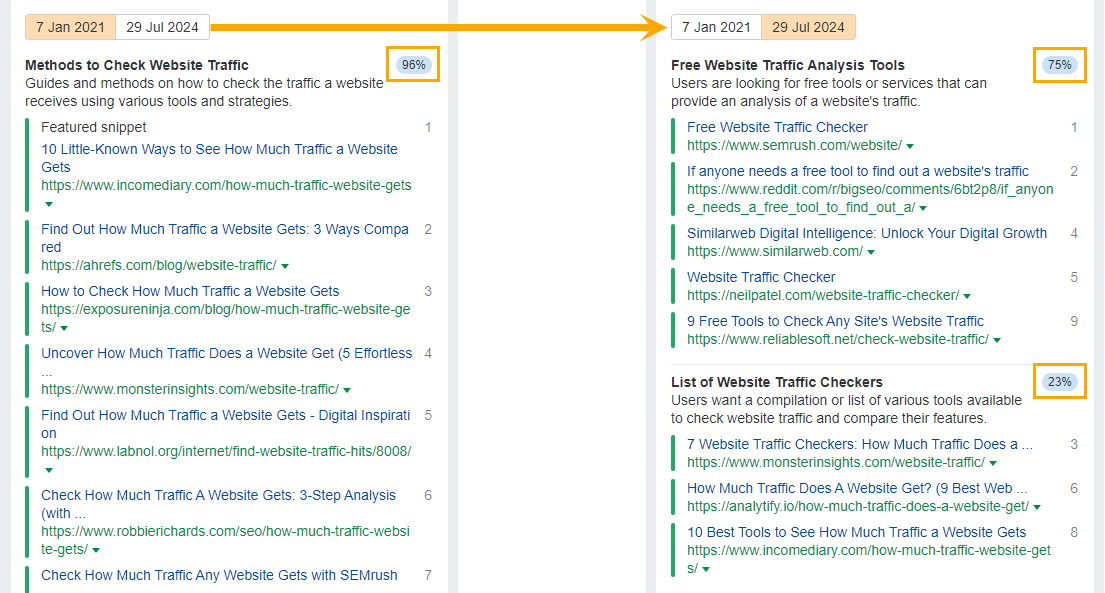

Looking at the SERP comparison metrics, I noticed the top 10 positions had changed 17 times, and both pages had received a SERP similarity score of just 10/100.


All signs pointed to slow-burning volatility and a near-total SERP switch.
Search intent can also change quickly
For queries deserving freshness, like the trending “Willy Wonka experience” example I mentioned earlier, the SERPs flipped within months as interest in the viral story waned.
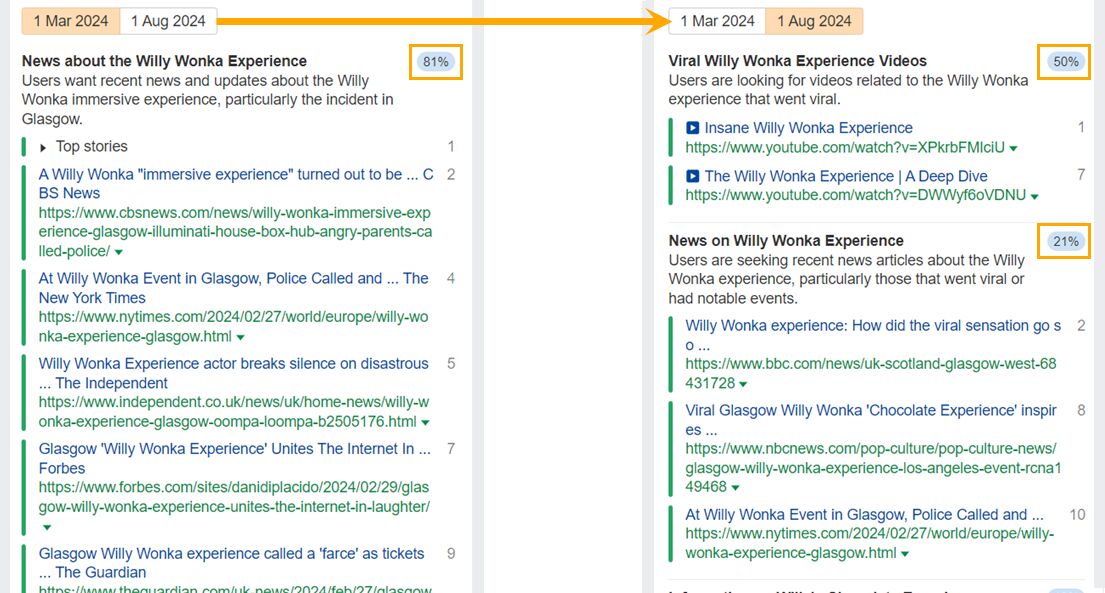

This rapid shift was once again reflected in the SERP Similarity score, which came in at just 2/100.


If you want to better understand how the SERPs are evolving – whether they’re experiencing volatility or undergoing a complete transformation – it’s useful to analyze results in this way.
Volatility can manifest at the page, site, or industry level; to identify each type you’ll need to take a slightly different approach.
Below I run you through the tools you’ll need to spot SERP volatility in all its incarnations.
Check on an industry level
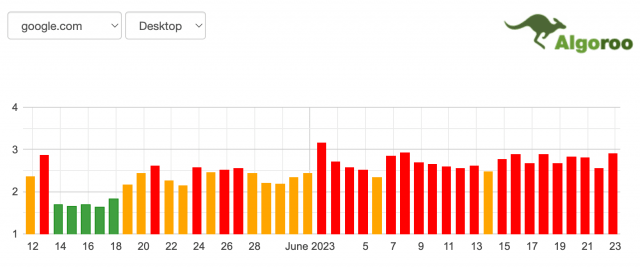
To anticipate when the SERPs are about to shift, many SEOs monitor top-level SERP volatility using algorithm “weather” tools like Algoroo.
This particular tool tracks macro-level SERP volatility by measuring both positive and negative ranking changes. The output is a simple, traffic-light-coded chart showing SERP flux over time.

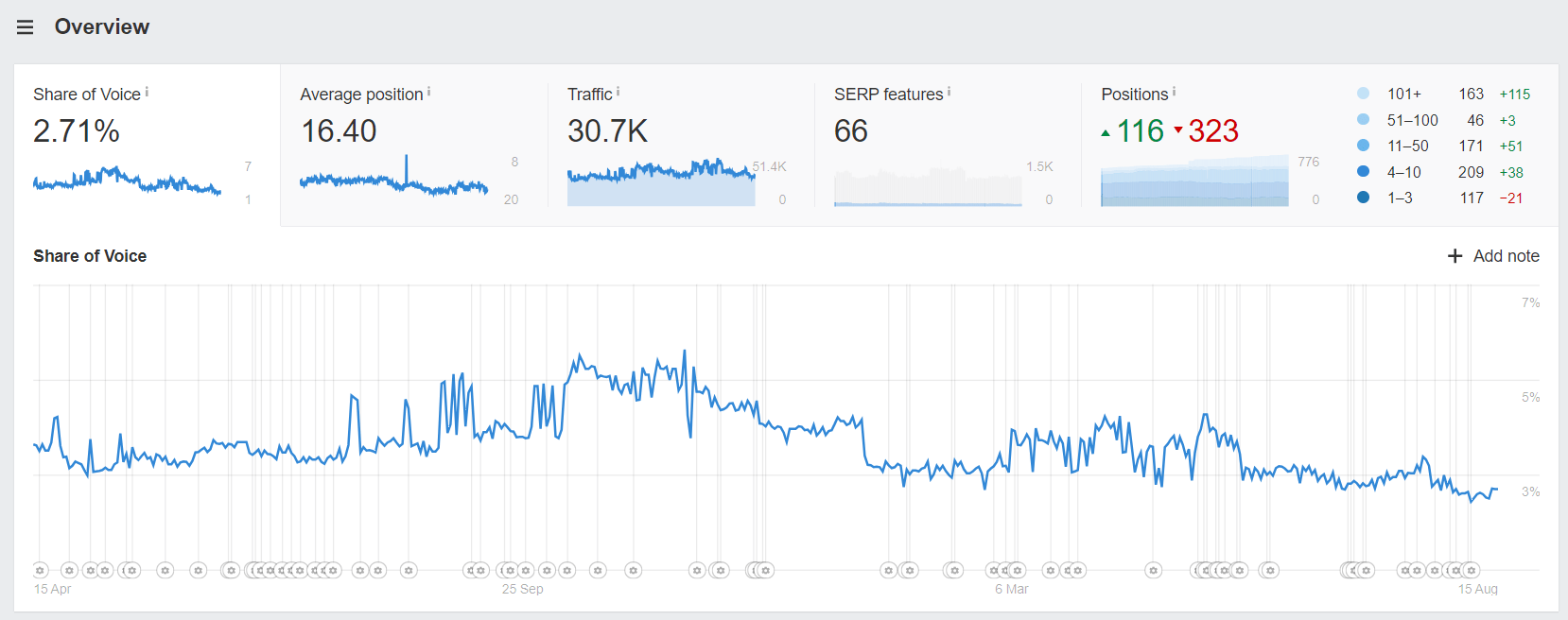
If you want to analyze your own industry-wide volatility, head to Ahrefs Site Explorer and search your site or subfolder…

Then add your competitors in the organic search view.
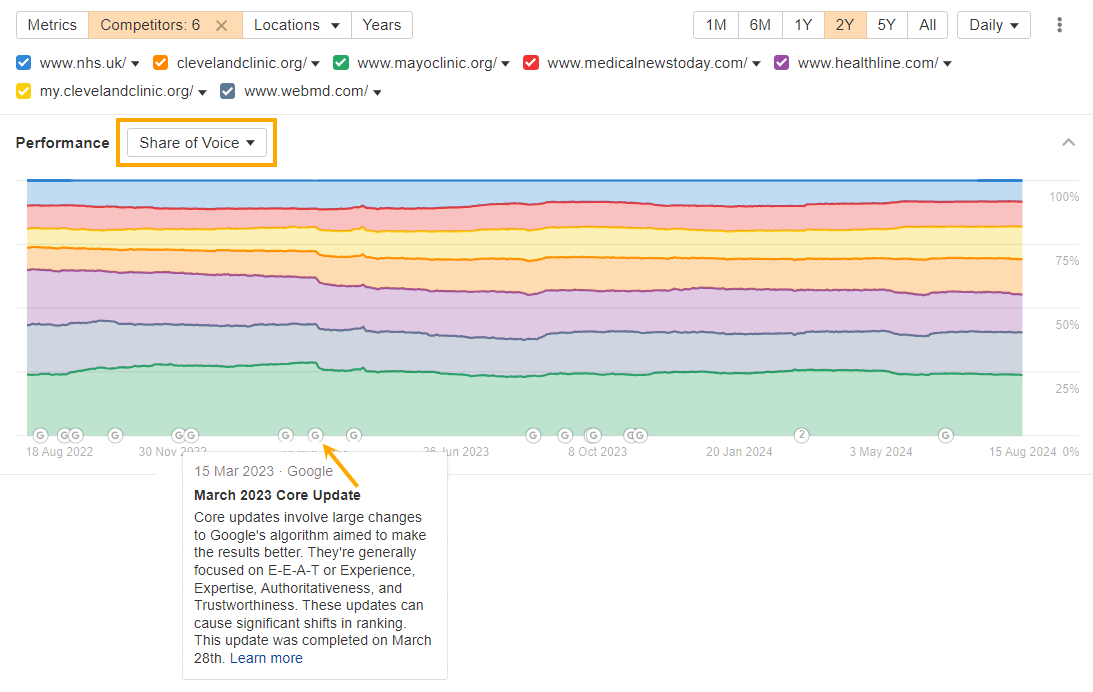

In this example, I’m monitoring “Share of Voice” for a group of YMYL ( “Your Money or Your Life”) sites.
Sidenote.
These sites handle content that directly affects a user’s health, finances, and safety. Any incorrect information can cause real-life harm, so search engines have much stricter standards to ensure accuracy and trust. As a result, these sites tend to feel the impact of updates more acutely – meaning we’re able to see the impact of volatility more clearly.
Hovering over the Ⓖ symbols in Site Explorer reveals detailed information about official, macro-level algorithm updates. This helps us tie the obvious SERP volatility we can see to the March 2023 core update.
Share of voice, being a percentage, offers a more accurate way to compare sites than total traffic figures. While traffic can vary widely between sites, share of voice allows you to look past those discrepancies and zero in on relative performance and shared volatility.
Check on a site level
You can easily check site volatility in Google Search Console, based on metrics like clicks and impressions.

And if you want to track site performance across a specific group of keywords, you can set up a Project in Ahrefs Rank Tracker.

Check on a page level
To analyze the fluctuation of a single keyword, you can search a keyword in Ahrefs Keywords Explorer and view SERP Position History Charts.
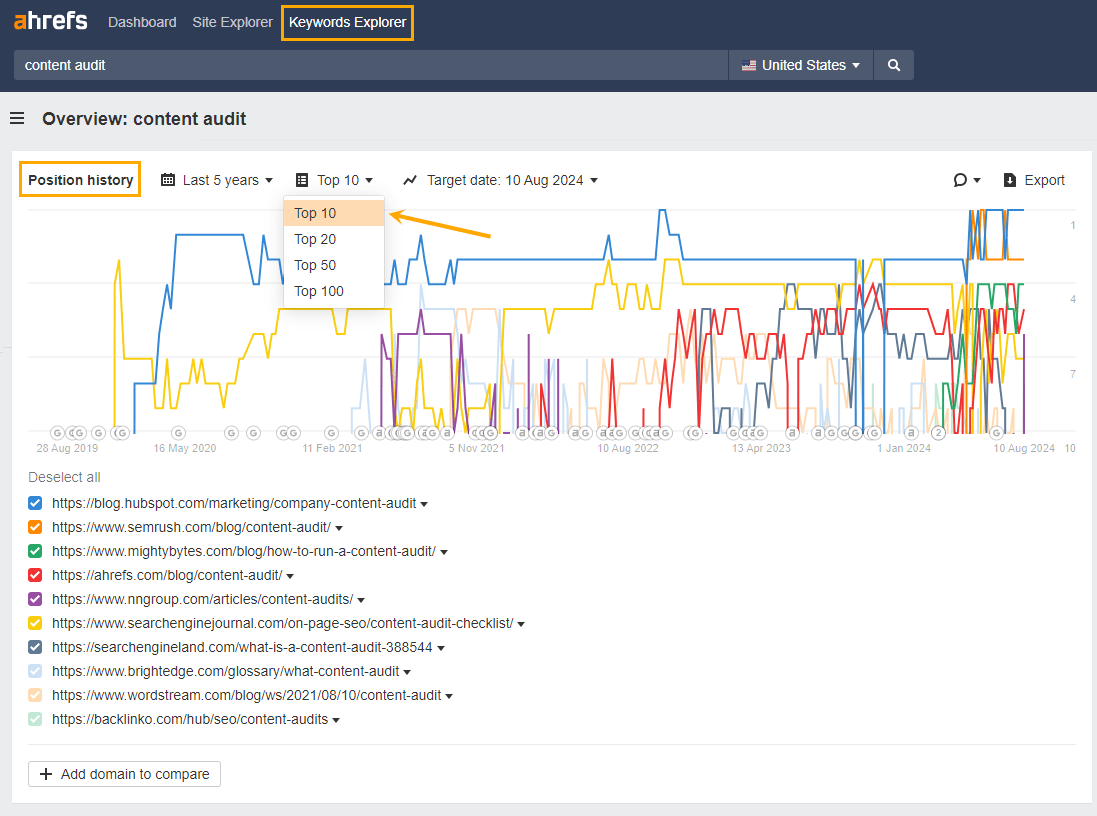

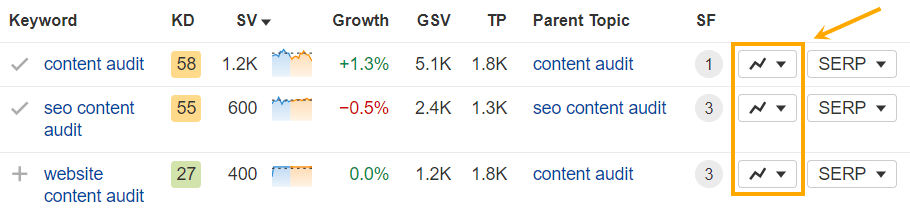
Focusing on the top 10 results will help you filter out the noise. You can also view Position History Charts whenever you see this chart icon next to a keyword…

You don’t have to just accept volatility. There are tons of things you can do to stabilize rankings – from improving your content’s E-E-A-T, to diversifying your traffic sources.
It’s beyond the scope of this article to go through every tactic, but I’ve included the most important ones below.
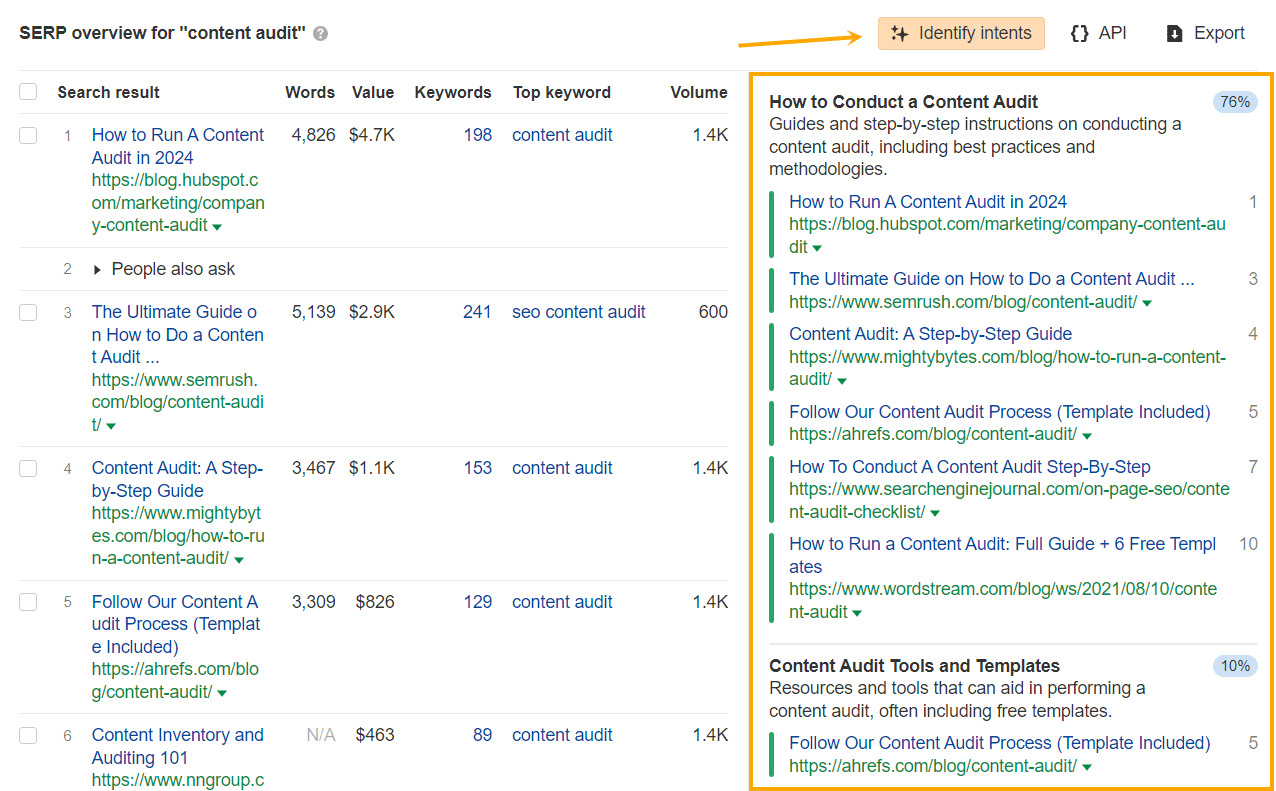
Regularly monitor intent
Search intent changes directly track to volatility. Use the Identifying Intents tool I mentioned earlier will help you assess how well your content hits the mark for the SERP’s dominant intents.

Keep content updated
Some topics crave freshness more than others. For these, regular updates aren’t just nice to have — they’re essential. Neglect them, and you risk dropping off the SERP entirely.
Here’s what to do:
- Create a “freshness portfolio” of your key content using Ahrefs Portfolios
- Prioritize your top-performing pages
- Update regularly to maintain rankings and prevent traffic loss
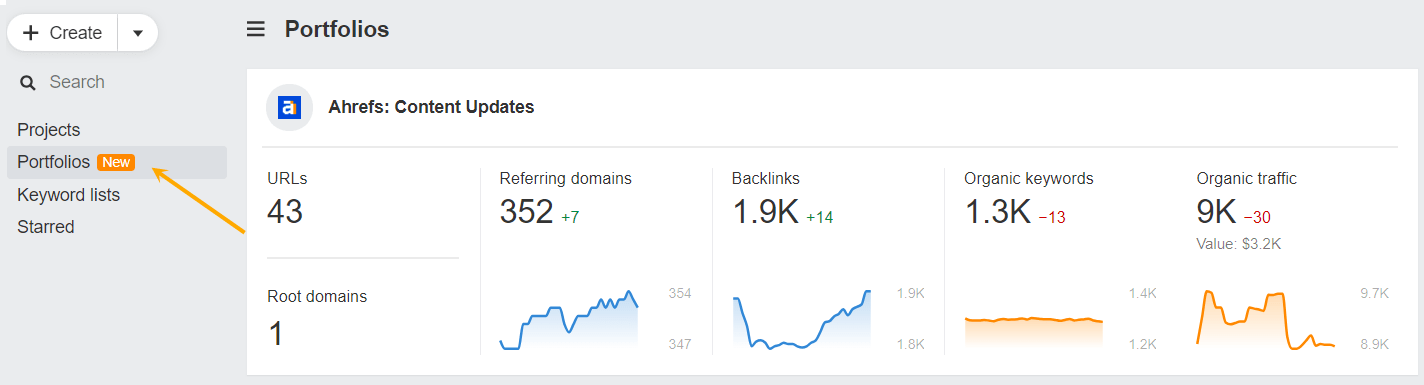

Remember: stale content can cost you traffic and conversions. Stay on top of updates to keep your SERP positions (and your revenue) healthy.
Content you might want to include in your “freshness portfolio”:
- Date specific content/research (e.g. statistics blogs, headlines featuring years)
- News and trend content
- Pages that mention deals and offers
- Pages that mention pricing or plan details
Fix cannibalization
To avoid duplicating content and intent, make sure you’re creating new content in the context of your existing back catalog.
A simple Google site operator search will help you find all existing pages on your site related to a topic.
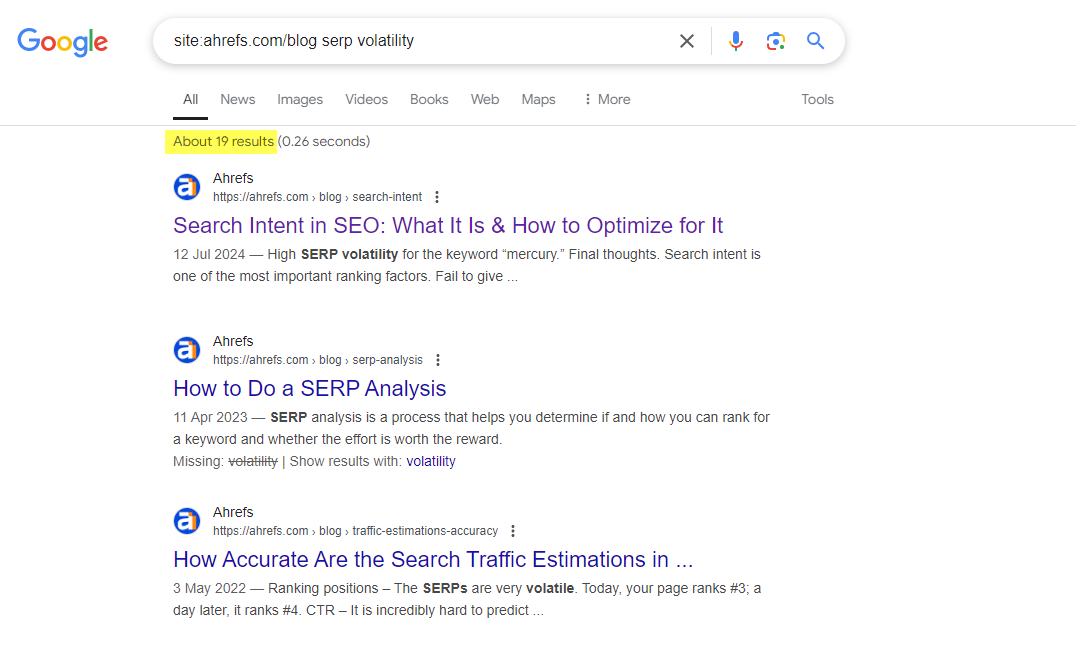

Ahrefs has approximately 19 pages that mention “SERP volatility” in passing, but zero that cover the topic in any real detail.
That means this article shouldn’t lead to any cannibalization (at least, I hope not!).
Toggling on the “Multiple URLs” filter in Ahrefs Organic Keywords report can also show you when you’re ranking more than once for a single keyword.
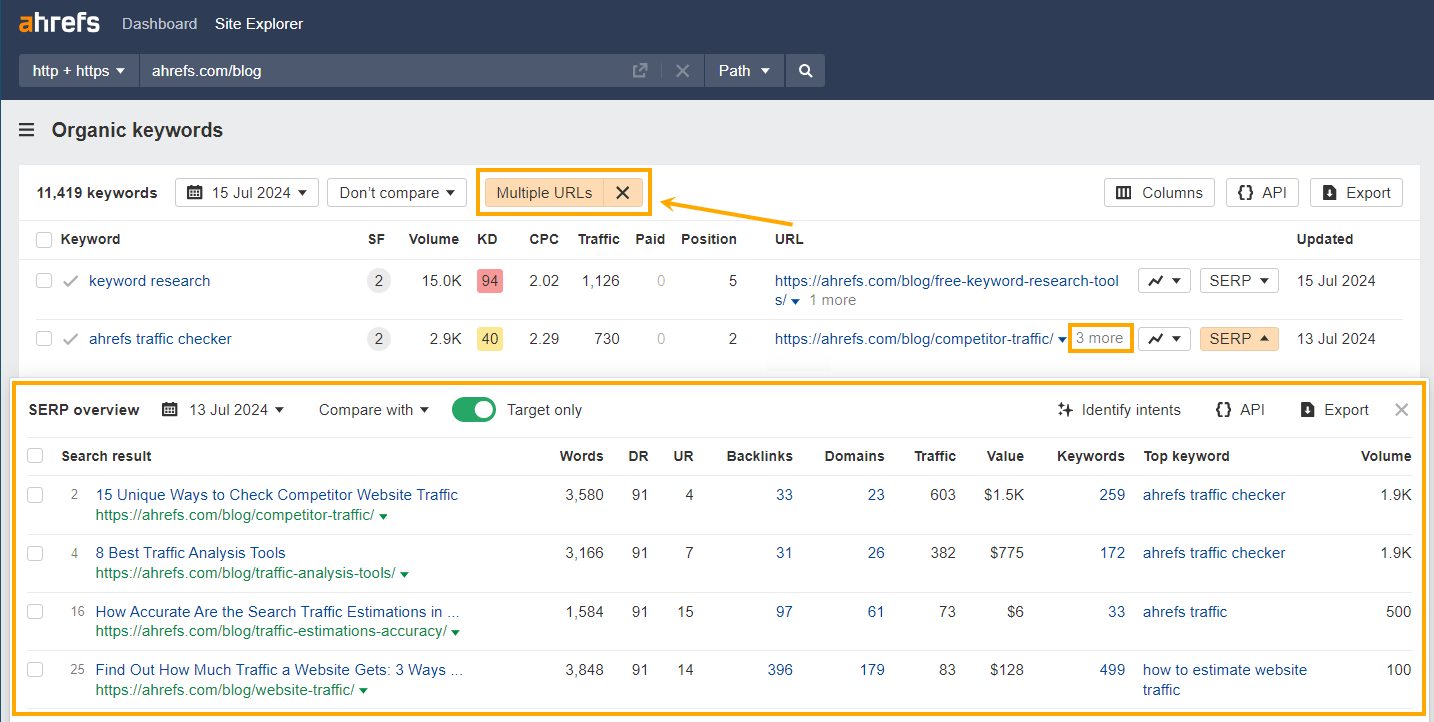

Use this workflow to spot pages that are at greater risk of cannibalization and SERP volatility.
Study competitor content
Assess rivals who rank consistently or often in volatile SERPs. What are they doing differently? How does their content satisfy intent? What topics are they covering that you’re missing?
Run your page through our Content Grader tool to spot content gaps and get actionable advice on how you can improve.

Audit and troubleshoot technical issues
If your site is experiencing SERP flux off the back of an algorithm update, it’s essential to run a thorough site audit.
When Google’s Site Reputation Abuse update specifically targeted sites with manipulative link practices, SEOs would have had to run an audit to clean up their external link profiles and earn back visibility.
Diagnosing and fixing technical issues can improve your site’s ability to get indexed consistently in the SERPs. Chris Haines has written a great 11 step site audit guide to get you started.
Final thoughts
SERP volatility can hit your traffic and revenue hard.
But stabilizing your rankings isn’t just about patching up a leaky bucket. It’s also about retaining a competitive edge and taking traffic away from your biggest competition.
To keep your site’s performance steady, you need to make a habit of monitoring search intent, regularly updating content, and troubleshooting any technical issues that could be dragging you down.
Do this right, and you might even be able to turn SERP volatility into an opportunity.

